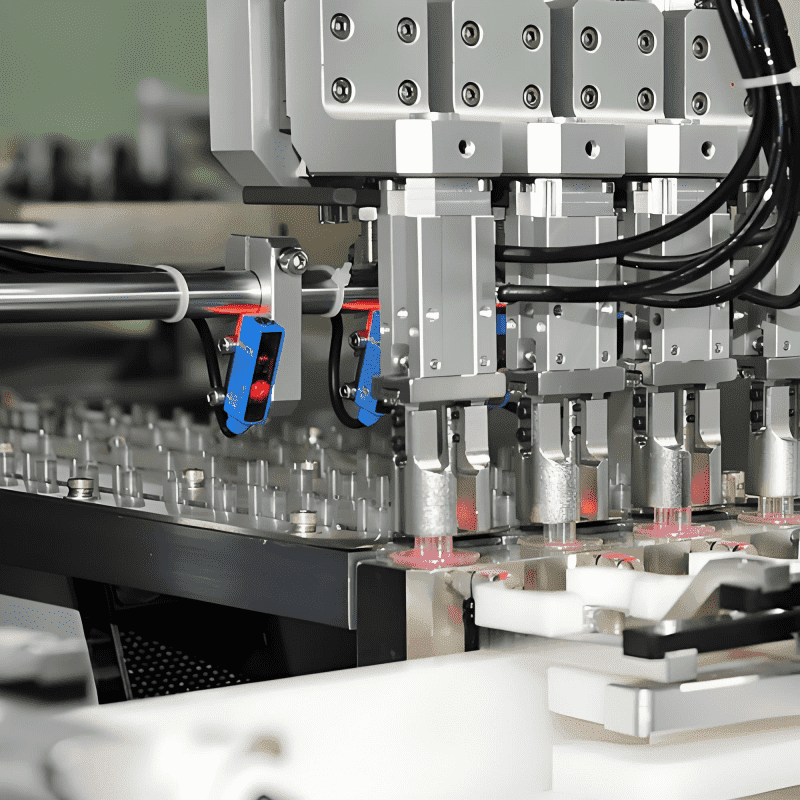
In an era where efficiency, precision, and adaptability define industrial success, AutomationSolutions have transcended their role as mere tools to become the backbone of modern operations. From manufacturing floors to healthcare facilities, from logistics hubs to smart cities, these integrated systems—combining hardware, software, and data-driven intelligence—are redefining productivity, sustainability, and scalability. More than just “automation,” they are holistic responses to the complex challenges of a fast-paced, interconnected world. This article explores the multifaceted nature of AutomationSolutions, their technological pillars, real-world applications, and their transformative impact across industries.
Table of Contents
ToggleDefining AutomationSolutions: Beyond Basic Automation
At its core, an AutomationSolution is a tailored system designed to streamline processes by reducing human intervention, enhancing accuracy, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Unlike isolated automated machines (e.g., a single robotic arm), AutomationSolutions are integrated ecosystems that connect people, processes, and equipment across entire operations. They adapt to context—whether scaling production to meet demand spikes, optimizing energy use to cut costs, or ensuring compliance with strict regulations.
Key Characteristics of Effective AutomationSolutions
- Customization: Designed to address specific industry or organizational needs (e.g., a food-grade automation system for a dairy plant vs. a 防爆 solution for an oil refinery).
- Interoperability: Seamlessly connects diverse technologies—robots, sensors, software, and legacy equipment—via universal protocols (e.g., OPC UA, MQTT).
- Scalability: Grows with the business, allowing for the addition of new machines, processes, or even facilities without overhauling the entire system.
- Intelligence: Uses AI, machine learning, and real-time data to predict issues, optimize workflows, and adapt to changing conditions (e.g., a logistics solution rerouting drones during bad weather).
- Human-Centric Design: Augments human capabilities rather than replacing them, freeing workers from repetitive tasks to focus on creativity, problem-solving, and oversight.
The Technological Building Blocks of AutomationSolutions
AutomationSolutions derive their power from a synergy of advanced technologies, each contributing to a specific aspect of efficiency and intelligence:
1. Hardware: The Physical Backbone
- Robotics and Actuators: From industrial robots (e.g., KUKA KR IONTEC for heavy lifting) to collaborative robots (cobots like Doosan 协作机器人 for assembly) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs such as Locus Robotics for warehousing), these machines execute physical tasks with precision. Actuators (pneumatic, hydraulic, electric) enable precise movement in valves, conveyors, and machinery.
- Sensors and IoT Devices: These “digital eyes and ears” collect real-time data on temperature, pressure, vibration, location, and more. Examples include 3D vision sensors (Cognex), RFID tags for asset tracking, and IIoT-enabled sensors (Siemens Simatic) that monitor equipment health.
- Control Systems: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Distributed Control Systems (DCS), and Edge Controllers (e.g., Rockwell Allen-Bradley) act as the “central nervous system,” processing sensor data and issuing commands to robots or machinery.
