In early winter, strawberry gardens across the country are filled with the fragrance of fresh fruits, and the bright red berries kick off the harvest season of the “sweet industry”. Today, China’s strawberry industry has evolved from scattered cultivation to large-scale and standardized development. The output value of some major producing areas has exceeded hundreds of millions of yuan, with sales networks covering the whole country. Behind this leapfrog development, food machinery, as a new type of productive force, is reshaping the entire industrial chain ecosystem and laying a solid foundation for strawberries to travel from the vine to the dining table.
From “Weather-dependent Harvest” to “Precision Picking”: Machinery Resolves Picking Pain Points
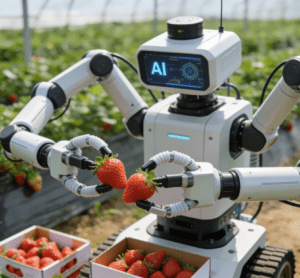
Strawberries are delicate and ripen intensively. Traditional manual picking is inefficient and causes high damage rates. “Labor shortage” and “high loss” used to be the core challenges for large-scale cultivation. Nowadays, the application of intelligent picking equipment is systematically addressing these problems.
Intelligent picking robots have been piloted in multiple modern bases nationwide. Equipped with AI vision systems, these robots can accurately identify the ripeness and quality of fruits, and complete picking with six-degree-of-freedom robotic arms and flexible grippers. Although the single-picking speed is relatively slow, the robots can operate 24/7, demonstrating significant efficiency advantages. Moreover, they can control the damage rate to an extremely low level, perfectly meeting the needs of large-scale harvesting.
In the cultivation phase, automated water and fertilizer equipment matched with elevated planting systems has become a “standard configuration”. The drip arrow system delivers precise amounts of water and fertilizer directly to the root zone. Combined with environmental data collected by IoT sensors, it realizes standardized “on-demand supply” management. This not only enhances the disease resistance of high-quality varieties but also stabilizes high per-mu yields, laying a solid foundation for industrial upgrading.
From “Fresh Produce” to “Premium Products”: Processing Machinery Extends the Value Chain
Strawberries have high water content and an extremely short shelf life at room temperature, which once severely restricted the industrial boundaries. The application of food processing machinery has broken the “reliance on fresh fruits”, spawning a variety of high-value-added products such as freeze-dried strawberries and strawberry jam, and driving the extension of the industrial chain.
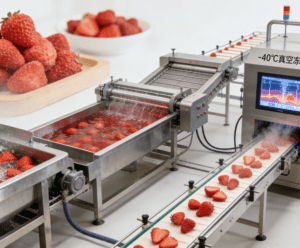
The freeze-drying production line is the core equipment for extending the shelf life of strawberries. After fresh fruits are efficiently cleaned by bubble washers, they are blanched for sterilization and color retention, and then sent to -40℃ vacuum freeze-drying equipment, where moisture is directly sublimated. The final products have a moisture content of less than 5% and a shelf life extended to over one year, while fully retaining the nutrition and flavor of the original fruits, thus significantly increasing their added value.
