December 1, 2025, marks the end of an era and the dawn of a new one for China’s electric bike industry. On this day, electric bikes complying with the old national standard completely withdrew from the stage of history, and the New National Standard was fully implemented.
Electric bike main engine manufacturers, lithium battery suppliers, and hundreds of millions of users have all been drawn into this transformation.
A Wave of Stock Replacement is Coming
China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of electric bikes. Data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology shows that the current domestic ownership of electric bikes has exceeded 350 million, which is equivalent to one electric bike for every four people, firmly ranking as the first choice for residents’ short-distance travel.
Industry experts predict that in the next three years, more than 100 million electric bikes that do not meet the New National Standard will need to be replaced, creating a market scale of hundreds of billions of yuan.
In the long run, with the advancement of urbanization and the popularization of green travel concepts, the electric bike market will continue to maintain steady growth.
Explosive Growth in Lithium Battery Demand
The New National Standard’s restriction on the total weight of the vehicle (including the battery, it must be less than 55 kg) has directly promoted the lithium-ionization process of electric bike power batteries. Lead-acid batteries, due to their heavy weight and low energy density, will gradually give way to lithium batteries.
At present, traditional lead-acid battery giants in the electric bike industry, such as Tianneng and Chaowei, are accelerating their layout in lithium batteries; power battery enterprises including CATL, BYD, Gotion High-Tech, EVE Energy, BAK Battery, and Sunwoda have also begun to enter this market, launching small power battery products suitable for electric bikes.
Lithium battery technology routes are also developing in a diversified manner. Technologies such as lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganate, ternary lithium, lithium titanate, and sodium batteries are also seeking opportunities in specific segmented fields.
Currently, lithium battery manufacturers are engaged in fierce competition in the electric bike field, showing three different development paths.
Full Industry Chain Layout Type: Enterprises represented by CATL, relying on technological advantages and capital strength, promote the integrated layout of “lithium battery – battery swapping – recycling”. They cooperate with shared platforms such as Meituan and Hellobike to promote the battery swapping model and strive to build an industrial ecosystem.
Technology Specialization Type: Enterprises such as EVE Energy and Penghui Energy focus on segmented markets and establish competitive advantages through differentiated technology routes. They have formed technical barriers in specific fields such as fast charging technology and cycle life.
Channel Deep Cultivation Type: Enterprises such as Starry Power, relying on years of accumulated channel advantages, have established in-depth binding relationships with main engine manufacturers and consolidated their market positions through a sound after-sales service network.

Technological Upgrading of Main Engine Manufacturers
Main engine manufacturers have felt the impact of the New National Standard most directly. Enterprises that previously relied on assembly and price wars to survive are facing severe challenges, while those with R&D capabilities and brand advantages are embracing development opportunities.
“This is not just a change in standards, but a change in the rules of the game,” a senior industry insider commented. In the era of the New National Standard, main engine manufacturers need to make breakthroughs in three aspects:
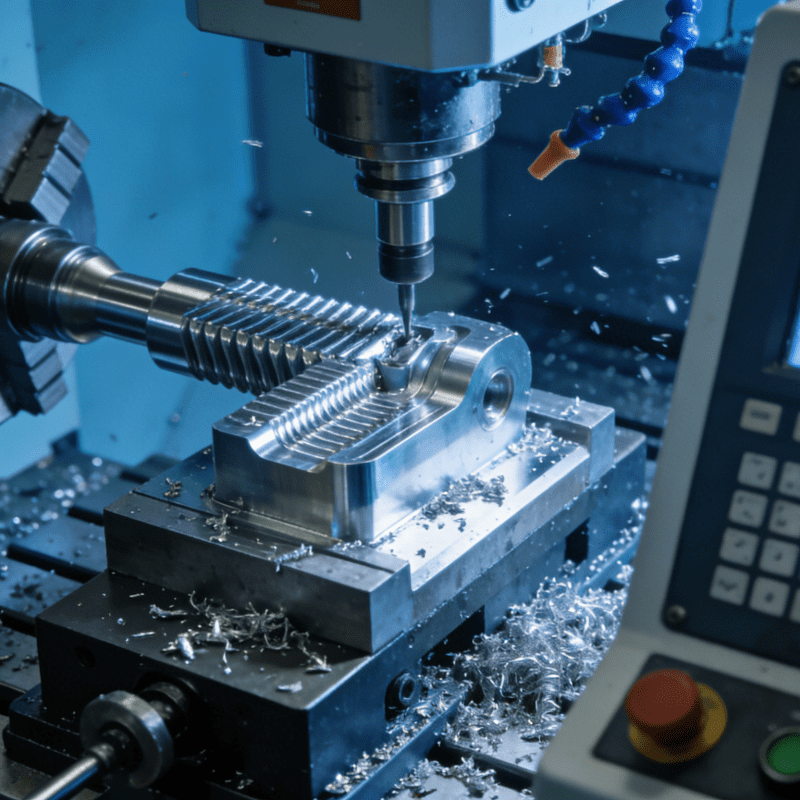
