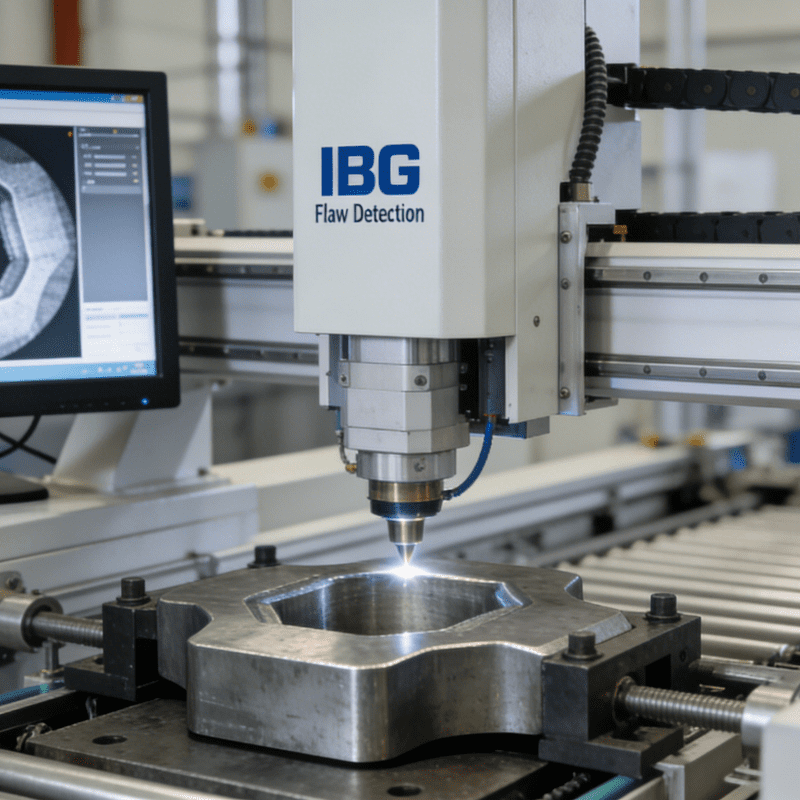
Midea’s Washing Machine Factory in Jingzhou has recently received the certification of “World’s Outstanding First Multi-Scenario-Covering Agent-Based Smart Factory” from WRCA (World Record Certification Agency), a London-based world record certification organization. This marks the official launch of the industry’s first agent-based smart factory.
The factory’s 14 smart agents cover 38 core production business scenarios and achieve collaboration based on the “Midea Factory Brain”. By deeply integrating Midea’s manufacturing experience, large-model technology, and embodied robotics technology, the factory possesses end-to-end capabilities spanning perception, decision-making, execution, feedback, and continuous optimization. Practical results from the factory show that in multiple core manufacturing scenarios, smart agents complete tasks that traditionally take humans hours in seconds, with an average efficiency improvement of over 80%—among which the scheduling response speed has increased by 90%.
After on-site verification, technical architecture analysis, and data validation, the WRCA World Excellence Certification Review Committee unanimously concluded that Midea has reconstructed production logic through a “multi-agent collaborative architecture”. It is the first in the industry to realize AI agent autonomous services and collaboration covering full scenarios such as energy, production, quality control, and operation and maintenance. Its technical architecture (Agent autonomous decision-making + industrial large-model integration + embodied interaction), scenario scope (38 launched agent scenarios), and implementation depth (extending from the entire factory, workshops, and production lines to workstations) have no existing comparable cases. This defines the future form of manufacturing—evolving from “digital factories” to “self-evolving agent ecosystems”.
Maxim, WRCA World Record Certifier, stated that this certification not only marks Midea’s Jingzhou Factory as the first smart manufacturing benchmark to achieve large-scale collaborative operation of multi-agent scenarios across multiple dimensions but also sets a new benchmark for an efficient, flexible, and resilient smart ecosystem in the global manufacturing industry through its in-depth coverage of full-business smart scenarios. It demonstrates China’s leading position in the integration and application of groundbreaking smart manufacturing technologies and holds epoch-making milestone significance.
01 Reconstructing the Essence of Manufacturing with AI: Self-Developed Factory Brain Builds a “Moat”
Zhang Xiaoyi, Chief Digital Officer of Midea Group, said that an agent-based smart factory is a “brand-new entity”. Under the command of the Factory Brain, every production factor in the factory—people, machines, materials, methods, and environment—are no longer isolated units. Various smart terminals, such as embodied robots, robotic arms, AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots), injection molding machines, cameras, and sensors, are all endowed with capabilities of perception, understanding, decision-making, and action.
Among them, the Midea Factory Brain serves as the “neural center” of the agent-based smart factory. It adopts a highly available and scalable distributed multi-agent architecture, realizing agent autonomous collaboration through Agent-to-Agent (A2A) communication and integrating an industrial large-model inference engine to enhance smart decision-making capabilities. If the agent-based smart factory is compared to a human, the Factory Brain is the center responsible for task scheduling, smart agents are the neural networks for specific tasks, and smart terminals are the limbs responsible for actual task execution.
