Introduction: The Symbiotic Evolution of Robots and Smart Cities
Robots are now being applied in urban environments, such as traffic management, cleaning and maintenance, and public safety improvement. Robot technology is easy to impress people, but it should not be forgotten that cities are built for humans, not machines. The concept of smart cities is evolving rapidly, and robot technology is at the core of this transformation. Robots are currently used in urban settings, including traffic management, cleaning maintenance, and public safety enhancement. In the near future, robot technology will definitely become a key driver of urban construction, operation, and lifestyles. Its potential is exciting, but it also raises issues related to ethics, employment, and accessibility.
Core Value: Why Robots Are Crucial for Smart Cities
Today’s cities are densely populated, developing rapidly, and full of challenges. Traditional infrastructure is often outdated and unable to keep up with the growing population. Robots can help bridge this gap because they can perform precise and continuous work, and efficiently carry out dangerous or repetitive tasks. Every system in a smart city is interconnected. Sensors, data networks, and artificial intelligence work together to ensure smooth operation of all processes. Robots integrate perfectly into this system. They act as tools to perform tasks in real time, which are certainly based on data collected from the surrounding environment.
Urban Sanitation Innovation: Practical Value of Waste Management Robots
A key practical application of robots is in urban sanitation. Cities around the world are gradually deploying cleaning robots to sweep streets, collect garbage, and clean public spaces. These machines can work day and night. Robot garbage collectors can automatically sort recyclable materials from regular waste. This not only improves the recycling rate but also keeps human workers away from hazardous waste and toxins. Over time, robots can help reduce urban pollution and make cities healthier.
Security Upgrade: Monitoring and Response of Public Safety Robots
Security is another field where robots are changing the game. Surveillance robots equipped with cameras and sensors are being used to monitor public areas. These robots patrol airports and busy festivals, and report abnormalities to authorities within seconds. Some people are concerned about privacy issues, but the fact is that with proper regulation, these modern tools help significantly reduce crime and shorten emergency response times.
Traffic Efficiency Optimization: From Delivery Robots to Intelligent Transportation Systems
Traffic congestion, accidents, and delays are part of daily life in our cities. Robot technology is leading transportation into a new era. Delivery robots have also become a hot topic in recent years. Small autonomous robots can navigate sidewalks and deliver groceries or medicines to people’s doorsteps. These robots are not only convenient but also reduce carbon emissions and human errors.
Early Hidden Danger Detection: “Physical Examination” Capability of Infrastructure Maintenance Robots
Problems such as bridge collapses, road cracks, and underground pipeline leaks occur from time to time in cities. It would be far better to detect these issues before disasters happen. Inspection robots, like spiders, can crawl into narrow spaces with the help of cameras and sensors to scan for damage. These machines report their findings to authorities in real time. Many cities are using such robots to monitor infrastructure without closing roads or endangering the safety of human workers.
Public Service Efficiency Enhancement: Service Robots in Hotels, Airports, and Hospitals
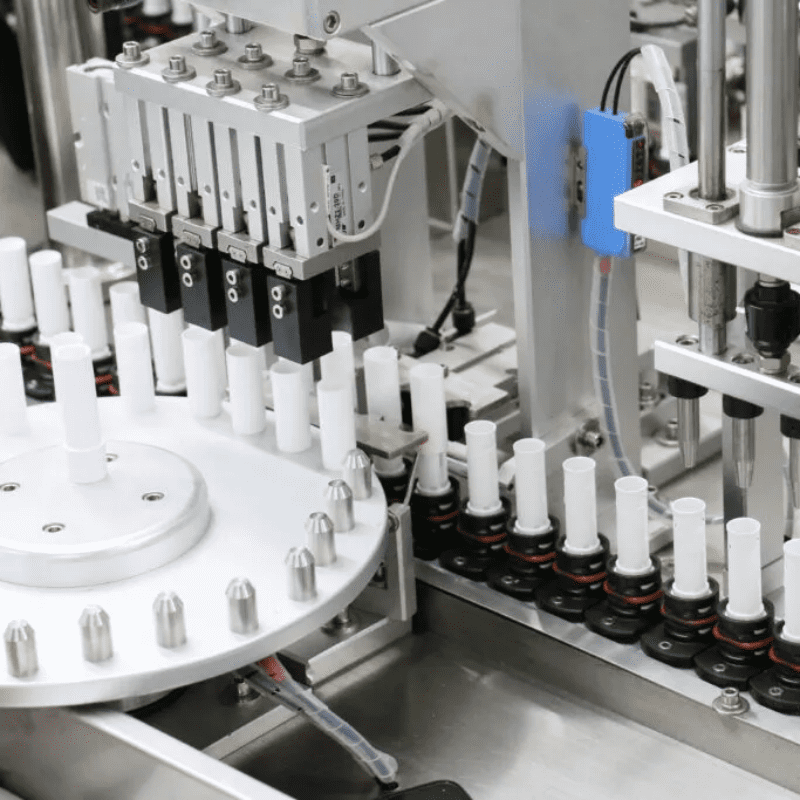
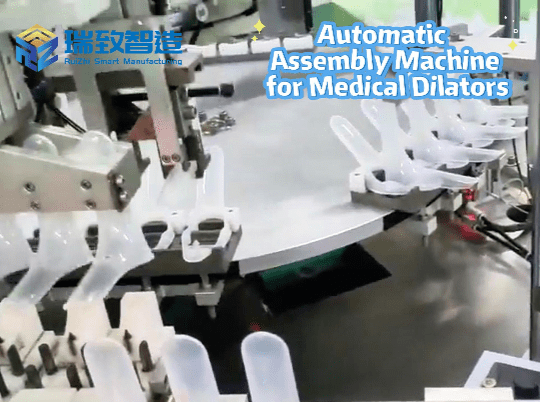
