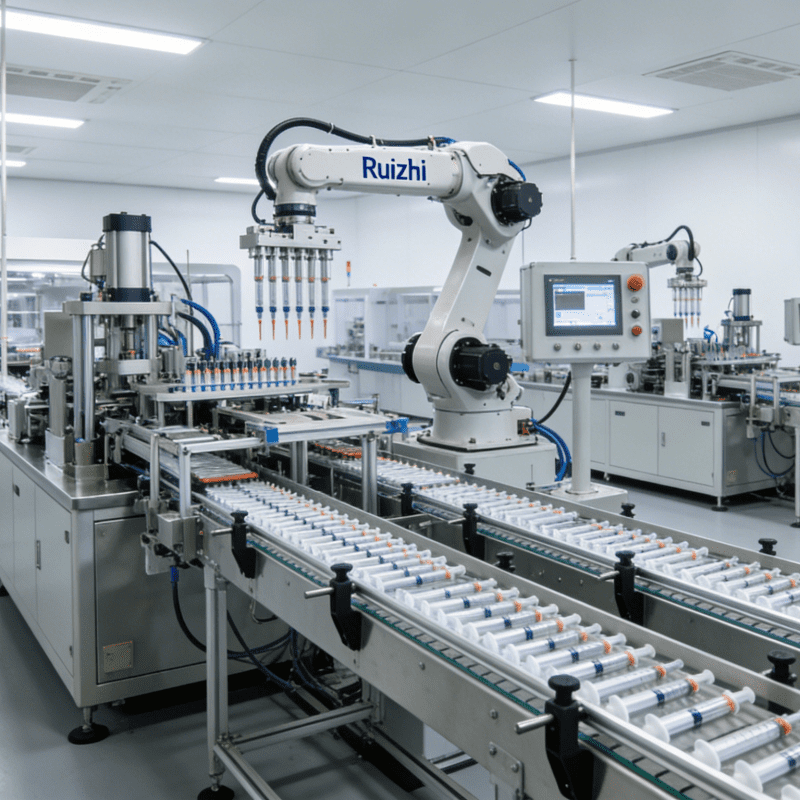
Definition: A “Precision Assembly Expert” Tailored for Automotive ManufacturingAn automotive assembly machine refers to specialized assembly equipment custom-designed and developed to meet the structural characteristics of automotive components, assembly processes, and production takt time requirements in the automotive industry. Unlike general-purpose assembly machines, it must satisfy three core demands of automotive manufacturing:High stability (to adapt to 24/7 continuous production);Ultra-high precision (with positioning accuracy reaching the 0.01mm level in some scenarios);Strong compatibility (to support flexible production of multiple vehicle models).Functionally, it is not a single device but an integrated system covering the entire workflow of “component grabbing, positioning, assembly, inspection, and conveyance.” Based on the complexity of the assembly object, it can be divided into:Single-machine automated assembly equipment (e.g., automatic bolt tightening machines);Fully automated assembly lines (e.g., engine block assembly lines).It is widely used in complete vehicle factories and automotive component supporting enterprises.
Application Scenarios: A “Versatile Tool” Covering the Entire Automotive Manufacturing ChainAutomotive assembly machines are applied throughout the entire “component-to-vehicle” production process of automobiles. While equipment designs vary significantly across scenarios, they collectively support the efficient operation of automotive manufacturing:
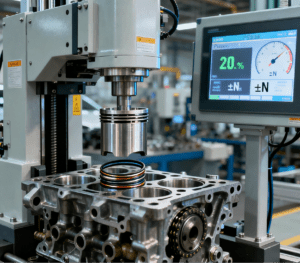
Powertrain Assembly: A “Cardiac Operating Table” Where Precision Determines PerformanceThe powertrain is the core of an automobile, and its assembly demands “millimeter-level rigor” in precision. Taking engine assembly as an example:Automotive assembly machines need to achieve precise alignment of key components such as cylinder blocks, pistons, and crankshafts. For instance, a precision press driven by a servo motor controls the pressure error within ±5N when pressing piston rings into cylinder liners—preventing engine noise or power loss caused by assembly deviations.In the assembly of new energy vehicle (NEV) battery packs, dedicated assembly machines perform integrated operations including cell stacking, module welding, and wire harness insertion. Simultaneously, vision systems detect for cold solder joints at welding points to ensure battery pack safety and range stability.
