In the field of precision manufacturing, precision component machining and medical component machining have far higher requirements for accuracy, stability, and consistency than ordinary component machining. Whether it is core precision components in industrial equipment or medical parts such as artificial joints and surgical instruments implanted in the human body, tiny dimensional errors may affect product performance and even personal safety. Relying on its technical characteristics, CNC machining centers have become a key support to meet such high-demand machining needs, providing reliable technical solutions for both machining scenarios.
Core Demands of Precision Component and Medical Component Machining: Why Traditional Machining Falls Short?
The machining needs of precision components and medical components share high commonalities, while the medical field also has more stringent special requirements. These demands directly determine the selection criteria for machining equipment:
– Micron-level accuracy requirement: As core components of equipment, precision components require dimensional tolerances to be controlled within 0.005-0.01mm; for medical components such as the surface accuracy of artificial joints and the edge tolerance of surgical tools, the accuracy must even reach the micron level. Otherwise, it may affect surgical effects or implantation safety.
– High difficulty in material machining: Both types of machining often involve special materials. For example, precision components commonly use aerospace aluminum alloys and titanium alloys, while medical components use medical-grade stainless steel, pure titanium, and bioceramics. These materials have high hardness and strong toughness, making it difficult for traditional machine tools to achieve efficient and low-loss machining.
– Batch consistency and stability: Precision components are mostly produced in batches for supporting purposes, requiring consistent dimensions and performance for each piece; medical components are subject to regulatory requirements, and products of the same batch must comply with unified standards. Traditional manual operations are prone to poor consistency due to human errors.
– Demand for complex structure machining: Medical components such as core cavities of diagnostic equipment and transmission parts of surgical robots often have complex curved surfaces, deep holes, or special-shaped structures; precision components may also involve multi-surface and multi-process composite machining. Traditional machine tools require multiple clamping operations, which easily accumulate errors.
Core Value of CNC Machining Centers: How to Adapt to the Two Machining Needs?
As equipment integrating computer control, high-precision transmission, and automated machining, CNC machining centers have technical characteristics that precisely match the needs of precision component and medical component machining, specifically reflected in three dimensions:
High Precision: Breaking Through from “Millimeter-level” to “Micron-level” Accuracy
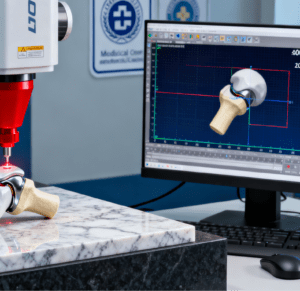
The numerical control systems equipped in CNC machining centers (such as mainstream systems like FANUC and Siemens) have extremely high positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy. Some high-end equipment can achieve a positioning accuracy of ±0.001mm and a repeat positioning accuracy of ±0.0005mm, stably meeting the micron-level tolerance requirements of precision components and medical components. At the same time, the spindle speed of the equipment (up to more than 20,000 rpm) and tool clamping accuracy (such as HSK high-speed tool holders) can reduce vibration and errors during material cutting, making it particularly suitable for high-precision forming of difficult-to-machine materials such as titanium alloys and bioceramics in medical components.

Complex Machining Capability: One-stop Solution for Multi-process and Special-shaped Structure Needs
The complex structures of medical components and precision components often require multiple processes such as milling, drilling, boring, and tapping. Traditional machining requires transferring workpieces between multiple pieces of equipment, and multiple clamping operations easily lead to error accumulation; CNC machining centers, however, can complete multi-process machining on a single piece of equipment through an automatic tool change system (usually with a tool magazine capacity of 16-60 tools), reducing the number of clamping operations and significantly lowering accumulated errors. In addition, CNC machining centers support CAD/CAM software programming, which can accurately realize the machining needs of complex curved surfaces, deep holes, thin-walled and other special-shaped structures. For example, the spherical contour of artificial joints and the micro-cavities of precision sensors can all achieve high-precision forming through program control. This automated and precise processing logic also extends to supporting medical equipment processes—such as Thermometer visual labeling machine, which, after CNC machining of thermometer casings and sensing components, uses high-precision visual positioning technology to complete automatic labeling of temperature scales and product information, ensuring that the labeling position error is within ±0.1mm, perfectly matching the precision requirements of medical device post-processing.
Stability and Consistency: Ensuring Reliability in Batch Machining
Precision component machining often involves multi-batch, small-batch production, while medical components need to strictly comply with GMP and other regulatory requirements for batch consistency. CNC machining centers reduce manual intervention through automated program control, avoiding error fluctuations caused by “reliance on manual experience” in traditional machining. At the same time, the equipment’s real-time monitoring functions (such as tool wear monitoring and machining accuracy compensation) can dynamically adjust parameters during the machining process to ensure consistent dimensions and accuracy of each component, which is particularly suitable for quality control in the batch production of medical components.
Core Reasons for Choosing CNC Machining: From Technical Advantages to Practical Value
In the scenarios of precision component machining and medical component machining, choosing CNC machining over traditional machining is essentially a comprehensive consideration of “accuracy reliability”, “cost efficiency”, and “compliance adaptability”:
– Higher accuracy reliability: Traditional machining relies on the technical level of operators, resulting in large accuracy fluctuations; CNC machining is driven by programs, with stable positioning accuracy and repeat positioning accuracy, and can maintain micron-level machining capabilities for a long time, meeting the strict standards of the medical and precision fields.
– Better balance between efficiency and cost: Although the initial investment in CNC machining centers is relatively high, during batch machining, their automated machining reduces labor costs and working hour consumption, while lowering the scrap rate caused by errors (excessively high scrap rates of medical components will significantly increase costs). In the long run, the comprehensive cost is lower.
– Stronger adaptability to materials and scenarios: For difficult-to-machine materials commonly used in medical components, such as titanium alloys and medical ceramics, CNC machining centers can achieve efficient cutting by adjusting spindle speed, cutting parameters, and matching special tools; for the multi-variety, small-batch needs of precision components, their rapid production change capability (convenient program switching) can also improve production flexibility.
– Easier quality traceability: The medical field has extremely high requirements for the traceability of component machining processes. CNC machining centers can record machining parameters (such as cutting speed, feed rate, and machining time) to form a complete production data chain, facilitating subsequent quality traceability and compliance audits.
CNC Machining Centers: Basic Support for Precision and Medical Machining
Whether it is the demand for core performance in precision component machining or the consideration of safety and compliance in medical component machining, they all rely on the technical empowerment of machining equipment. Through high precision, complex machining capabilities, stable consistency, and scenario adaptability, CNC machining centers solve the core pain points of traditional machining and become indispensable equipment in both machining scenarios. With the upgrading of manufacturing technology, the accuracy and automation level of CNC machining centers will be further improved. In the future, they will better adapt to the segmented needs of the precision and medical fields, promoting both machining scenarios to develop in the direction of higher quality and efficiency.