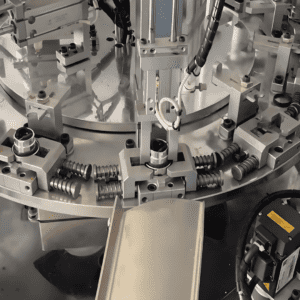
In the era of smart hardware—where smartphones, smart home appliances, and automotive electronics pursue “slimmer designs, more sensitive operations, and higher reliability”—the tap control button (a key component for human-machine interaction) has become a “small but critical” part. However, its assembly—characterized by tiny size (often 3-10mm in diameter), high precision requirements (assembly tolerance ±0.01mm), and complex processes (involving shell, contact, spring, and wire integration)—has long been a bottleneck for manual or semi-automatic production. Against this backdrop, the Tap Control Button Assembly Machine has emerged as a specialized automation solution, reshaping the efficiency and quality standards of button assembly across industries.
What Is a Tap Control Button Assembly Machine?
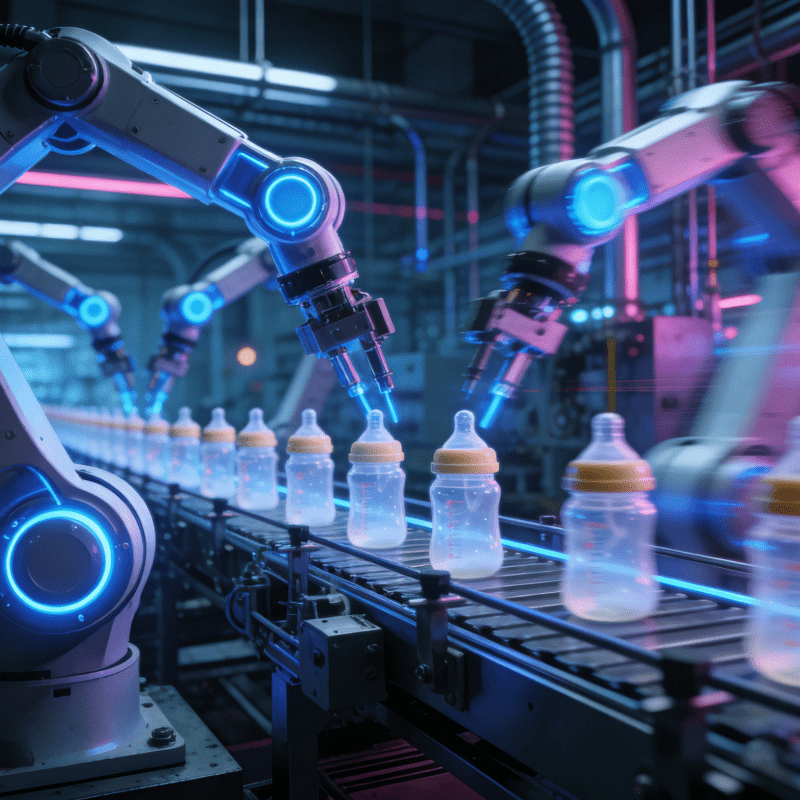
The Tap Control Button Assembly Machine is a dedicated automated equipment designed for the integrated assembly of tap control buttons (including light touch buttons, capacitive touch buttons, and mechanical tap buttons). Unlike general-purpose assembly lines, it targets the “micro, precise, and multi-step” characteristics of tap button production: it integrates automatic feeding, component positioning, press-fitting, soldering (if needed), and quality inspection into a single workflow, replacing manual operations that are prone to fatigue, error, and low efficiency.
At its core, the machine solves three core pain points of traditional assembly:
Precision bottleneck: Manual assembly often leads to misalignment between the button contact and the circuit board, resulting in unresponsive taps or short service life (failure rate up to 5-8%);
Efficiency limitation: A skilled worker can assemble only 800-1200 tap buttons per hour, while an automated machine can reach 3000-6000 units/hour;
Cost pressure: High labor intensity leads to a 20-30% annual turnover rate for assembly workers, increasing enterprise training and management costs.
Core Functions: How Does It Achieve “Precision + Efficiency”?