Chassis System Assembly: A “Structure Builder” Bearing Safety ResponsibilitiesAs the “skeleton” of an automobile, the chassis assembly quality directly affects driving safety. In this scenario, automotive assembly machines primarily handle the assembly of suspension, steering, and braking systems—many of which rely on sturdy iron rod components (such as suspension connecting rods and brake system support rods). Here, the Automatic Iron Rod Loading/Unloading System plays a critical role in streamlining the material flow: it uses servo-driven conveyors and pneumatic grippers to automatically retrieve iron rods from storage bins, clean their surfaces to remove rust or debris (via built-in air blowers), and precisely load them onto chassis assembly stations. The system integrates with laser positioning technology to align iron rods with mounting holes on the chassis frame—eliminating manual lifting (which risks injury and position errors) and ensuring a consistent feed rate that matches the production takt time. After assembly, it also automatically unloads leftover or defective iron rods into dedicated collection boxes, while uploading loading/unloading data (e.g., rod specifications, feeding time) to the MES system for full-process traceability.For example, on a chassis suspension component assembly line, robotic arms grab control arms, shock absorbers, and other parts. Combined with laser positioning technology, parts are accurately aligned with mounting holes on the chassis frame. Automatic tightening machines then fasten bolts, and the tightening torque of each bolt is fed back to the control system in real time to comply with VDA standards (standards of the German Association of the Automotive Industry).
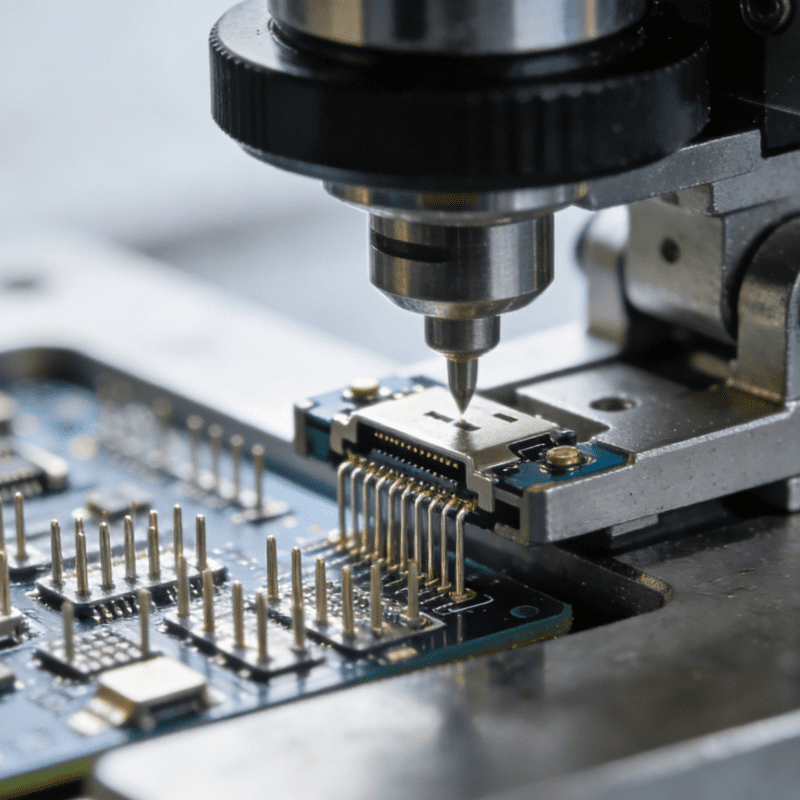
Electronic Control System Assembly: A “Neural Connector” for Smart VehiclesWith the intelligent upgrading of automobiles, demand for assembling electronic control systems (e.g., autonomous driving domain controllers, in-vehicle infotainment systems) has surged. Such assembly machines must balance “precision” and “flexibility”:In in-vehicle chip assembly, equipment uses vacuum nozzles to gently grab chips (avoiding electrostatic damage) and corrects alignment deviations between chips and circuit boards via visual recognition.For mixed-model production on the same line, assembly machines can switch between assembling central control screens for Model A and Model B within 10 minutes by quickly replacing fixtures—meeting the “small-batch, multi-variety” production needs of automotive factories.
Interior and Body Accessory Assembly: A “Detail Craftsman” Enhancing User ExperienceWhile interior and body accessory assembly has slightly lower precision requirements than powertrain assembly, it directly impacts user experience. Automotive assembly machines in this scenario mostly operate in a “semi-automated + human-machine collaboration” mode:For door trim panel assembly, equipment automatically pre-installs speakers and ambient lights, and workers perform final buckle fixing—reducing fatigue from manual repetitive operations while ensuring consistency in accessory installation.In body glass assembly, assembly machines use glue application robots to precisely apply sealant before attaching glass to the body—preventing water leakage or noise issues later.