2. Software: The Intelligent Brain
- Industrial Software Platforms: Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) like SAP Digital Manufacturing coordinate production schedules, track materials, and ensure quality. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems like Ignition by Inductive Automation monitor and control industrial processes at scale.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms analyze data to predict equipment failures (predictive maintenance), optimize energy use (e.g., adjusting HVAC in a factory based on occupancy), or improve quality control (e.g., vision systems using deep learning to detect micro-defects in semiconductors).
- Cloud and Edge Computing: Cloud platforms (e.g., AWS IoT Core, Microsoft Azure IoT) aggregate data from multiple sites for global insights, while edge computing processes data locally for real-time decisions (critical for low-latency tasks like autonomous vehicle navigation in warehouses).
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical systems (machines, factories, supply chains) allow for simulation, testing, and optimization. For example, a digital twin of a wind turbine can predict performance under varying wind speeds, enabling proactive maintenance.
3. Services: Ensuring Seamless Implementation
- Consulting and System Design: Experts assess organizational needs, design custom solutions, and integrate new technologies with existing infrastructure (e.g., retrofitting AI into a 20-year-old production line).
- Integration and Deployment: Specialized teams ensure hardware, software, and data flows work in harmony, minimizing downtime during transition.
- Training and Support: Workforce training (e.g., teaching employees to program cobots or interpret AI insights) and ongoing maintenance (remote monitoring, troubleshooting) ensure long-term effectiveness.
Industry Applications: How AutomationSolutions Transform Sectors
AutomationSolutions are not one-size-fits-all; their impact varies by industry, but the core goal—enhancing efficiency, reliability, and agility—remains consistent:
Manufacturing: From Mass Production to Smart Factories
The manufacturing sector was an early adopter of automation, but modern AutomationSolutions have taken it beyond assembly lines. A automotive plant using a comprehensive solution might integrate:
- Robotic welding cellswith vision guidance to adapt to varying car body sizes.
- AI-powered predictive maintenanceon conveyor belts, reducing unplanned downtime by 35%.
- Digital twinsof the entire factory to simulate production changes (e.g., adding a new model) before physical implementation.
- MES integrationwith suppliers for just-in-time material delivery, cutting inventory costs by 25%.
Result: A 40% increase in throughput, 50% reduction in defects, and the ability to switch between 10+ car models on a single line.
Logistics and Supply Chain: Speed and Precision in Movement
E-commerce and global trade demand faster, more reliable logistics, and AutomationSolutions deliver:
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)in warehouses, where robots fetch items in seconds (e.g., Amazon’s robotic fulfillment centers).
- AI-driven route optimizationfor delivery trucks, reducing fuel use by 15% and ensuring on-time deliveries even in traffic.
- RFID and computer visionfor automated inventory checks, eliminating manual counting errors (e.g., Walmart’s use of RFID to track 100% of inventory in real time).
- Autonomous forkliftsin ports, loading/unloading containers 24/7 without fatigue.
Result: Order fulfillment times cut from days to hours, and supply chain visibility improved by 60%.
Healthcare: Precision, Safety, and Patient-Centric Care
In healthcare, AutomationSolutions enhance patient outcomes while reducing errors:
- Robotic surgery systems(e.g., Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci) enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with sub-millimeter precision, reducing recovery times.
- Automated medication dispensingin hospitals, where robots track prescriptions, reduce human error in dosing, and alert staff to drug interactions.
- AI-powered diagnostic tools(e.g., IBM Watson for Oncology) that analyze medical images and patient data to assist doctors in identifying diseases earlier.
- Smart inventory managementfor medical supplies, ensuring critical items (e.g., ventilators) are always in stock, even during crises.
Result: A 30% reduction in medication errors, 20% faster diagnosis times, and healthcare workers freed to focus on patient care.
Energy and Utilities: Sustainability and Reliability
The energy sector uses AutomationSolutions to balance supply, demand, and sustainability:
- Smart grid systemsthat monitor electricity usage in real time, rerouting power during outages and integrating renewable sources (solar, wind) seamlessly.
- Automated oil and gas drilling platformswith AI sensors that detect leaks early, reducing environmental risks and maintenance costs.
- Energy management solutionsin factories and buildings, optimizing lighting, heating, and machinery use to cut energy consumption by 20–30%.
- Predictive maintenanceon wind turbines, where vibration sensors and AI predict component failures, extending turbine lifespans by 10 years.
Result: Lower carbon emissions, more reliable energy supply, and operational costs reduced by billions annually.
Agriculture: Feeding the World Efficiently
AutomationSolutions are revolutionizing farming, addressing labor shortages and climate challenges:
- Autonomous tractors and dronesthat plant, water, and harvest crops with precision, using AI to adjust for soil conditions (e.g., John Deere’s autonomous farming systems).
