CNC, short for Computer Numerical Control, is a technology that uses computer programs to precisely control the movement of machine tools. 5-axis machining, on the other hand, adds two rotary axes—usually two out of the A, B, and C axes—to the traditional three linear axes (X, Y, Z). These two rotary axes enable the workpiece to rotate at different angles, allowing the cutting tool to machine the workpiece from more orientations.
The principle of 5-axis machining may seem complex, but it actually embodies sophisticated engineering design. First, programming and design are carried out using professional CAD/CAM software. Based on the workpiece’s shape, dimensions, and machining requirements, designers precisely plan the tool path, cutting parameters, and the movement mode of the rotary axes. After programming is completed, the program is input into the control system of the CNC machine tool.
When machining starts, the control system of the CNC machine tool accurately controls the movement of the five axes, making the cutting tool machine the workpiece according to the preset path. The addition of the two rotary axes allows the tool to access various parts of the workpiece more flexibly, easily handling complex curved surfaces, inclined angles, and internal grooves alike.
CNC 5-Axis Machining Boasts Numerous Distinct Advantages
Improved Machining Precision
By enabling cutting from more angles, it reduces errors caused by multiple clamping operations. Meanwhile, it enhances tool stability, resulting in machined parts with more accurate dimensions and higher surface quality.
Enhanced Machining Flexibility
Whether it is complex aerospace components, automotive molds, or medical devices, 5-axis machining can meet the machining requirements of various complex shapes, providing designers with greater creative space.

Higher Production Efficiency
Multiple surfaces can be machined in a single clamping, which greatly reduces machining time and auxiliary time. In addition, multi-axis linkage can realize high-speed cutting, further improving production efficiency. To further amplify this efficiency advantage in batch production scenarios, many manufacturers equip their 5-axis machining lines with 4-Axis Robotic Tray Loading Systems—these systems can automatically transport stacked workpiece trays to the machine tool table, precisely position and load/unload workpieces through multi-angle rotation and linear movement, eliminating downtime caused by manual clamping and ensuring positioning consistency that matches the high precision of 5-axis machining, thus forming a seamless efficient flow from workpiece feeding to machining completion.
Application Fields of CNC 5-Axis Machining
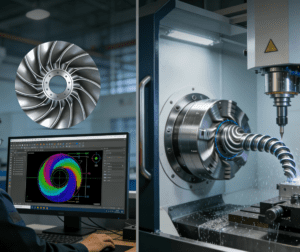
CNC 5-axis machining is widely used in many fields. In the aerospace industry, the machining of key components such as aircraft engine blades and impellers is inseparable from 5-axis machining technology. These components typically feature complex curved surfaces and high-precision requirements, and 5-axis machining can ensure their performance and safety.
In the automotive manufacturing industry, engine blocks, cylinder heads, and various complex molds can be produced efficiently and with high precision through 5-axis machining.
In the medical device industry, high-precision components such as artificial joints and dental instruments also require 5-axis machining to guarantee their quality and reliability.
Besides, 5-axis machining also plays an important role in fields such as electronic communication and handicraft manufacturing.