The healthcare industry is undergoing a major transformation, with the new wave of medical AI trends and the widespread adoption of IoT solutions serving as its primary drivers. This surge of new technologies is sweeping across the industry, and startups are leveraging them to develop innovative solutions that are completely reshaping the concept of patient care in the digital age.
This article will delve into medical AI trends, examine the barriers to progress, and explore the areas where new enterprises may achieve breakthroughs.
The Evolution of Medical AI Trends
Medical AI trends are evolving at a rapid pace, impacting every aspect from clinical diagnosis to operational workflows. The implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms has enabled the analysis of massive volumes of data, supporting decision-making and personalizing patient experiences in an unprecedented manner.
As a result, the outcomes of healthcare services are becoming more accurate, efficient, and successful.
What are the Key AI Trends in IoT Healthcare Applications?
Below are the major medical AI trends, particularly when applied in conjunction with the Internet of Things:
Wearable Devices and Remote Patient Monitoring
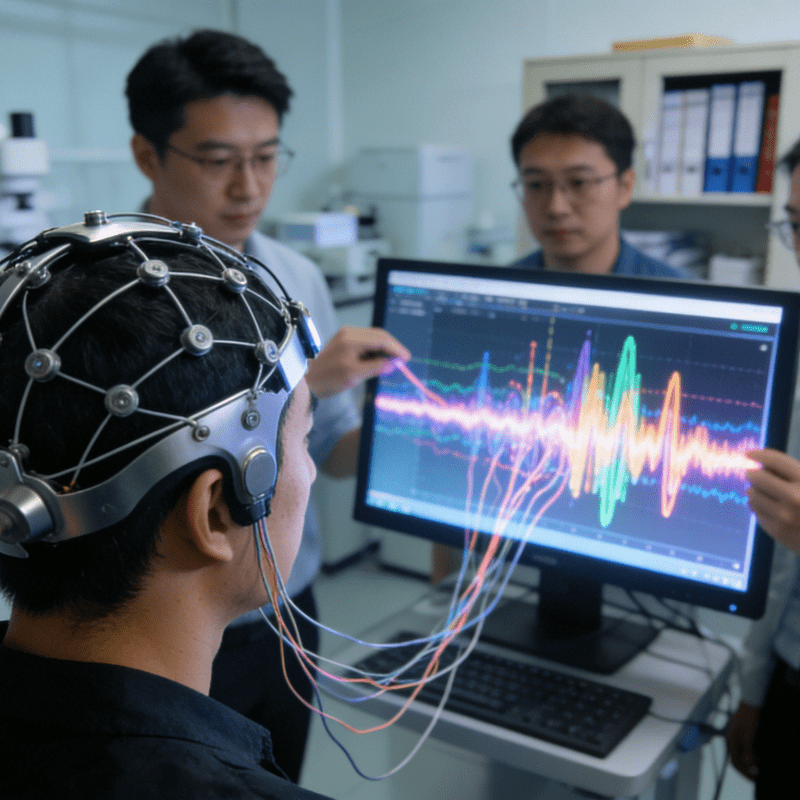
Wearable devices and IoT-enabled devices continuously monitor vital signs such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and blood glucose levels. AI models process this information to predict disease progression or recommend interventions, thereby reducing hospital visits and enhancing preventive care.
Environmental Audio Sensing and Clinical Documentation
Audio systems powered by machine learning are transforming how healthcare providers document patient consultations, creating faster documentation methods and alleviating professional burnout among caregivers.
Prevention and Analytical Countermeasures for Disease Development
IoT information (sensors, new wearable devices, and advanced medical equipment) and AI are applied to predict potential threats. Examples include the prediction of perioperative cardiovascular events, early detection of imaging abnormalities, or identification of initial manifestations of chronic diseases.
Trustworthy AI, Regulatory Focus, and Governance
As the volume of health information transmitted via IoT devices and AI models continues to grow, the focus of discussions has shifted to concepts such as privacy, bias, regulatory compliance, and equity.
AI Applications in Women’s Health
With the support of AI, Femtech (female technology) has finally begun to address women’s health needs, improving diagnostic processes and developing personalized treatment applications.
AI in Diagnosis, Imaging, and Clinical Decision Support
Especially with the assistance of real-time data generated by IoT, AI-enhanced diagnostic tools are becoming increasingly accurate. For instance, medical imaging and continuous monitoring enable clinicians to interpret patient conditions more quickly and comprehensively.
Administrative and Workflow Automation
Startups leveraging AI are also automating non-clinical tasks, including scheduling, document processing, and claims management. IoT devices enable automatic data communication with workflows, eliminating time-consuming manual data entry and reducing the likelihood of errors.

