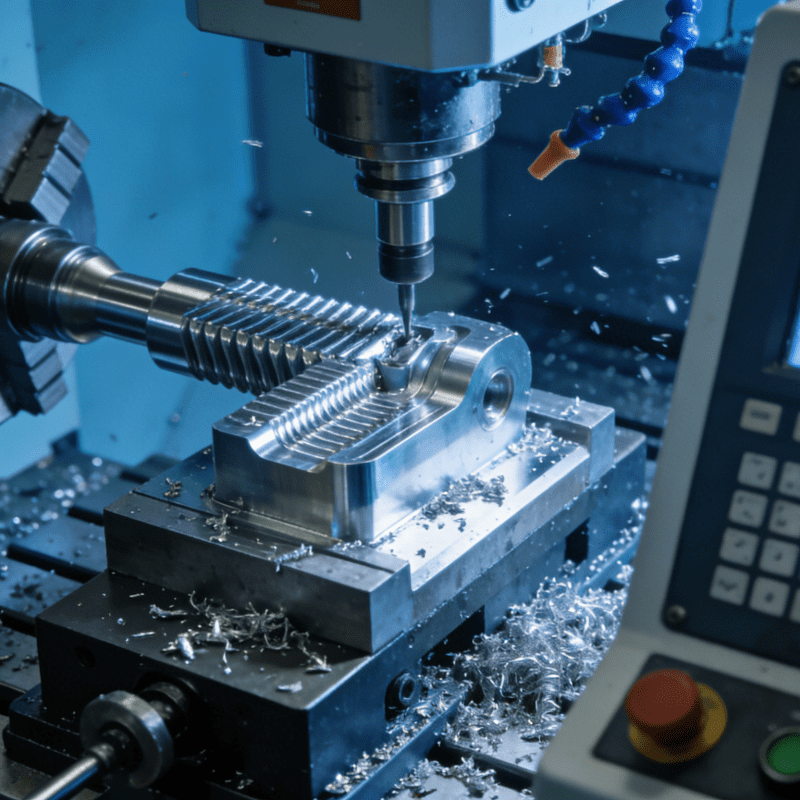
Amid the wave of high-end and intelligent transformation in the manufacturing industry, precision manufacturing and CNC machining stand out as core keywords. From core components in aerospace to precision structures in consumer electronics, CNC machining has become a pivotal pillar of precision manufacturing, thanks to its advantages of high precision, high efficiency and high stability. This article will analyze the core correlation, technical advantages, application scenarios and development trends of these two elements.
Core Cognition: The Inherent Connection Between Precision Manufacturing and CNC Machining
The core requirements of precision manufacturing are accuracy and stability, which demand products to meet extremely high standards in dimensional, geometric and positional accuracy as well as surface quality. CNC machining (Computer Numerical Control Machining) controls machine tools through computer programs, converting digital instructions into precise movements to achieve automated and high-precision machining of workpieces.
CNC machining serves as the core implementation method of precision manufacturing. Traditional mechanical machining relies on manual operations, where precision is susceptible to interference, making it difficult to meet precision requirements. In contrast, CNC machining avoids human errors through digital control, achieving micron-level or even nanometer-level precision and ensuring batch production consistency. The two complement each other: upgrades in CNC technology drive the advancement of precision manufacturing, while the demands of precision manufacturing in turn spur innovations in CNC technology.
Technical Advantages: Core Capabilities of CNC Machining in Supporting Precision Manufacturing
As a core technology of precision manufacturing, CNC machining boasts multiple irreplaceable advantages, which form the technical barriers of precision manufacturing and serve as the key reasons for enterprises to adopt this technology.
Ultra-high machining precision to meet precision requirements
The precision of CNC machining depends on the accuracy of machine tools and programs. Modern high-end CNC machine tools can achieve positioning accuracy at the 0.001mm level, precisely controlling tool cutting parameters to ensure workpiece precision. For example, in the machining of mobile phone chip carriers in the electronics industry, errors in key dimensions such as slot width and aperture can be controlled within the micron range, ensuring chip bonding and stable equipment operation.