- Smart irrigationcontrolled by soil moisture sensors, reducing water use by 50% compared to traditional methods.
- AI-powered crop monitoringvia drones with multispectral cameras, identifying pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies before they spread.
- Automated sorting and packingin food processing plants, ensuring only high-quality produce reaches consumers.
Result: Crop yields increased by 25%, resource use optimized, and farmers equipped to adapt to climate variability.
The Strategic Advantages of AutomationSolutions
Organizations adopting AutomationSolutions gain a competitive edge through:
- Efficiency Gains: Reduced cycle times, minimized waste (e.g., 30% less material scrap in manufacturing), and 24/7 operation without downtime.
- Cost Reduction: Lower labor costs (reallocating workers to skilled roles), reduced energy and resource use, and fewer errors (e.g., $2 billion saved annually in healthcare via reduced medication errors).
- Quality Improvement: Consistency in processes (e.g., robotic welding produces uniform joints) and AI-driven inspections catch defects humans might miss.
- Scalability: Easily adjust production or service capacity to meet demand (e.g., a logistics firm adding 100 robots during holiday peaks without hiring).
- Risk Mitigation: Automated safety systems (e.g., emergency shutdowns in factories) reduce accidents, while AI predicts supply chain disruptions, enabling proactive planning.
- Sustainability: Optimized resource use (energy, water, materials) and reduced emissions align with global climate goals, enhancing brand reputation.
Challenges in Adopting AutomationSolutions
While transformative, implementing AutomationSolutions comes with hurdles:
1. High Initial Investment
Comprehensive solutions—including hardware, software, and integration—require significant upfront costs, which can deter small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Solution: Phased implementation (e.g., starting with AI-driven energy management before adding robotics) and financing options (leases, pay-as-you-go models) reduce upfront burdens.
2. Integration Complexity
Legacy systems (e.g., a 30-year-old PLC) often struggle to communicate with new technologies (e.g., cloud platforms), creating data silos.
Solution: Use middleware (e.g., Kepware) and open protocols (OPC UA) to bridge old and new systems, and partner with integrators specializing in legacy modernization.
3. Skills Gap
Workers need training in robotics, AI, and data analysis to operate and maintain these solutions. A 2023 survey found 70% of manufacturers report a shortage of skilled automation technicians.
Solution: Collaborate with vocational schools to design training programs, offer on-the-job certifications (e.g., Siemens Automation Certification), and use user-friendly software (drag-and-drop interfaces for robot programming).
4. Cybersecurity Risks
Increased connectivity (via IoT) exposes automation systems to hacking—critical in sectors like energy (e.g., a hacked power grid) or healthcare (e.g., ransomware on medical devices).
Solution: Implement end-to-end encryption, regular security audits, and “air-gapped” systems for critical infrastructure (e.g., nuclear plants) to limit internet access.
5. Resistance to Change
Employees may fear automation will replace their jobs, leading to resistance.
Solution: Communicate that automation augments human work (e.g., robots handle heavy lifting, workers manage quality control), involve staff in solution design, and offer reskilling opportunities.
Future Trends: The Next Frontier of AutomationSolutions
As technology evolves, AutomationSolutions will become smarter, more connected, and more human-centric:
- Generative AI Integration: AI will not only optimize existing processes but design new ones. For example, a generative AI tool could create a custom assembly sequence for a new product, testing thousands of possibilities in minutes.
- Human-Robot Collaboration 2.0: Cobots will use advanced sensors (tactile, voice recognition) to anticipate human needs. A factory worker gesturing toward a part could trigger a cobot to fetch it, creating seamless teamwork.
- Edge AI Expansion: Processing data locally (on edge devices) will become faster, enabling real-time decisions in milliseconds—critical for autonomous vehicles and surgical robots.
- Circular Economy Integration: AutomationSolutions will optimize recycling processes, e.g., AI-powered systems that sort and repurpose electronic waste, reducing landfill use.
- Ethical and Transparent AI: As AI plays a larger role, solutions will include “explainable AI” (XAI), so humans understand how decisions are made (e.g., why a diagnostic tool flagged a patient for further testing).
Conclusion: AutomationSolutions as Catalysts for Progress
AutomationSolutions are more than a collection of technologies—they are enablers of progress, empowering industries to do more with less, adapt to change, and focus on what matters most: creating value, improving lives, and sustaining the planet. From factories producing custom goods at scale to hospitals delivering precise care, from logistics networks moving goods efficiently to farms feeding growing populations, these solutions are the invisible hands driving the modern world.
As they evolve—becoming more intelligent, collaborative, and ethical—AutomationSolutions will continue to redefine what is possible, proving that the future of industry is not just automated, but smart, sustainable, and human-centric. For organizations willing to embrace them, the reward is not just efficiency, but resilience in an unpredictable world.
#flexible automation and programmable automation #integrated automation examples