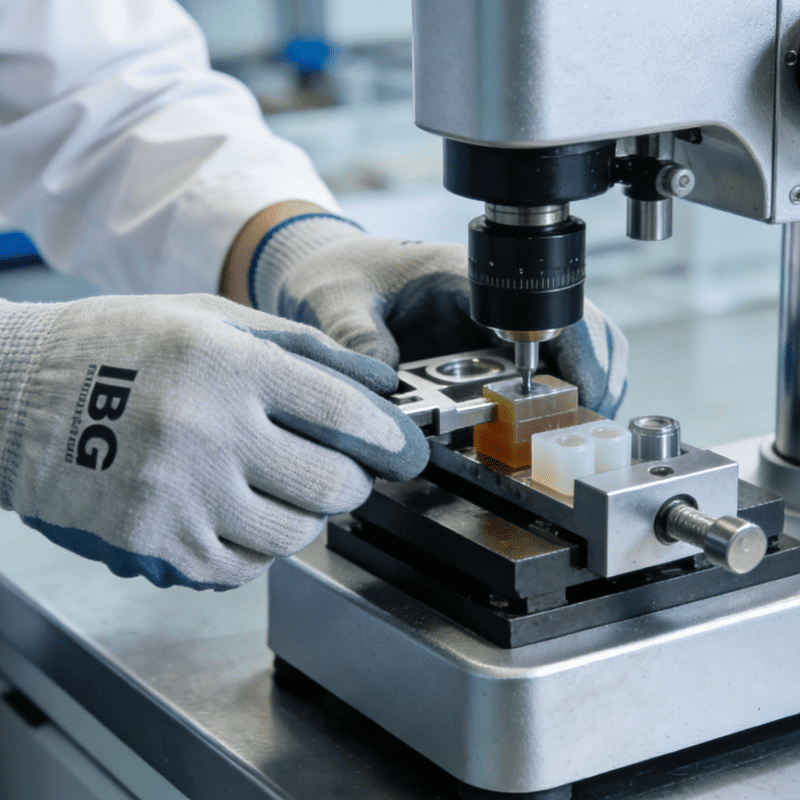
Take quality inspection at Midea’s Jingzhou Washing Machine Factory as an example. Supported by the “Midea Factory Brain”, AI glasses assist workers in receiving reminders about error-prone points based on market issues and first-inspection historical data. Moreover, relying on visual technology, they connect R&D and quality agents, automatically obtain drawings from the R&D system based on material information, compare them with photos of physical objects, and feed inspection results back to the quality agent—forming a complete closed loop. The first-inspection efficiency has been reduced from 15 minutes to 30 seconds.
In the production of key components such as washing machine rubber seals, the 3540 Rubber Visual Dispensing Machine acts as a core smart terminal, achieving in-depth collaboration with process agents and quality agents. It uses a high-precision visual positioning system to capture real-time position information of rubber components, automatically adjusts the dispensing path and glue volume based on process parameters issued by the Factory Brain, and synchronizes dispensing process data and finished product appearance inspection results to the quality agent. Once glue volume deviations or sealing surface defects are detected, it immediately triggers parameter optimization instructions from the process agent, realizing a millisecond-level closed loop of “inspection-feedback-adjustment”. This not only increases the dispensing qualification rate of rubber seals to 99.8% but also shortens the production cycle of a single component by 20%, perfectly meeting the high-precision and high-stability production needs of core washing machine components.
Meanwhile, at the automatic locking workstation for dryer back covers, KUKA’s “iico collaborative robot” achieves in-depth collaboration with planning agents. Through images uploaded to the Factory Brain in real time, it automatically parses model features and quickly matches multiple product models. Even in mixed-flow production scenarios with different washing machine models, the Factory Brain can complete real-time model identification and automatically update the screw locking program, realizing flexible and efficient operations comparable to human workers. This dual improvement in the accuracy and efficiency of mixed-line production is achieved.
02 Humanoid Robots Bridge the “Last Mile”: Fully Realizing the Autonomous Operation Ecosystem of Dark Factories
In recent years, humanoid robots have developed at an unprecedented speed and have become a hot track for future industrial layout. Different from other industrial manufacturing enterprises that are still in the conceptual stage, Midea Group, relying on its own manufacturing factories and production lines, has realized the leap of humanoid robots from laboratories to on-site applications. Phased debugging has been completed in injection molding workshops, forming a business closed loop with the factory’s business system.
