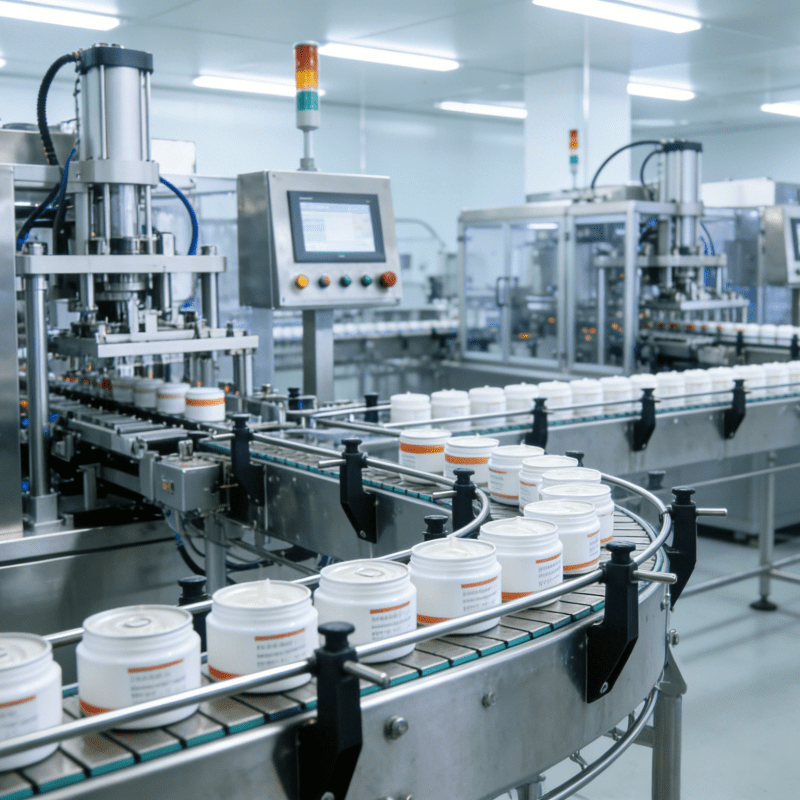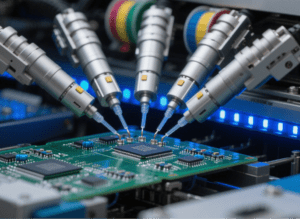
In the dynamic realm of modern manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are the cornerstones of success, the automatic placement machine has emerged as a transformative force. Whether it’s the intricate world of electronics manufacturing, the high – precision demands of the medical device industry, or the complex assembly processes in automotive electronics, this machine is reshaping how components are placed, leading to higher quality products and streamlined production lines.
- The Imperative for Automatic Placement in Modern Manufacturing
- The Challenge of Manual Placement
In the early days of manufacturing, manual component placement was the norm. Workers would painstakingly position tiny components, such as integrated circuits in circuit boards or small parts in medical devices. However, this approach was fraught with limitations. Manual placement was extremely time – consuming, with workers able to place only a limited number of components per hour. For example, in a small – scale electronics assembly line, a skilled worker might be able to place 50 – 100 components in an hour.
Moreover, human error was a significant issue. Even the most experienced workers could make mistakes in component orientation, misalignment, or incorrect placement. In the electronics industry, a misaligned microchip can render an entire circuit board useless, resulting in costly rework and production delays. Additionally, the physical strain of repetitive manual placement tasks often led to worker fatigue, further increasing the error rate.
The Rise of High – Volume and High – Precision Manufacturing
With the growth of consumer electronics, medical technology, and automotive electronics, the demand for high – volume production of complex products has skyrocketed. At the same time, the miniaturization trend has made components smaller and more delicate, requiring a higher level of precision in placement. For instance, in the production of smartphones, where hundreds of components need to be placed on a small printed circuit board (PCB), the margin for error is in the micrometer range. Manual placement simply cannot meet these high – volume and high – precision requirements, paving the way for the development and adoption of automatic placement machines.
