With the rapid development of the precision manufacturing industry, demand for various high-precision components is surging. As a fundamental core process in precision manufacturing, cutting technology directly determines the accuracy, quality, and service life of components. Cutting technology is a machining method that processes workpieces using cutting tools. It occupies an indispensable position in precision manufacturing, serving as a critical link connecting raw materials to finished components, and supporting the stable development of numerous high-end industries.
What is Cutting Technology? The Core Processing Method in Precision Manufacturing
Many people only understand cutting technology as “material cutting” on a superficial level. In reality, it has strict definitions and specifications in precision manufacturing. Cutting technology refers to a processing method that uses relative motion between cutting tools (such as turning tools, milling cutters, drills, etc.) and workpieces to remove excess material from blanks, so that the workpiece achieves the required dimensions, shape, surface roughness, and mechanical properties as designed.
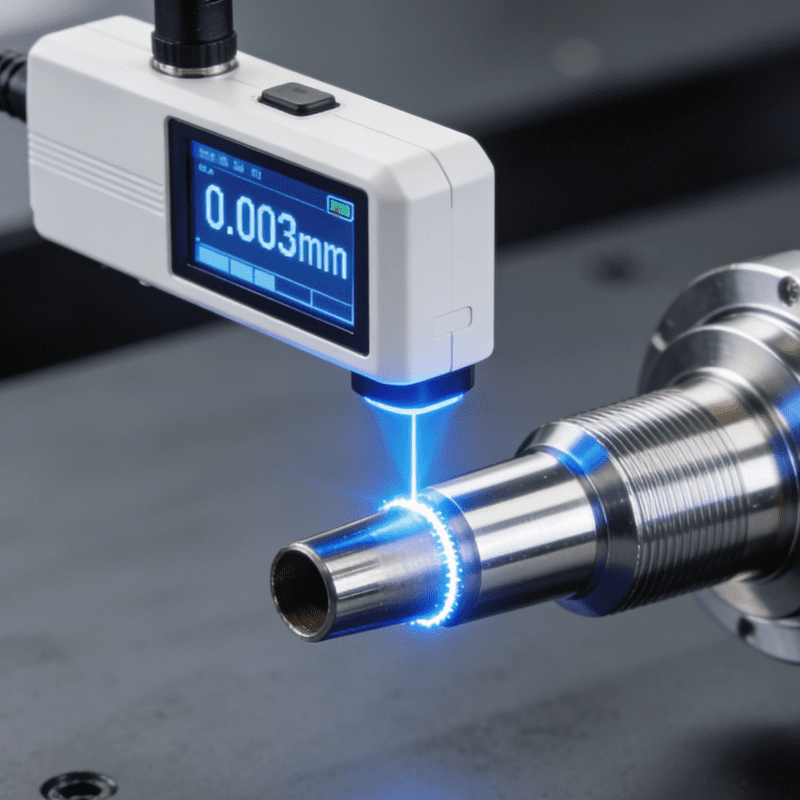
Unlike ordinary cutting, cutting in precision manufacturing has extremely high precision requirements, with errors typically controlled at the micrometer or even nanometer level. The process relies on high-precision equipment, high-quality cutting tools, and scientific process parameters to ensure every cutting step is precise and controllable, avoiding performance degradation caused by machining deviations. This is the core reason why cutting technology is deeply integrated with precision manufacturing.
Simply put, cutting technology is like “precision carving.” Raw materials are like uncut jade; through precise “carving” with cutting tools, excess parts are removed, finally forming qualified products that meet precision manufacturing standards. It is one of the most basic and widely used processes in precision manufacturing.
Core Functions of Cutting Technology in Precision Manufacturing
The core demands of precision manufacturing are “high precision, high quality, and high efficiency,” and cutting technology precisely meets these three requirements, making it an indispensable pillar of the industry. Its role is reflected in four main aspects throughout the entire processing of precision components.

Accurate Transformation from Raw Materials to Finished Products
Most raw materials used in precision manufacturing are blanks that cannot be directly applied. The core function of cutting technology is to achieve the precise conversion from blanks to finished products. Through cutting, excess material is removed, so that the workpiece meets design standards in dimensions, shape, and surface accuracy, turning ordinary raw materials into precision components for high-end equipment.
