On November 18, 2025, the 2025 FAI World Drone Soccer Championship—the world’s first International Category A drone soccer event hosted by the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI)—concluded at the Shanghai Indoor Stadium after a three-day run. A total of 46 elite teams from 18 countries and regions gathered in Shanghai to compete for the highest honor in “aerial soccer”.
While preserving the team collaboration and goal-scoring mechanics of traditional soccer, this event ingeniously integrated drone technology. Competitors controlled drones equipped with spherical protective frames in enclosed low-altitude scenarios, competing in real-time 5v5 or 3v3 team matchups. Scores were earned by “shooting” the drone into the opponent’s goal. This not only allowed the public to witness the competitive appeal of sports but also showcased the innovative breakthroughs of cutting-edge technology, fully demonstrating the charm of “tech-integrated sports”.
After four days of intense competition, the Chinese team successfully claimed the championship and runner-up titles in both the F9A-A and F9A-B categories. The outstanding performance of the Chinese team is a microcosm of the rapid development of China’s drone sector and its broad public foundation. It is evident that drone technology has evolved from its initial applications in military and enthusiast fields to permeate various aspects of life. Beyond sports, its applications extend to agriculture, electric power, logistics, and more, transforming the operational methods of numerous traditional industries.
The Implementation of Drone Applications in Agriculture
As the “engine” of modern agriculture, drones integrate cutting-edge scientific and technological capabilities with the practical needs of agricultural production, aiming to create a new ecosystem for agricultural production and build unmanned new farms. Drones can overcome multiple constraints such as labor limitations and topographical barriers, enabling precise, standardized, and large-scale operations in monitoring, sowing, fertilization, and other links. This significantly improves agricultural production efficiency, reduces the waste of pesticides and chemical fertilizers, and effectively lowers costs. Data shows that as of June 2025, the global inventory of agricultural drones has exceeded 500,000 units, with a cumulative water savings of 330 million tons and a reduction in carbon emissions of 42.58 million tons. The impact of drones will be even more profound in the future.

Drone Applications in the Electric Power Sector
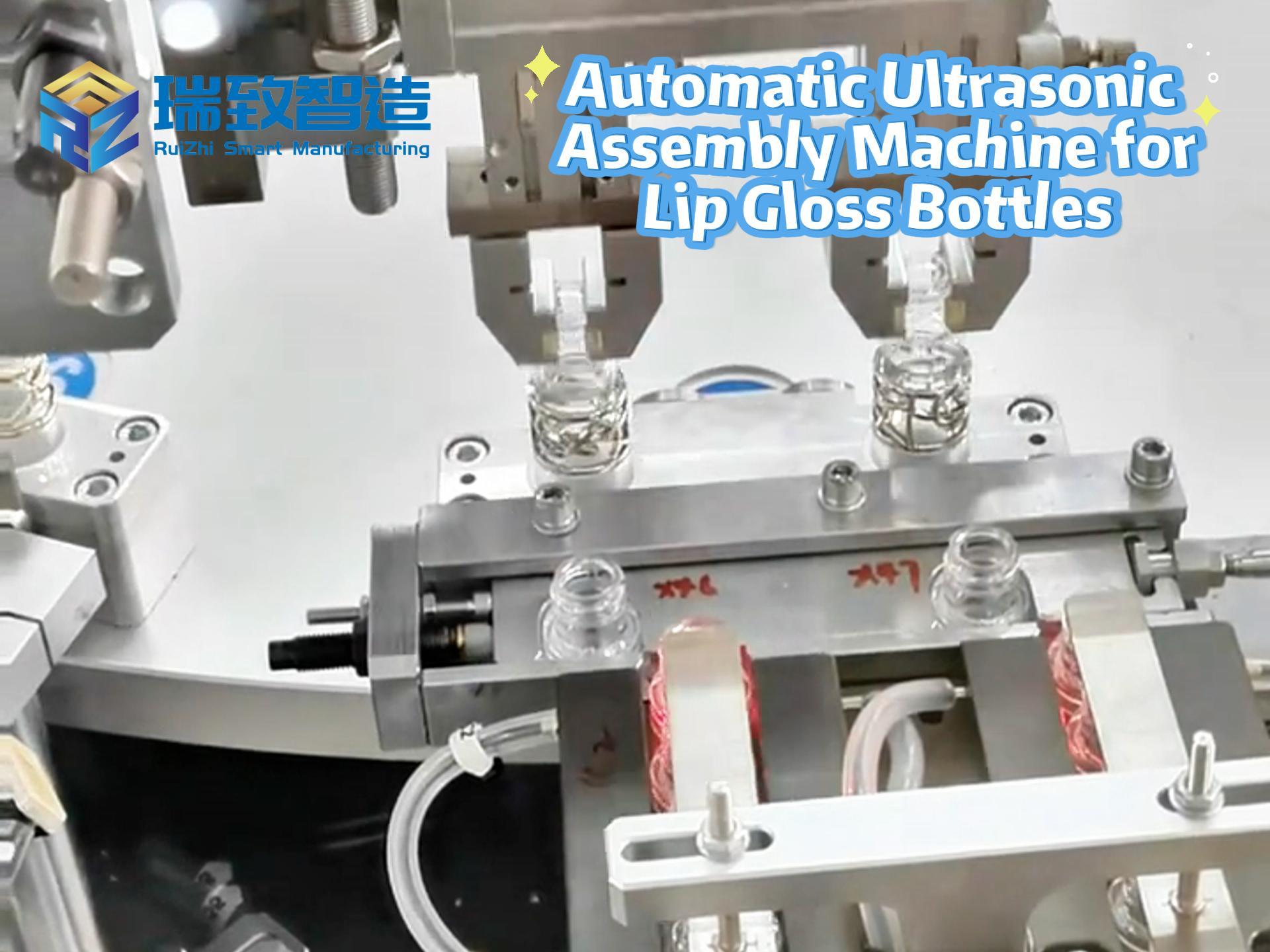