A mature Tap Control Button Assembly Machine relies on a modular design and intelligent control system to cover the entire assembly process of tap buttons. Its core functions can be broken down into five key links:
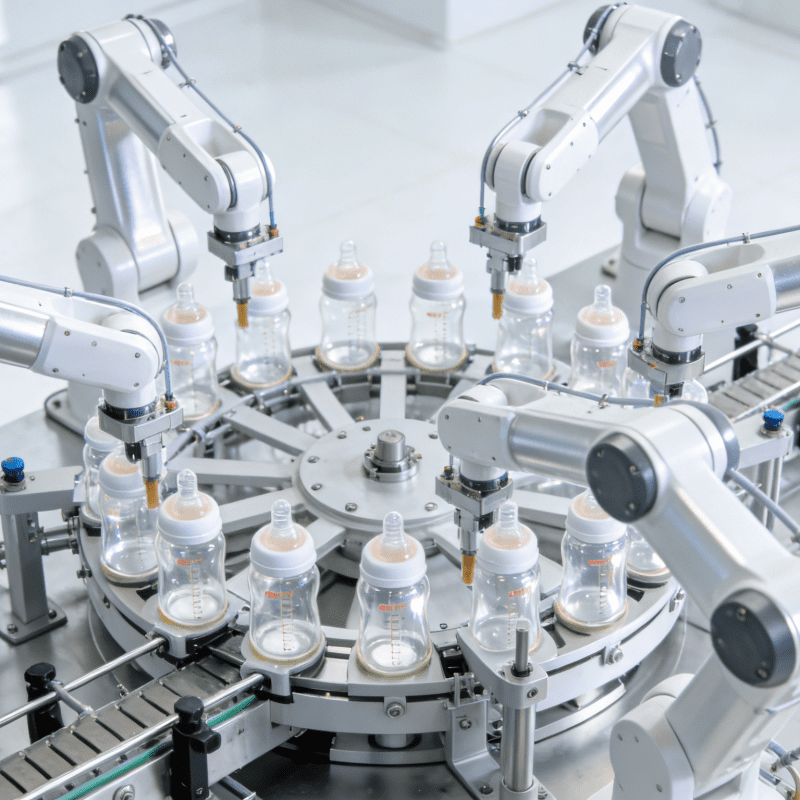
- Multi-component Automatic Feeding: No Manual Loading, No Jamming
Tap control buttons typically consist of 4-6 components (e.g., plastic shell, metal contact, return spring, conductive pin, and protective film). The machine uses vibratory feeders for small parts (springs, pins) and visual-guided robotic arms for fragile components (protective film, circuit board fragments), ensuring:
Feeding accuracy: ±0.02mm for component positioning, avoiding offset during subsequent assembly;
Anti-jamming design: Built-in pressure sensors and reverse blowing devices to clear stuck parts in 0.5 seconds, reducing downtime to less than 0.5% of total operating time.
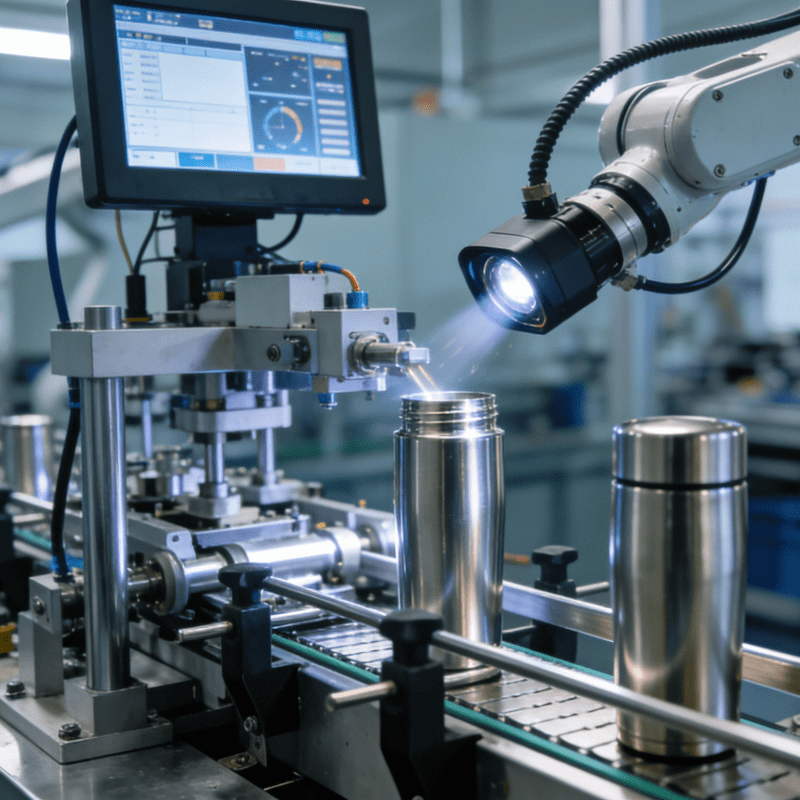
- High-Precision Positioning & Press-Fitting: The “Heart” of Assembly Quality
The most critical step in tap button assembly is ensuring the contact and spring are perfectly aligned with the shell’s mounting hole—any deviation will affect the button’s tactile feedback and service life. The machine adopts two core technologies here:
CCD Visual Positioning: 2-4 high-resolution industrial cameras capture component coordinates in real time, correcting positioning errors within 0.005mm (equivalent to 1/20 the diameter of a human hair);
Servo-Driven Press-Fitting: A servo motor controls the press-fitting force (adjustable between 5-50N) and stroke, ensuring the spring is compressed to the optimal length (e.g., 1.2±0.05mm for a 3mm spring) to balance “sensitive tapping” and “durability” (tested to withstand 100,000+ presses without failure).