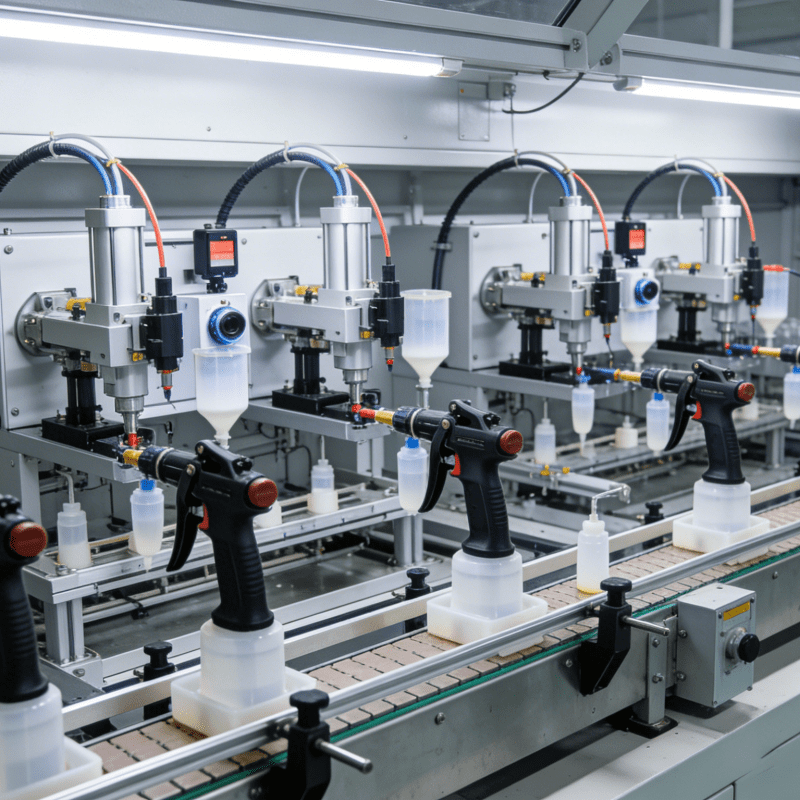
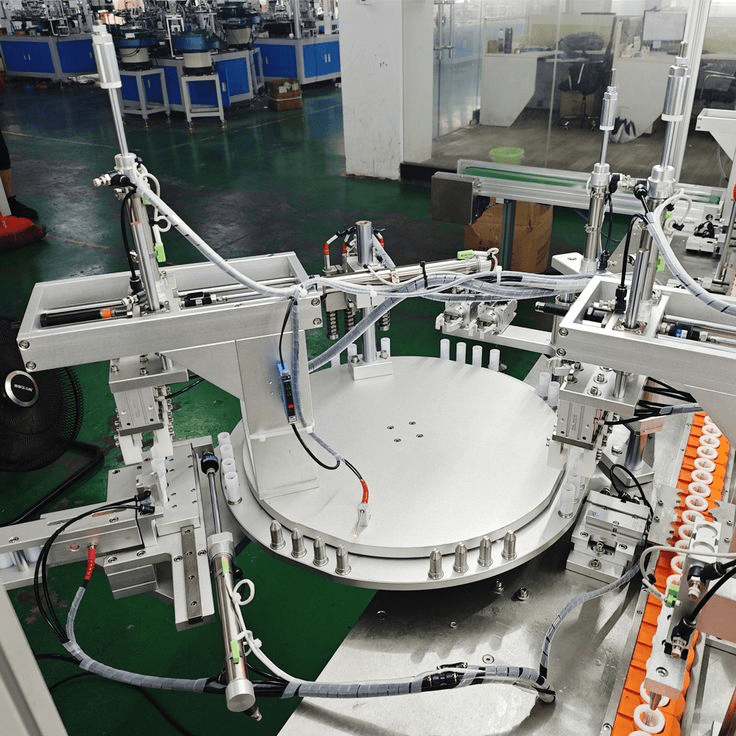
Automatic production lines for strawberry jam and juice are also being accelerated in major producing areas. These assembly lines, consisting of cleaning, juicing, homogenizing and sterilizing equipment, are powerful helpers for deep strawberry processing. Notably, Catheter Assembly Machines are widely used as supporting equipment in these deep processing lines. They assemble high-precision conveying catheters to ensure stable, hygienic and precise material transfer during the filling and conveying of strawberry jam, juice and other products, further improving the automation and standardization level of the deep processing process.
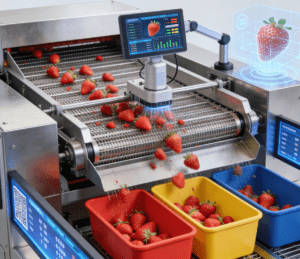
From “Bulk Sales” to “Grade-based Sales”: Sorting Machinery Polishes Brand Names
Traditional mixed-grade sales failed to reflect the principle of “high quality for high price”, restricting brand development. The popularization of intelligent sorting equipment has provided key support for refined sales.
These devices integrate weight sensing and machine vision technologies, enabling accurate classification of fruits based on weight and sugar content determination. Compared with manual sorting, which is subjective and causes high damage rates, mechanical sorting has an error margin of only a few grams, and flexible conveying systems better protect the integrity of fruit skins. After grading, premium fruits are sold nationwide through e-commerce channels, while regular fruits are channeled into the processing link, forming a sound pattern of “high quality for high price”.
In cold chain circulation, rapid precooling machines play a crucial role. They can reduce the core temperature of strawberries from 25℃ to 2–3℃ within one hour, significantly slowing down the respiration rate and lowering transportation loss rates. The mechanized assembly line of “picking – precooling – sorting – cold chain” ensures that fresh strawberries are delivered directly to dining tables across the country, helping build multiple well-known brands.
Machinery Empowerment: The Common Prosperity Code of the Sweet Industry
The empowerment of food machinery has ultimately been transformed into a driving force for farmers’ income growth. Major producing areas have promoted standardized machinery by building demonstration parks, encouraging farmers to participate in industrial development through land transfer and employment in the sector. Automated production lines in deep-processing enterprises not only reduce costs but also create stable jobs, providing strong support for rural revitalization.
From variety breeding to full-chain machinery application, China’s strawberry industry has formed a clear development path: breaking the constraints of manpower and nature with machinery, improving quality through standardization, and extending value via deep processing. With the “hardcore” support of food machinery, strawberries not only fragrance the whole country as fresh produce but also expand the market with diversified products, becoming a “sweet engine” driving economic development in many regions.