Against the backdrop of growing demand for precision manufacturing, CNC grinding, as a crucial process in the metal cutting field, is widely applied in industries such as machinery, mold-making, automotive, aerospace, electrical machinery, and bearings. Renowned for its high precision, high stability, and excellent surface quality, it serves as a key method for producing high-performance components. This article will systematically introduce CNC grinding from aspects including its concept, equipment composition, processing characteristics, and functions.
CNC Grinding (Computer Numerical Control Grinding) is a processing method that uses a numerical control system to control a grinding machine, enabling the grinding wheel to perform micro-cutting on the workpiece, thereby achieving high-precision surface processing. Unlike traditional manual grinding, CNC grinding relies on program control to realize automated feeding, continuous trajectory processing, and high repeatability precision. It is suitable for processing parts that require high dimensional accuracy, geometric form and position accuracy, and surface quality.
It is typically used for processing high-hardness materials such as hardened steel, cemented carbide, and ceramics. It is also commonly employed in the fine grinding, semi-fine grinding, and ultra-precision processing of parts.
What Constitutes CNC Grinding?
CNC grinding is composed of the CNC grinding machine, grinding tools, control system, and auxiliary devices, with all components working in coordination to achieve high-stability processing.
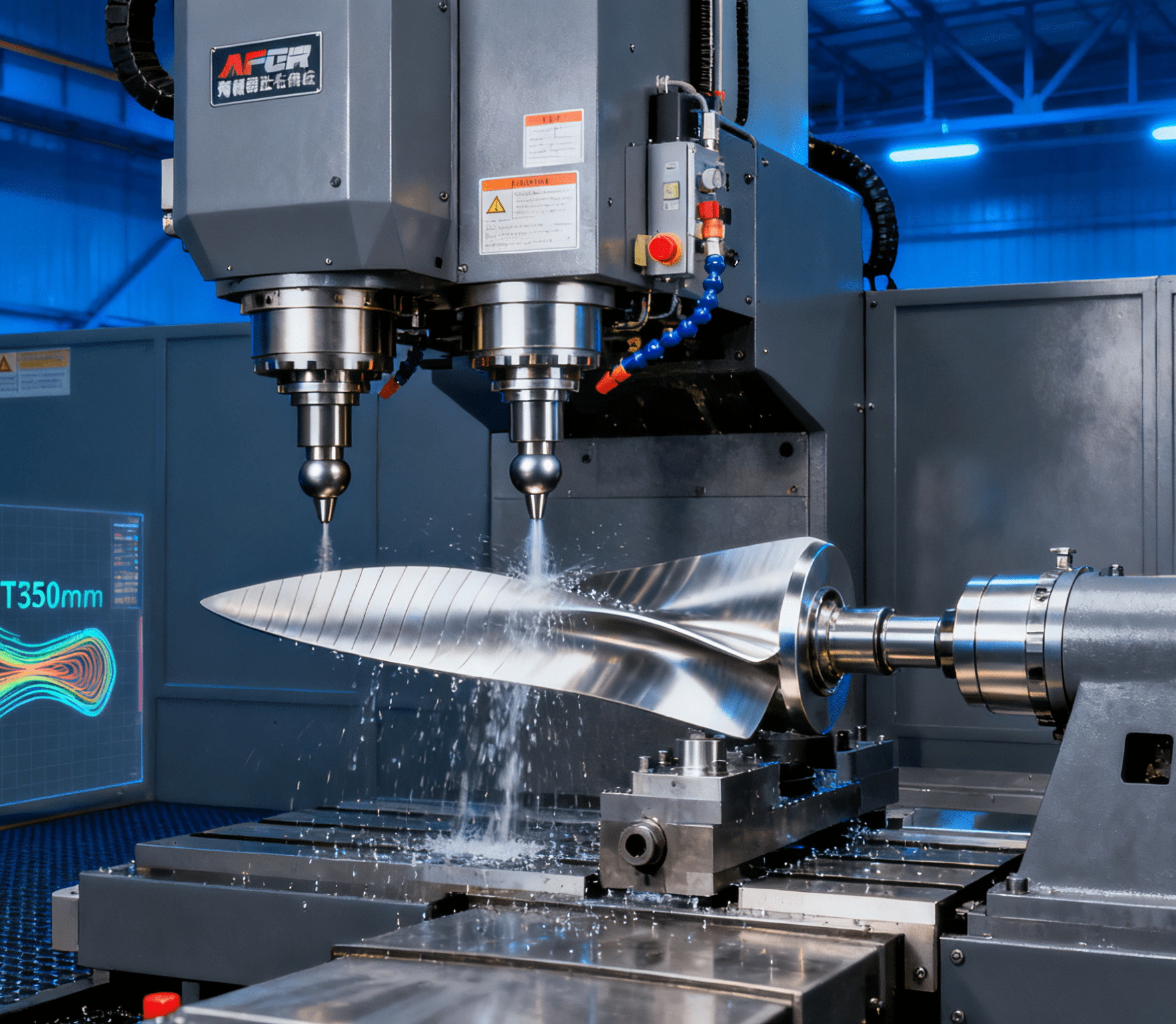
CNC Grinding Machine Main Body: The CNC grinding machine includes components such as the machine bed, spindle, feed system, and worktable, serving as the core equipment for grinding operations. Based on different processing requirements, it can be categorized into various types, including cylindrical grinding machines, internal grinding machines, surface grinding machines, centerless grinding machines, and jig grinding machines. (Cylindrical grinding machines: Used for the outer cylindrical surfaces of shaft and sleeve parts; Surface grinding machines: Applied for flat surface processing, such as mold reference planes; Centerless grinding machines: Suitable for high-efficiency, mass processing of cylindrical parts.)