High automation to improve production efficiency
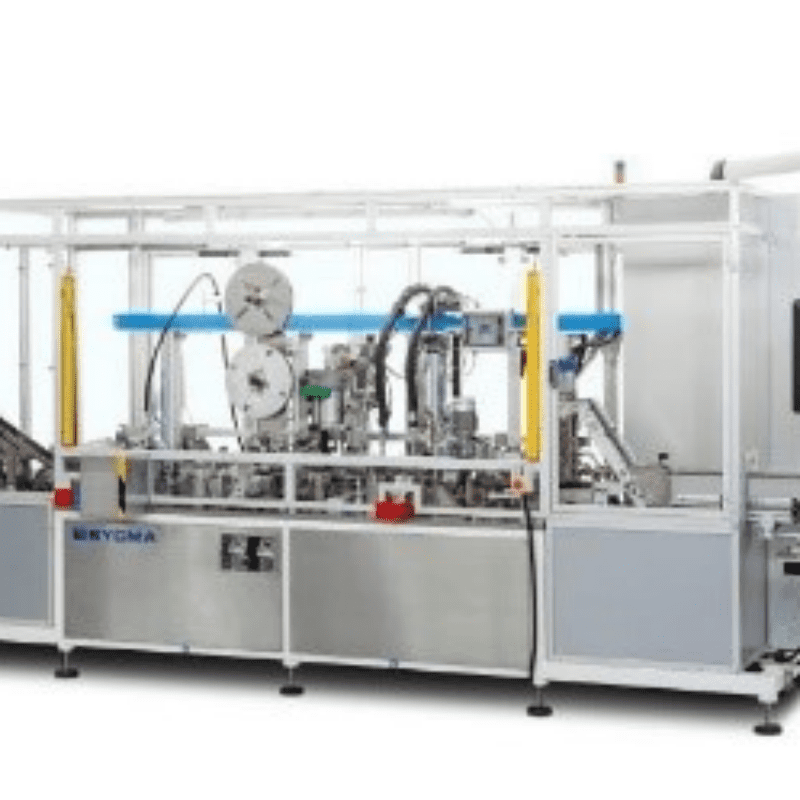
CNC machining realizes automated mass production through pre-set programs, eliminating the need for frequent manual intervention, thus significantly reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. Meanwhile, it enables integrated processing of multiple procedures such as milling, drilling, boring and tapping, reducing the number of workpiece clamping operations, minimizing clamping errors and shortening production cycles. Notably, in the automated production line of small precision parts (such as miniature electronic components and tiny medical accessories), CNC machining equipment can be seamlessly connected with Robotic Small Product Tray Loading System. After the CNC machining of workpieces is completed, the robot system can automatically grab, sort and place the small products into the specified trays with high precision, forming an automated closed loop from machining to finished product storage. This not only further reduces manual participation and avoids secondary damage to precision parts caused by manual handling, but also improves the regularity and traceability of finished product storage, effectively enhancing the overall efficiency of automated mass production.
Strong stability to guarantee batch consistency
Precision manufacturing requires consistent quality in mass production. Traditional manual machining is prone to precision fluctuations due to factors such as operator skills and fatigue. In contrast, CNC machining is precisely controlled by programs with unified processing steps, ensuring consistent precision across batches of workpieces and reducing defect rates. This advantage is particularly crucial in fields such as automotive parts and medical devices.

Flexible machining to adapt to diverse demands
The personalization and diversification of market demands have driven the need for flexible machining in precision manufacturing. CNC machining allows switching between different workpieces simply by modifying programs, without the need for large-scale adjustments to machine tools, enabling rapid responses to market changes. For instance, programs can be adjusted as needed for customized medical device machining, and the technology can flexibly adapt to the machining of different models of products in the aerospace sector.
Application Scenarios: Multi-field Practices of CNC Machining Empowering Precision Manufacturing
With its core technical advantages, CNC machining is widely applied in various fields of precision manufacturing, driving the high-end development of different industries. Below is an analysis of typical scenarios:
Aerospace: Ultimate Precision Ensures Flight Safety
The aerospace sector imposes extremely high requirements on the precision and reliability of components. Core parts such as engine blades and landing gear all require precision manufacturing. CNC machining can accurately process complex structures (such as the curved surfaces of engine blades) to ensure aerodynamic performance, and can also machine high-strength materials such as titanium alloys and superalloys to meet high-temperature and high-pressure resistance requirements. For example, the curved surface precision error of an aero-engine blade processed by five-axis CNC machining can be controlled within 0.005mm, ensuring flight safety.
Consumer Electronics: Compact Precision Enhances Product Experience
Consumer electronic products are evolving toward thinner, lighter and smaller designs, leading to a surge in demand for precision structural components such as mobile phone middle frames and camera modules. CNC machining enables high-precision and small-size machining of electronic components, precisely controlling dimensions such as middle frame thickness and aperture to ensure assembly accuracy. It can also process materials such as aluminum alloys and stainless steel to enhance product texture. Its high efficiency can also meet large-scale production needs, ensuring market supply.
Medical Devices: Precise Adaptation Guarantees Diagnosis and Treatment Effects
The precision of medical devices is directly related to diagnosis and treatment effects and patient safety. Minimally invasive surgical instruments and artificial joints all require extremely high precision. CNC machining can accurately process complex structures of instruments (such as the slender rods of minimally invasive surgical tools) to ensure operational flexibility. For implantable devices such as artificial joints, it can process biocompatible materials such as titanium alloys and ceramics, controlling surface smoothness and dimensional precision to reduce rejection reactions. For example, the thread precision of artificial dental implants processed by CNC machining can be controlled within 0.01mm, improving stability and service life.
Automotive Industry: High-end Manufacturing Improves Vehicle Performance
The electrification and intelligent transformation of the automotive industry has driven the demand for precision manufacturing of high-end components. High-precision machining is required for new energy vehicle battery casings and motor rotors. CNC machining can accurately process complex structures to improve assembly precision and operational stability, and can also machine lightweight and high-strength materials such as aluminum alloys and carbon fiber composites to reduce vehicle weight and improve cruising range. For example, CNC laser cutting and milling of battery casings can precisely control dimensions and sealing performance, ensuring battery safety.