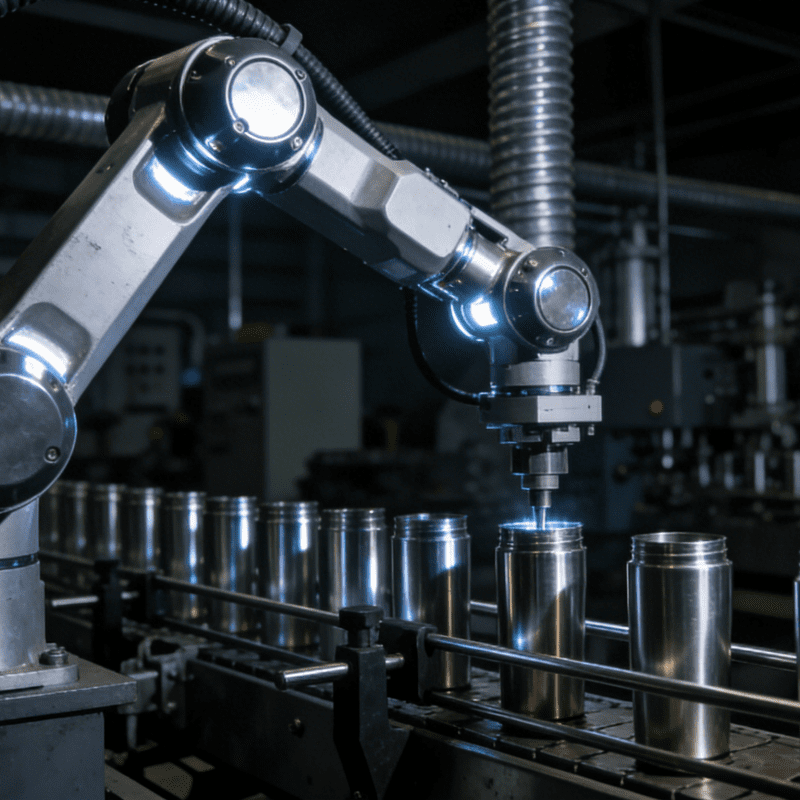
- In-Line Quality Inspection: Reject Defects at the Source
Traditional post-assembly inspection (e.g., manual sampling) often misses hidden defects (such as loose springs or poor soldering). The Tap Control Button Assembly Machine integrates three inspection modules into the assembly line:
Force-Displacement Monitoring: During press-fitting, the machine records the force-stroke curve; if it deviates from the standard range (e.g., abnormal force due to a missing spring), the defective product is automatically rejected;
Electrical Conductivity Test: For conductive tap buttons, probes test the contact resistance (required to be <5Ω); non-conductive products are sorted out immediately;
Visual Defect Detection: Cameras check for surface scratches on the button shell, missing labels, or misaligned pins—detection accuracy up to 99.98%.
- Flexible Changeover: Adapt to Multi-Spec Production
In the context of “small-batch, multi-variety” production (e.g., a smartphone factory producing 5-8 models of tap buttons per year), the machine’s modular design shines:
Quick-Change Fixtures: Replacing the fixture for different button sizes takes only 15-20 minutes (vs. 2-3 hours for traditional equipment);
Parameter Storage: The HMI (Human-Machine Interface) can store 50+ sets of assembly parameters (e.g., press-fitting force, feeding speed); switching between models requires only one click.