Notably, the reliable operation of these IoT healthcare devices—from wearable monitors to diagnostic equipment that powers AI analysis—relies on high-quality electrical control components, and contactor assembly machines play a foundational role in this ecosystem. These machines produce precision contactors, which regulate stable power transmission in the control systems of medical IoT devices, ensuring consistent data collection and operation even in critical clinical environments where device failure could compromise patient care or data integrity.
Challenges Faced by IoT Healthcare and AI Startups
Despite the exciting prospects of medical AI trends, they also present several challenges that startups must overcome, including technical and structural hurdles.
Data Quality, Privacy, and Security Risks
IoT devices generate massive amounts of data. If the data is messy, biased, or inconsistent, AI models are prone to failure or produce unreliable results. Additionally, patient privacy is paramount, and any data breach can erode trust.
Startups typically must comply with stringent laws and implement robust security measures. A breach of medical data can undermine confidence and lead to legal action.
Secure network communication, data at-rest encryption, and strict privacy guidelines can serve as effective strategies.
Integration/Interoperability Issues
Poorly supported IoT devices often rely on disparate protocols. Legacy infrastructure is commonly used in hospital systems. Enabling all devices to communicate securely and reliably is far more complex than it appears.
Facilitating communication between power supply systems through scalable and effective solutions is a daunting yet essential task.
Open APIs and standardized health protocols can help address these issues.
Clinical Audits, Regulatory Barriers, and Data
Building a functional prototype is far from sufficient. Startups must subject their AI models to clinical testing, obtain regulatory approval, and secure peer-reviewed results. This is one of the prerequisites for widespread adoption of their products; otherwise, the adoption process will be extremely slow.
Cost and Resource Constraints
Developing reliable equipment, collecting data, recruiting domain experts (including medical and AI professionals), and maintaining infrastructure—all of these are costly endeavors. Most startups fail to fully recognize the costs associated with maintenance, legal compliance, and tool quality. Scaling pilot projects to production environments is an expensive process.
Trust, Bias, and Ethical Considerations
AI models may replicate biases (present in data and labels). A solution that works for one population but fails for another can exacerbate health disparities. Users (including patients and clinicians) must be confident that the system is safe and easy to use.
AI models may produce unfair judgments in treatment due to bias. Startups should ensure their models are trained on high-quality datasets and are transparent and interpretable to users.
Regulatory Barriers
Navigating healthcare regulations and obtaining compliance certifications (including HIPAA compliance) can pose costly and time-consuming challenges for small companies.
Opportunities for Startups: Focus Areas and Winning Strategies
For investors and startups looking to capitalize on IoT and medical AI trends, the following areas offer fertile ground. Choose your battlefield wisely.
Niche Application Scenarios with Clear ROI
Rather than attempting to address broad gaps, target specific aspects of clinical or operational problems. For example, remote monitoring for chronic diseases, or automating administrative processes that consume a large portion of hospital budgets. Demonstrating a clear return on investment (ROI) helps secure adoption and funding.
Collaboration with Healthcare Institutions and Legacy System Vendors
Formal collaboration with hospitals, clinics, and quality authorities at an early stage helps understand actual workflows, data requirements, and compliance obligations. Additionally, providing integration with electronic health records (EHRs)/medical record systems can minimize barriers during deployment.
Federated Learning and Edge AI: Balancing Privacy and Latency
By leveraging federated learning or edge computing technologies, data does not need to be processed centrally. This helps protect privacy and reduce latency.
Regulatory-by-Design and Explainable AI
Regulatory and ethical considerations must be integrated into the design from the outset. Strive for clinical validation and ensure your models are explainable. This can be a competitive advantage over rivals.
Funding Trends and Investor Focus Areas
Notably, investors are currently directing capital toward AI healthcare startups that focus on specific domains (e.g., diagnostics, mental health, precision medicine) and have demonstrated scalable potential—rather than just teams with ideas. Staying abreast of funding dynamics is effective.
Immediate Action Strategies and Steps for Startups
– Start with measurable pilot problems. Demonstrate clinical effectiveness and cost reduction outcomes.
– Invest in data collection and management early on. Establish secure data pipelines that comply with established standards and regulations.
– Adopt scalable and modular architectures to accommodate the addition of new IoT devices, edge computing, and cloud services as needed.
– Secure clinical partners and advisors. Trust within the medical community is crucial.
– Monitor the regulatory landscape closely (AI governance regulations, medical device approvals). Be proactive.
Conclusion
The future of healthcare based on IoT (driven by AI) is no longer a hypothetical concept but an ongoing reality. For startups, there are tremendous opportunities if you are strategic: target unmet clinical/operational needs, build solutions in an ethical and validated manner, and address privacy, integration, and trust issues. When you do this, you will not be overwhelmed by medical AI trends but will ride the wave to success.