Core Technologies: “Hardcore Strength” Supporting High Automotive Manufacturing StandardsAutomotive assembly machines meet the strict standards of the automotive industry thanks to four core supporting technologies—key differentiators from assembly machines for other industries:
High-Precision Positioning and Drive TechnologyAssembly clearances of automotive components are often measured in “microns,” requiring assembly machines to have extremely high positioning accuracy:Current mainstream equipment mostly adopts a “servo motor + ball screw” drive solution, combined with a linear encoder feedback system, achieving a positioning error of ≤0.005mm.Some high-end equipment also integrates piezoelectric ceramic drive technology for assembling micro-components (e.g., sensor pins) to further improve precision.
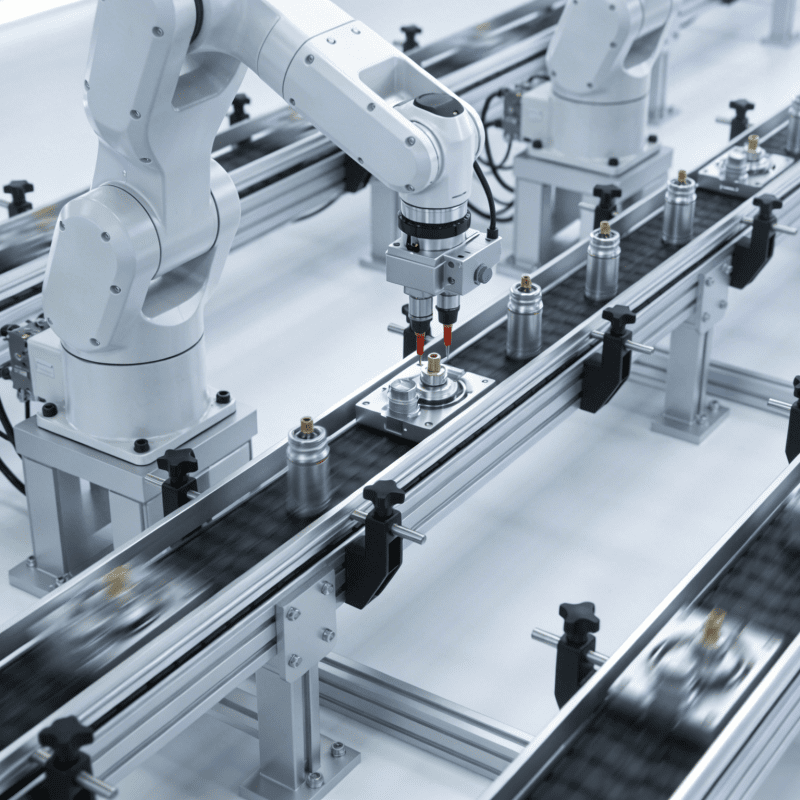
Automation and Intelligent Integration TechnologyModern automotive assembly machines are no longer “single robotic arms” but integrated systems combining PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) control systems, industrial robots, and visual inspection:PLC coordinates the action logic of equipment to ensure synchronized takt times across all processes.6-axis or SCARA robotic arms flexibly grab parts to adapt to complex assembly angles.Machine vision systems real-time detect part posture and assembly positions. If deviations (e.g., missing bolts, wrong parts) are found, the system immediately triggers a shutdown alarm to prevent defective products from entering the next process.
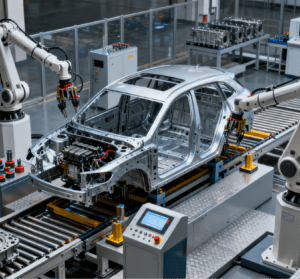
Flexible Production and Rapid Changeover TechnologyTo adapt to the automotive market’s “fast model iteration and high customization demand,” assembly machines must have strong flexibility. The current mainstream solution is “modular fixtures + parameterized programming”:Fixtures use quick-release designs, eliminating the need for recalibration during replacement.Equipment programs preset parameters for multiple vehicle models; switching models only requires calling the corresponding program to automatically adjust part dimensions, assembly paths, and inspection standards—greatly shortening changeover time (some equipment can reduce changeover time to less than 5 minutes).
Safety and Traceability TechnologyThe continuous production nature of automotive manufacturing workshops requires assembly machines to have comprehensive safety protection and data traceability capabilities:Safety light curtains or guardrails are installed around equipment, which automatically decelerate or shut down when personnel approach.Each assembly machine is connected to the factory’s MES (Manufacturing Execution System), uploading assembly data (e.g., tightening torque, pressing pressure, inspection results) in real time. In case of quality issues, the traceability system can quickly locate the specific equipment, time, and operator—enabling “full-process traceability.”