- How Automatic Placement Machines Work: A Technological Marvel
- Component Feeding System
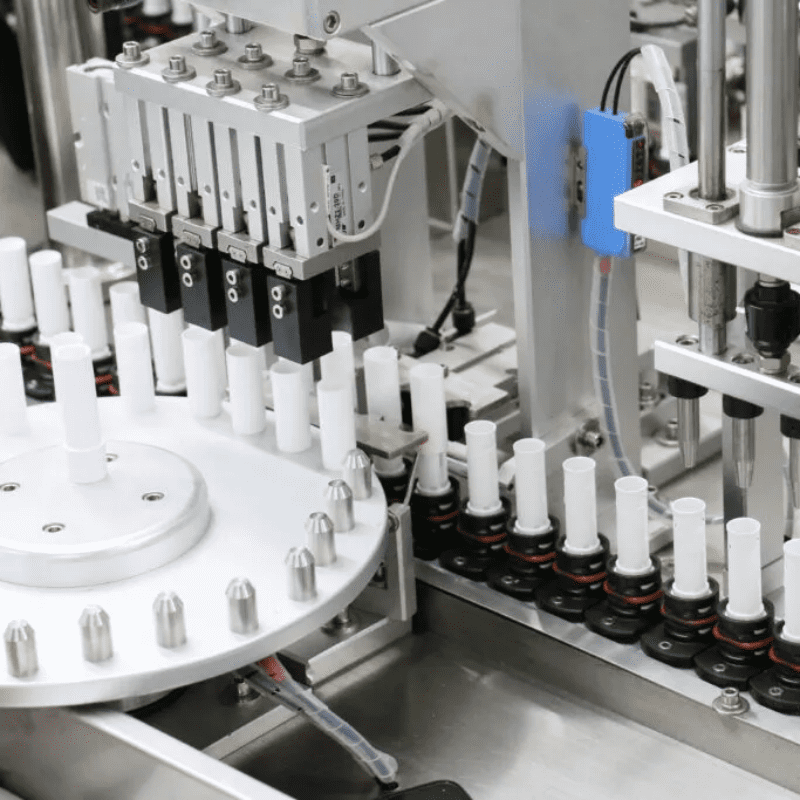
The first stage of an automatic placement machine’s operation is the component feeding system. This system is responsible for supplying components to the placement head in an organized manner. There are several types of feeding mechanisms, such as tape – and – reel feeders, tray feeders, and tube feeders. Tape – and – reel feeders are commonly used for surface – mount devices (SMDs). The components are placed in pockets on a tape, which is wound on a reel. The feeder unwinds the tape at a controlled speed, presenting the components one by one to the placement head. Tray feeders, on the other hand, are suitable for larger or more irregularly shaped components. The components are placed in a tray, and a robotic arm picks them up from the tray according to the placement program.
Visual Inspection and Positioning
Once the component is presented to the placement head, visual inspection comes into play. High – resolution cameras are installed on the placement head or around the work area. These cameras capture images of the component and the target placement location on the substrate (such as a PCB). Advanced image processing algorithms analyze the images to determine the component’s orientation, size, and position accurately. For example, if a component is slightly rotated or offset in the feeder, the system can calculate the necessary adjustments to ensure correct placement.
The machine then uses a combination of servo motors and precision mechanical systems to position the placement head accurately over the target location. The servo motors provide precise control over the X, Y, and Z axes (for movement in the horizontal plane and vertical height adjustment), allowing for placement accuracy within a few micrometers.
Placement Process
The placement head itself is a crucial component of the machine. It typically uses a vacuum – based or mechanical gripper to pick up the component from the feeder. In the case of a vacuum gripper, a vacuum is applied to the tip of the gripper, which sucks the component onto it. The placement head then moves to the target location and releases the vacuum to place the component. Some high – end placement machines also have the ability to apply solder paste or adhesive during the placement process, further streamlining the assembly workflow.
III. Core Advantages of Automatic Placement Machines
Precision and Consistency
One of the most significant advantages of automatic placement machines is their ability to achieve extremely high levels of precision. With placement accuracy often in the range of ±0.05mm or even better, they can place components with a level of consistency that is impossible to achieve manually. This precision is crucial in industries such as medical device manufacturing, where even a slight misplacement of a sensor or a micro – component can affect the device’s functionality and safety. In a medical implant production line, an automatic placement machine ensures that all components are placed correctly, reducing the risk of product failure and improving patient outcomes.