“Meiluo” is a humanoid robot independently developed by Midea Group’s Humanoid Robot Innovation Center for industrial scenarios. As the core execution unit of the factory’s embodied smart agents, under the unified scheduling of the Factory Brain, it achieves in-depth collaboration with factory agents such as quality, DMS (Daily Management System), TPM (Total Productive Maintenance), and EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety). Combining multi-modal perception technology and embodied smart operation technology, it independently performs high-frequency tasks such as quality first inspection, DMS regular meetings, TPM inspections, and EHS inspections, realizing real-time response and full-process autonomous decision-making. For example, when performing the first-inspection delivery task, it will transport the injection-molded rear barrel to the smart first-inspection station, where a self-developed high-precision 3D camera integrated into the station independently conducts dimensional and appearance inspections. Quality inspection data is synchronized to the quality agent in real time to form a closed loop of the first-inspection work order. Only when the system confirms that the component is qualified will the robot be dispatched to return for picking. If the inspection fails, it will further collaborate with the process agent and TPM agent to optimize and adjust the parameters of the injection molding machine.
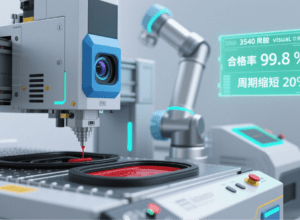
In addition to “Meiluo”, the “Yutu” AI inspection robot deployed in the laboratory achieves accurate spatial understanding of complex industrial scenarios through multi-modal data spatial perception, endowing the robot with human-like environmental perception capabilities. Deeply integrated with the Factory Brain, its edge-cloud collaborative architecture enables efficient and accurate inspections—inspection frequency has been increased by 100% compared with manual inspections. Based on the VLA (Visual-Language-Action) multi-modal large model, it realizes end-to-end cross-scenario adaptive operations, evolving from single actions and single tasks to multi-process and multi-task connection. By completing the full-link closed loop of autonomous inspection, autonomous diagnosis, and real-time processing, it enables anomaly detection and handling to enter the “second-level era”.
The smart agents of the Jingzhou Factory are not limited to robots. In actual production, 81 AMRs are used for logistics in the injection molding workshop. When factory cameras capture the status of the shelves, the information is reported to the Factory Brain in real time. Under the command of the logistics agent, the AMRs perform logistics transportation, with capabilities such as cross-domain scheduling, dynamic path perception, flexible route changing, pedestrian recognition, and autonomous obstacle avoidance. They are like cars on a highway—under the guidance of traffic lights, traffic signs, and “traffic police”, they can quickly and efficiently transport workshop materials to the designated location without any congestion or waiting. At the same time, the AMRs also proactively report task status, equipment status, and QR code health to the Factory Brain, and push maintenance information to employees via the Midea Messenger app in real time, simplifying operation and maintenance.
Wei Chang, Chief Technology Officer of Midea Group, stated that although the humanoid robot industry is developing rapidly, large-scale applications are still in the exploration stage. Starting from its own application needs, Midea Group promotes the integration of humanoid robots into industrial smart manufacturing scenarios—especially the collaborative application of multiple robots (including humanoid robots) with the Factory Brain. Midea Group’s recent demonstrations show that embodied terminals such as humanoid robots can perform multi-agent collaborative operations under the unified scheduling of the Factory Brain, effectively improving work efficiency. Moreover, combined with multi-modal perception technology and embodied smart operation technology, a closed loop from the digital world to the physical world is realized, laying a technical foundation for solving the “last mile” problem of dark factories.
03 Redefining Global Smart Industrial Standards: Providing a Reusable New Paradigm for Agent-Based Smart Factories
In recent years, driven by its technology-leading strategy, Midea Group has focused on new industrial fields, with key layouts in robots, medical care, new energy, and other industries; focused on new technology tracks, deeply engaged in artificial intelligence, humanoid robots, new materials, and other fields; and focused on introducing high-level talents to build a high-level talent team. It has accelerated breakthroughs in key areas, pressing the “fast forward button” for Midea’s strategic transformation into a world-leading technology enterprise.
Zhang Xiaoyi revealed that Midea Group will take the recognition of its Jingzhou Washing Machine Factory as the “World’s Outstanding First Multi-Scenario-Covering Agent-Based Smart Factory” as a new starting point. It will further expand the number of scenarios covered by smart agents, integrate more embodied smart terminal equipment, and continue to promote the continuous evolution of the Factory Brain. At the same time, the agent-based smart factory solution will be quickly replicated to other Midea factories around the world, helping China’s manufacturing industry gain a more favorable position in the global industrial competition pattern.
Industry insiders pointed out that the launch of the industry’s first agent-based smart factory is not only Midea’s path choice for the evolution paradigm of smart manufacturing capabilities but also a new exploration of the “Made in China Solution” in the AIGC era. It marks a major leap for China’s manufacturing industry from “following” to “defining” global smart manufacturing standards. Covering 14 smart agents, Midea’s agent-based smart factory solution replaces experience dependence with “system autonomy” and replaces post-event remedies with real-time closed-loop optimization. Through cross-scenario agent collaboration, it drives paradigm upgrades in production efficiency, flexibility, and quality control, providing the global manufacturing industry with a reusable new paradigm of agent-based smart factories featuring “full-process unmanned intervention and full-factor self-evolution”.
What is the work done using automated equipment and machines called?