From unmanned inspections in power distribution rooms to millimeter-level plastering at construction sites, robots are stepping into the frontlines of the power and construction sectors as “new colleagues”.
Power Operation and Maintenance: From “Solo Operation” to “Collaborative Intelligent Inspection”
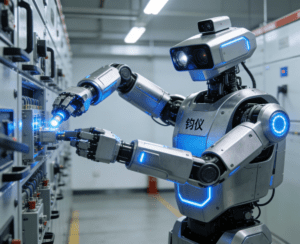
According to reports on December 1st, Junyi, the world’s first dual-arm collaborative inspection and operation robot, has been successfully put into operation in power distribution rooms. It provides strong support for building a new power system and a modern, robust power grid. Developed by UISEE, Junyi performs multi-threaded parallel operations through high-precision dual-arm collaboration, enabling stable and efficient unmanned inspection, realizing the interconnection of enterprise operation and maintenance data, and assisting enterprises in making scientific management decisions.
During the 15th National Games, the Fuyun Xieying power robot, jointly developed by Dongguan Power Supply Bureau of Guangdong Power Grid, the iRobotCNC team led by Academician Ding Han from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and Lenovo Shanghai Research Institute, made its debut. Breaking through the limitations of traditional “solo operation”, this robot achieves multi-legged and multi-arm collaborative work. Equipped with a multi-functional end-effector, it integrates various operation tools such as infrared temperature measurement, partial discharge detection, and handcart operation. In the future, Fuyun Xieying will be further applied in various substation scenarios, driving power operation and maintenance into a new era of “intelligent inspection and maintenance”.
Notably, the intelligent Contactor Assembly Machine has also become a key supporting force in the power equipment manufacturing link. Integrated with collaborative robot technology and precision sensing systems, this equipment realizes automated assembly, calibration and quality inspection of contactors—core components in power systems—with assembly accuracy reaching micron-level standards and production efficiency increased by over 60% compared with manual operations. It seamlessly connects with power operation and maintenance robots through data interconnection, forming a “manufacturing-inspection-operation” full-chain intelligent closed loop and strongly supporting the high-quality development of the power industry.
Currently, robots in the power sector are evolving towards multi-threaded and multi-functional collaborative operations, promoting the transformation of operation and maintenance models towards unmanned and intelligent development.
Construction: From “Manual Operation” to “Robot Assembly Line”
Reported on December 8th, the automatic construction plastering robot, jointly developed by a central enterprise stationed in Tianjin and Shandong University, was officially put into use in Tianjin recently. As stated in the report, this robot can real-time sense the setting state of concrete, achieve millimeter-level precision operation, and is equipped with functions such as intelligent scanning and positioning, dynamic trajectory planning, and automatic plastering repair.
Recently, Jianke Intelligence launched three new products: the GWCAK4000-3 intelligent steel bar mesh welding robot, the QTGJ30 intelligent wall steel cage welding robot, and the BGSM50 intelligent steel bar threading and capping robot. It is reported that these three new robot products will inject new impetus into the digital transformation of the construction industry with a full-chain automated solution.
In November 2025, the intelligent drilling robot, jointly developed by Beijing Company of China Construction Third Engineering Bureau and the R&D team of Tsinghua University, made successive appearances at industry expos in Wuhan and Beijing, attracting widespread attention. It is understood that this robot integrates a variety of advanced technologies, including a visual positioning system, dynamic steel bar avoidance technology, a negative pressure dust collection system, and an intelligent obstacle-stopping module. It has achieved multiple breakthroughs in key technologies, innovatively adopting a “support-type” drilling positioning device to realize three-stage collaborative high-precision positioning, and is equipped with a wear-resistant omnidirectional wheel chassis system, which solves the industry pain points such as high error rate and low operation efficiency of traditional manual drilling.
Construction robots have covered multiple links such as plastering, welding, drilling, and construction. As “robot construction teams” gradually become the norm at construction sites, the construction industry is ushering in an intelligent revolution, and the human-robot collaborative operation mode will become the mainstream of future construction sites.
In Conclusion
Both the “collaborative inspection” in the power sector and the “robot assembly line” at construction sites clearly outline the path for the in-depth integration of robot technology into traditional industries.
With continuous technological breakthroughs and the expansion of application scenarios, traditional industries will enter a new stage of “intelligent inspection and maintenance” and “intelligent construction”. This not only means a leap in efficiency and precision, but also indicates that an industrial transformation centered on human-robot collaboration is accelerating.