Service robots are also gradually appearing in public-facing environments such as airports, hotels, and hospitals. At airports, robot assistants can help passengers check in, find boarding gates, and answer traveler questions in multiple languages. Hotels have also started using robots to deliver food, towels, and provide room service. Some hospitals have begun to experiment with using robots to deliver medicines and assist in patient transportation. Meanwhile, in the medical supplies production process of hospitals, Syringe Automatic Assembly Equipment serves as a key automated device. Through robotized precision operations, it can realize the integrated assembly of syringe barrels, push rods, and scale marks. It not only controls the assembly accuracy within ±0.01mm to ensure medical safety but also, by linking with the hospital’s material management system, provides real-time feedback on production progress and inventory data. This provides backend support for the “stability of material supply” in the smart city medical system and forms a “production-delivery” medical service closed loop with front-end service robots. These innovations reduce the pressure on human staff and speed up service delivery.

Educational Model Innovation: Empowerment of Robot Teaching Assistants in Classrooms
Schools are also witnessing the impact of robot technology. Robot teaching assistants in Japan and South Korea are being used to help students learn English, mathematics, and programming. These robots are now very useful for students with disabilities, as they can benefit from one-on-one interaction. Such educational robots may soon appear in classrooms around the world. However, they can never replace teachers, but they can obviously help teachers create more engaging learning experiences.
New Form of Collaborative Work: Urban Task Management by Swarm Robots
An important and fascinating trend is swarm robot technology, which requires many small robots to work collaboratively. These robots are being used in emergency situations, such as searching for survivors after earthquakes and cleaning up toxic leaks. Swarm robots are easy and quick to deploy, and highly flexible. They can be used to manage city-wide tasks such as delivery, construction, and traffic flow management.
Practical Constraints: Three Major Challenges of Integrating Robots into Smart Cities
While the advantages of robot technology in smart cities are exciting, there are also some real challenges. Cost is the primary challenge, as most intelligent robots are equipped with advanced sensors and AI chips. They require high-speed connectivity to operate quickly and in real time. Many developing cities around the world are still struggling to meet basic needs, making investment in robots seem out of reach. In addition, there is the issue of job displacement. Robots take on many tasks in cities, replacing humans. This is a legitimate concern, as cities must also invest equally in upskilling and retraining the workforce. Jobs will certainly change, but with proper preparation, they may not disappear entirely. Furthermore, there are privacy and security issues. Robots collect data, which may be misused or stolen. Governments and enterprises need to formulate strong cybersecurity policies while ensuring that robots operate in a transparent and accountable manner.
Core Principle: People-Centered Orientation for Smart City Construction
Robot technology is easy to impress, but we must not forget that cities are built for people, not machines. Robots should help enhance human capabilities, not replace them. Smart cities also need to be efficient and human-friendly. It is essential to ensure that human connections, emotions, and community values remain at the center. The elderly can receive medicine from robots, but they still need emotional support from nurses or family members. Even if robots can answer questions, they cannot comfort a lost child at the airport. Humanistic care is crucial.