Ensuring the Quality of Precision Components
Precision manufacturing imposes extremely high requirements on component quality, including not only dimensional accuracy but also strict standards for surface roughness and mechanical properties. The quality of cutting technology directly determines component quality. High-quality cutting effectively controls surface roughness, avoids defects such as scratches and burrs, preserves internal mechanical properties, and prevents component failure caused by stress concentration during processing.
In precision manufacturing, even a 0.1micrometer deviation can render components unusable. By precisely controlling cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, and other parameters, cutting technology keeps errors within allowable ranges and maximizes product quality.
Improving Production Efficiency in Precision Manufacturing
With the large-scale development of precision manufacturing, production efficiency has become a core corporate competitiveness. Optimized cutting technology can significantly improve efficiency. Traditional cutting is relatively inefficient, while modern precision cutting, supported by high-precision automated equipment, enables batch and continuous processing, greatly shortening single-part production time.
Furthermore, optimizing cutting tools and process parameters reduces tool wear, machining downtime, and reject rates, further enhancing efficiency, lowering production costs, and strengthening market competitiveness.
Adapting to Diverse Precision Component Processing Needs
Precision manufacturing covers a wide variety of components with different shapes, sizes, and accuracy requirements. Cutting technology offers strong adaptability: processing methods and parameters can be flexibly adjusted to match different component types.
Whether for simple cylindrical or planar parts, or complex curved and special-shaped components, corresponding cutting processes (turning, milling, grinding, drilling, etc.) can be applied without replacing core equipment, greatly improving the flexibility and applicability of precision manufacturing.
Main Application Fields of Cutting Technology in Precision Manufacturing
Due to its accuracy, efficiency, and versatility, cutting technology is widely applied across core high-end manufacturing sectors. Almost all precision component processing relies on cutting technology. The four most important fields are:
Aerospace Precision Manufacturing
The aerospace industry has the strictest requirements for precision components, as accuracy directly affects equipment safety and reliability. Cutting technology is the core process here. Key components such as aero-engine blades, casings, and landing gear parts are all produced via high-precision cutting.
For example, aero-engine blades feature complex shapes and ultra-high precision requirements, relying on 5axis milling and grinding to control profile accuracy and thickness errors. Casings require turning and boring to ensure sealing and dimensional stability — all dependent on advanced cutting technology.
Automotive Precision Manufacturing
As the automotive industry moves toward high-end and intelligent development, precision requirements for components continue to rise, expanding the application of cutting technology. Critical parts such as engine crankshafts, camshafts, pistons, transmission gears, shafts, and brake system components all require cutting.
Taking transmission gears as an example, meshing accuracy directly affects efficiency and service life. Gear hobbing, shaping, and grinding ensure precise tooth profile and pitch, enabling smooth meshing — a typical example of cutting’s essential role.
Electronic Precision Manufacturing
Electronic components feature small size, high precision, and large volumes, placing high demands on cutting accuracy and efficiency. Cutting technology plays a vital role in processing chip carriers, connectors, radiators, and precision housings for mobile phones, computers, and other electronic devices.
For instance, miniature connector pins require micro-cutting to control diameter and length errors for stable electrical conductivity. Electronic radiators rely on milling to form dense fins for efficient heat dissipation, both enabled by high-precision cutting.
Medical Device Precision Manufacturing
Medical device safety and accuracy directly affect patient health, resulting in extremely high standards for component precision and quality. Cutting technology is critical in manufacturing surgical instruments, implantable devices, and precision parts for medical testing equipment.
Precision surgical scissors and tweezers require grinding and polishing for sharp edges and accurate dimensions. Implantable heart stents rely on micro-cutting to form delicate, precise structures. All these depend on reliable cutting processes.
Conclusion
In summary, cutting technology is the most fundamental and core process in precision manufacturing. It not only enables the precise conversion from raw materials to finished components but also guarantees quality, improves efficiency, and adapts to diverse processing needs. In aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices, cutting technology is indispensable and supports the sustainable development of high-end manufacturing.
As precision manufacturing advances, cutting technology is evolving toward higher precision, efficiency, and environmental friendliness. Deeper integration with precision manufacturing will bring more advanced cutting technologies and solutions, providing stronger support for high-end precision component processing and elevating the entire industry to new heights.