Speed and Efficiency
Automatic placement machines can place components at a much faster rate than human workers. Modern machines can place thousands of components per hour, significantly increasing production throughput. In a large – scale electronics manufacturing facility, a single automatic placement machine can replace several manual workers, leading to a substantial reduction in production time. For example, a high – speed placement machine can place over 50,000 components per hour, enabling the rapid assembly of complex circuit boards. This increased speed also allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands and reduce lead times for product delivery.
Cost – Effectiveness
Although the initial investment in an automatic placement machine can be substantial, it offers long – term cost savings. By reducing the need for a large number of manual workers, labor costs are significantly decreased. Additionally, the reduction in rework and scrap due to improved precision means that material costs are also lower. For example, in a PCB assembly operation, the use of an automatic placement machine can reduce the scrap rate from 5% (in manual assembly) to less than 1%, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
Flexibility
Automatic placement machines are highly flexible and can be programmed to place a wide variety of components. They can handle different component sizes, shapes, and package types, from tiny 0201 SMD resistors to large integrated circuits. This flexibility allows manufacturers to use a single machine for multiple product lines, reducing the need for dedicated equipment for each product. Moreover, the machine’s programming can be easily updated to accommodate design changes or new product introductions, enabling quick adaptation to market trends.
- Applications across Industries
- Electronics Industry
In the electronics industry, automatic placement machines are the workhorses of PCB assembly. They are used to place a wide range of components, including resistors, capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits. In the production of consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, these machines ensure the precise and efficient assembly of complex PCBs. For example, in a smartphone manufacturing plant, multiple automatic placement machines work in tandem to place hundreds of components on the main PCB and sub – PCBs, enabling the production of thousands of devices per day.
Medical Device Industry
The medical device industry has strict requirements for precision and quality. Automatic placement machines are used to assemble medical devices such as insulin pumps, heart monitors, and surgical instruments. They can place tiny sensors, micro – controllers, and other components with high precision, ensuring the reliability and functionality of the devices. In the production of implantable medical devices, where the components need to be placed in a sterile environment, automatic placement machines can be integrated with cleanroom systems to meet the stringent hygiene standards.
Automotive Electronics Industry
With the increasing complexity of automotive electronics, automatic placement machines play a vital role in the production of components such as engine control units (ECUs), infotainment systems, and advanced driver – assistance systems (ADAS). They can place components that are resistant to high temperatures and vibrations, ensuring the durability and performance of automotive electronics in harsh operating conditions. For example, in the production of an ECU, the automatic placement machine accurately places components that control engine functions, contributing to the overall reliability of the vehicle.
- Future Trends of Automatic Placement Machines
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning
In the future, automatic placement machines will increasingly integrate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. AI algorithms can analyze real – time production data, such as component placement accuracy, machine performance, and defect rates, to optimize the placement process. For example, ML models can predict component shortages or machine malfunctions based on historical data, allowing for proactive maintenance and production scheduling.
Miniaturization and Higher Precision
As components continue to shrink in size, automatic placement machines will need to achieve even higher levels of precision. Research is underway to develop machines that can place components with sub – micrometer accuracy, enabling the production of even more complex and miniaturized products. Additionally, the development of new placement technologies, such as nanoscale placement for emerging applications in quantum computing and nanotechnology, is on the horizon.
Smart Factory Integration
Automatic placement machines will become an integral part of smart factories. They will be connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) and other factory systems, allowing for real – time monitoring, remote control, and data sharing. For example, the machine’s production data can be integrated with the factory’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to optimize inventory management and production planning. This integration will lead to more efficient and intelligent manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
The automatic placement machine has become an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing. Its ability to provide high precision, speed, cost – effectiveness, and flexibility has transformed the way components are assembled across various industries. As technology continues to evolve, these machines will play an even more significant role in enabling the production of advanced products and the development of smart manufacturing systems. Manufacturers who embrace this technology are well – positioned to gain a competitive edge in the global market, meeting the ever – increasing demands for high – quality, high – volume production.
Automatic Process Control of Automatic Fiber Placement Machine