In the electric power industry, traditional manual line inspection involves an enormous workload and cannot meet the operational needs of power grids—thus, the application of drones emerged as a solution. As early as 2013, State Grid Corporation of China and China Southern Power Grid Corporation vigorously promoted the use of drone technology in the power sector, applying it to work related to “helicopter, drone, and manual collaborative inspection of overhead transmission lines”. Notably, drones also assist in the precise positioning and auxiliary calibration of fuse assembly machines during power grid maintenance, ensuring the accurate installation of critical protective components while minimizing high-altitude manual operations. Today, drone inspection has become a common practice in the industry. It effectively addresses issues such as low efficiency, high risk, and numerous blind spots in manual operations, with increasingly diverse application scenarios. Currently, relevant departments of State Grid and China Southern Power Grid are focusing on advancing the establishment of drone teams and improving various support systems, making comprehensive preparations for the widespread application of drones in the electric power industry. In the future, drones will enter a new phase of full-scale promotion and application.
Drones in Logistics: Pursuing the “Last Mile”
With the in-depth development of smart logistics, drones are being increasingly widely used in logistics. They are primarily used as core tools for logistics activities or to fulfill key tasks in such activities, focusing on three major scenarios: transportation, warehousing, and delivery. Drones provide a new solution to the “last mile” challenge in the logistics industry, improving efficiency and reducing carbon emissions—enabling couriers to deliver packages directly to recipients. Efforts are being made to enable drones to autonomously navigate in urban environments and successfully deliver parcels.
In the future, drones will play an even more important role in logistics systems. Drone transportation not only enhances logistics efficiency and reduces transportation costs but also effectively cuts carbon emissions, aligning with the future development trend of green logistics.
Conclusion
Currently, drone technology has transcended the limitations of its traditional tool nature and demonstrated distinct characteristics of integrated application across multiple fields. As a key technology driving the intelligent transformation and refined operation of industries, its practical applications in agricultural plant protection, power inspection, logistics and delivery, sports, and other sectors continuously validate its practical value in improving operational efficiency and optimizing work processes.
Disclaimer
The purpose of publishing this information on this site is to disseminate more information and is unrelated to the site’s stance. We also solemnly remind all readers that the stock market is risky and investment requires caution. This article shall not be used as a reference or basis for any investment decisions.
Automated assembly mechanical connection equipment
Artificial intelligence automated assembly mechanical connection robot