Restructuring of Product R&D System: Everything from frame design, material selection to power system matching needs to be re-planned. Lightweight and intelligence have become core competitive elements. Leading enterprises such as Yadea and Aima have seen their annual R&D investment grow by more than 30%, and the number of patent applications has increased significantly. In the component processing link, some leading main engine manufacturers have introduced the Robotic Irregular-Shaped Metal Part Removal System. This system uses high-precision visual recognition and flexible grasping technology to accurately handle irregular metal parts of key structural components such as frames, effectively improving processing efficiency and assembly accuracy, and providing process support for lightweight body design.
Upgrading of Supply Chain Management: The full application of lithium batteries requires main engine manufacturers to reshape their supply chain systems and establish in-depth cooperative relationships with lithium battery manufacturers. Many enterprises have begun to adopt the “battery bank” model to reduce procurement costs and unify technical standards.
Transformation of Channel and Service Networks: The maintenance and recycling of lithium batteries require professional technical support, so traditional channels must undergo service upgrades. Establishing professional lithium battery testing, maintenance and recycling systems has become a new task for main engine manufacturers.
User Experience and Cost Anxiety
Users have mixed attitudes towards the New National Standard. On the one hand, the portability of lithium batteries makes charging more convenient (as the battery is easy to pick up and place), and the handling of the entire vehicle is improved; on the other hand, the cost of purchasing a new vehicle and subsequent usage costs have increased significantly.
“It used to cost only more than 200 yuan to replace a set of batteries, but now it costs nearly 1,000 yuan,” a user said frankly. The price of lithium batteries is 3-5 times that of lead-acid batteries. Although their service life is longer, the upfront investment has increased significantly.
At the same time, users’ anxiety about battery life has not been completely resolved. The New National Standard’s restriction on the total weight of the vehicle restricts the improvement of battery capacity.
In addition, charging convenience is also a key concern for users. Although lithium batteries support fast charging, the construction of public charging facilities is lagging behind, creating a contradiction.
Final Thoughts
After the full implementation of the New National Standard, the electric bike industry will develop in three directions.
In-depth Integration of Intelligence: With the development of 5G and IoT technologies, functions such as intelligent central control, remote control, and automatic driving assistance will be gradually popularized. Electric bikes are evolving from simple means of transportation to mobile intelligent terminals.
Improvement of Standardization System: Battery specifications, charging interfaces, safety standards, etc. will be gradually unified, promoting the standardized development of the industry. The dispute over battery swapping standards will become the focus of industry competition in the next stage.
Accelerated Global Layout: China’s electric bike industry chain has obvious advantages. After the baptism of the New National Standard, leading enterprises are expected to accelerate their global layout relying on technological advantages and scale effects. Markets such as Southeast Asia and Europe will become key expansion areas.
The implementation of the New National Standard is a watershed for the electric bike industry from unregulated growth to standardized development. Growing pains are inevitable, but only through this baptism can China’s electric bike industry truly transform from a large scale to a strong one and occupy a leading position in the global market.
This transformation has only just begun. Its impact will go beyond the industry itself, profoundly changing the travel methods of hundreds of millions of Chinese people and providing new possibilities for the green transformation of urban transportation.