Grinding Tools (Grinding Wheels): The grinding wheel is the primary tool for grinding, composed of abrasive grains, a bonding agent, and pores. The hardness, grain size, and material of the grinding wheel must be selected appropriately based on the workpiece material and processing requirements. (Common types of grinding wheels include alumina grinding wheels, diamond grinding wheels, and cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheels. CBN grinding wheels are widely used in high-precision processing due to their excellent wear resistance and processing stability.)
Numerical Control System (CNC): The CNC system is responsible for program-controlled management of various movements of the grinding machine, including rotational speed adjustment, feed rate control, trajectory planning, and compensation control. It enhances the degree of processing automation and ensures processing repeatability and consistency.
Cooling and Lubrication System: A large amount of heat is generated during the grinding process. The cooling fluid is used to reduce temperature, improve surface quality, prevent thermal damage, and remove grinding chips to extend the service life of the grinding wheel.
Measurement System and Auxiliary Devices: These include on-machine measuring instruments, grinding wheel dressers, and automatic clamping fixtures. They improve processing precision and efficiency while reducing clamping time.
What Functions Does CNC Grinding Serve?
CNC grinding offers significant advantages and plays important roles in precision manufacturing, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
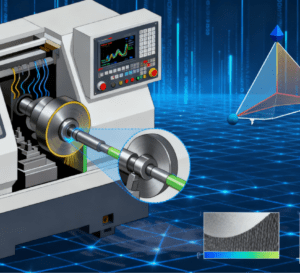
Enabling High-Precision Processing: Grinding belongs to micro-cutting, which can achieve dimensional accuracy at the micrometer level or higher. It is often the final processing procedure for many high-precision components. For example, bearing raceways, mold profiles, and high-precision shaft parts are usually finalized through CNC grinding.
Achieving Excellent Surface Quality: CNC grinding can achieve extremely low surface roughness, typically with Ra values less than 0.2μm. It is suitable for parts requiring high surface finish, such as sliding components, sealing surfaces, and precision guideways.
Applicability to High-Hardness Material Processing: High-hardness materials that are difficult to process with ordinary cutting tools (such as hardened steel, ceramics, and cemented carbide) can be efficiently processed through grinding. It is a key method for finishing after heat treatment.
High Processing Stability and Good Repeatability Precision: The CNC system enables a high degree of automation in the processing process, reducing human errors and improving the consistency of batch processing. It is particularly suitable for large-batch, high-precision production tasks.
Capability for Complex Curved Surface and Micro-Structure Processing: With advancements in grinding equipment and software, CNC grinding can process complex curved surfaces, precision grooves, and micro-structures. This provides processing capabilities for mold-making, aerospace parts, and high-end equipment manufacturing.
Typical Applications of CNC Grinding
CNC grinding is widely used across multiple industries, including:
Machinery Manufacturing: Precision shafts, guideways, and gear parts, etc.
Mold Industry: Fine grinding of mold reference planes and profiles.
Automotive Industry: Engine parts, rotors, and gear shafts, etc.
Electronics and Electrical Machinery Industry: Motor shafts and micro-bearing components.
Aerospace: Precision processing of high-hardness, wear-resistant components.
As manufacturing requirements continue to rise, the value of CNC grinding in high-end equipment manufacturing becomes increasingly prominent.
Future Development Trends of CNC Grinding
The modern manufacturing industry demands higher precision, efficiency, and automation, driving CNC grinding to exhibit new development trends:
Intelligence and Automation: Functions such as automatic measurement, on-line dressing, and intelligent compensation are continuously maturing.
Ultra-Precision Development: Applied in mirror-finish processing and ultra-low roughness processing.
Upgrading of Grinding Materials: The usage ratio of CBN grinding wheels and ceramic-bonded grinding wheels is gradually increasing.
Hybrid Processing Trend: Integration of grinding with turning, milling, and other processes to improve overall production efficiency.