Industry Value: Multiple Contributions from “Cost Reduction and Efficiency Improvement” to “Empowering Transformation”For the automotive industry, the value of automotive assembly machines has long exceeded “replacing manual labor.” Instead, they are deeply integrated into the entire value chain of automotive manufacturing, delivering three core contributions:
Enhancing Production Efficiency to Meet Automotive “High Takt Time” DemandsA traditional manual engine block assembly line requires 15–20 workers and produces approximately 30 units per hour. With a fully automated assembly line:Only 2–3 workers are needed for supervision;Hourly output can increase to over 60 units (doubling production efficiency).For a vehicle factory with an annual production capacity of one million units, this means easily meeting the takt time requirement of “one vehicle rolling off the line per minute”—avoiding delays in the overall production schedule caused by bottlenecks in the assembly process.
Ensuring Assembly Quality to Reduce Industry “Quality Costs”Quality costs in the automotive industry are extremely high; a single assembly deviation may lead to a vehicle recall (e.g., insufficient bolt tightening torque may cause chassis component loosening). Automotive assembly machines, through “automated operations + online inspection,” reduce the assembly defect rate from 0.5% (manual assembly) to below 0.01%—significantly cutting rework and recall costs.For example, a joint-venture automotive enterprise reduced the welding defect rate of battery packs from 0.3% to 0.02% after introducing a fully automated battery pack assembly line, saving over RMB 10 million in quality losses annually.
Supporting Intelligent Transformation to Adapt to NEV and Smart Vehicle TrendsWith the popularization of NEVs and smart vehicles, new demands are placed on assembly machines:Battery pack assembly requires explosion-proof designs;Autonomous driving sensor assembly requires dust-free environments.The new generation of automotive assembly machines addresses these needs by integrating explosion-proof modules, clean benches, and AI visual inspection (capable of identifying component defects at the 0.001mm level). Moreover, they support “dark factory” (unmanned production) operations through data interconnection, helping automotive enterprises transition to Industry 4.0.
Future Trends: “Smarter, More Flexible, Greener” Through Technology IntegrationAs the automotive industry advances toward “electrification, intelligence, and connectivity,” automotive assembly machines will embrace three key development trends:
Deep Integration of AI and Digital Twins for “Predictive Maintenance + Virtual Commissioning”In the future:Automotive assembly machines will integrate AI algorithms to predict potential faults (e.g., bearing wear) by analyzing equipment operation data (e.g., motor temperature, bearing vibration)—avoiding sudden shutdowns.Digital twin technology will enable enterprises to commission and optimize assembly lines in a virtual environment before deploying parameters to physical equipment—shortening the commissioning cycle of new production lines from the traditional 3 months to less than 1 month.
Modular and Standardized Design to Lower “Multi-Variety” Production ThresholdsTo adapt to the “customization” trend in the automotive industry:Assembly machines will become more modular: Functional modules such as grabbing, positioning, and inspection can be freely combined, allowing enterprises to “purchase on demand” based on their needs—eliminating the need for large investments in customizing entire production lines.The industry will gradually establish unified interface standards, enabling interconnection of modules from different brands and reducing equipment investment costs for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Green and Energy-Efficient Design in Response to “Dual Carbon” GoalsThe automotive industry’s “dual carbon” (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality) goals are driving equipment upgrades. Future automotive assembly machines will adopt energy-saving technologies:Servo motors will use energy-efficient models, reducing energy consumption by 15%–20%;Equipment will automatically enter low-power mode during standby;Recyclable steel will be used for machine bodies to reduce resource waste—achieving “green manufacturing processes.”
Conclusion: From “Equipment” to “Partner,” Jointly Building the Future of Automotive ManufacturingThe development of automotive assembly machines is not only a microcosm of automotive industry automation but also a testament to technological progress in manufacturing. From initial single-machine automation to today’s intelligent integrated systems, they have evolved from mere “production equipment” to “strategic partners” that help automotive enterprises achieve efficient, precise, and green manufacturing.Amid the wave of NEVs and smart vehicles, automotive assembly machines will continue to focus on technological innovation, constantly breaking boundaries in precision, flexibility, and intelligence—injecting stronger momentum into the high-quality development of the automotive industry. After all, behind every safe and reliable automobile, there is the silent support of these “precision assembly experts.”
Automation engineering of production lines in the automotive industry
AI production line automation robots in the automotive industry