Typical Application Scenarios: From Consumer Electronics to Automotive
The Tap Control Button Assembly Machine’s “high precision + high flexibility” makes it indispensable in industries where tap buttons are core components:
- Consumer Electronics: The “Hidden Driver” of Sensitive Taps
In smartphones, tablets, and smart speakers, the tap control button (e.g., power buttons, volume keys) demands ultra-high assembly precision to avoid “false touches” or “unresponsive presses.” A leading smartphone manufacturer in China adopted this machine, reducing the button failure rate from 4.2% (manual assembly) to 0.3%, and increasing daily output from 120,000 to 350,000 units—directly supporting the mass production of its flagship models.
- Home Appliances: Ensuring Durability in Daily Use
Washing machines, air conditioners, and microwave ovens rely on tap buttons for daily operation, which need to withstand repeated presses (up to 50,000 times in their service life). A household appliance enterprise used the machine to assemble washing machine control panel buttons, achieving a spring compression accuracy of ±0.02mm—ensuring consistent tactile feedback (e.g., 3N pressing force) for every button, and reducing after-sales complaints related to buttons by 65%.
- Automotive Electronics: Meeting Strict Vehicle-Grade Standards
In automotive central control systems, tap buttons (e.g., air conditioning adjustment keys, infotainment system keys) must withstand high temperatures (up to 85℃), vibration, and electromagnetic interference. The machine’s soldering module (equipped with laser soldering technology) ensures stable wire connections between the button and the vehicle circuit board, passing the automotive industry’s “1000-hour high-temperature aging test” with a pass rate of 100%.
- Medical Devices: Guaranteeing Sterility and Reliability
Medical monitors, infusion pumps, and diagnostic equipment require tap buttons to be sterile and error-free (a single button failure could affect treatment). The machine’s closed assembly chamber (equipped with UV disinfection) and 100% inline inspection ensure that every button meets medical device standards (ISO 13485), making it a key equipment for medical device manufacturers.
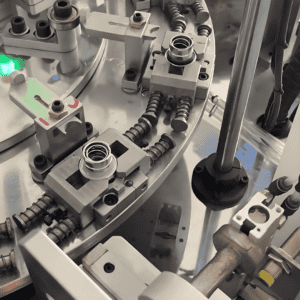
The Value of Tap Control Button Assembly Machine for Enterprises
For manufacturers, investing in this machine is not just about “replacing labor”—it’s about building core competitiveness in the smart hardware era:
Efficiency Leap: Compared with manual assembly, the machine’s output is 3-5 times higher, and it can run continuously for 24 hours (with only 1-2 operators for supervision), significantly shortening production cycles;
Cost Reduction: In the long run, it reduces labor costs by 40-60% (avoiding recruitment and training costs for skilled workers) and material waste by 8-12% (reducing defective products);
Quality Assurance: Stable assembly precision and 100% inspection ensure that products meet international standards, helping enterprises enter high-end markets (e.g., exporting to Europe and the United States);
Intelligent Upgrade: Most machines support data integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution System), enabling real-time monitoring of assembly parameters (e.g., output, failure rate) and laying the foundation for “Industry 4.0” transformation.
Future Trends: Toward More Intelligent and Integrated Solutions
As smart hardware becomes more miniaturized and functional, the Tap Control Button Assembly Machine is also evolving in three directions:
AI-Powered Inspection: Integrating AI visual algorithms to identify more subtle defects (e.g., micro-cracks on button contacts) that traditional cameras cannot detect, further improving inspection accuracy to 99.99%;
Collaborative Robot Integration: Combining with collaborative robots to handle “semi-automatic” links (e.g., loading large circuit boards), reducing manual intervention and adapting to more complex assembly scenarios;
Green Energy Design: Adopting energy-saving servo motors and low-power sensors, reducing the machine’s energy consumption by 15-20% compared with traditional models, in line with global carbon neutrality goals;
Digital Twin Application: Building a digital twin of the assembly line to simulate production processes, predict maintenance needs (e.g., replacing worn press-fitting heads), and reducing unplanned downtime by 30%.
Conclusion: A “Small Machine” Empowering Big Industries
The Tap Control Button Assembly Machine may not be as “eye-catching” as large-scale production lines, but it is a “hidden cornerstone” of the smart hardware supply chain. It solves the “precision and efficiency” bottleneck of tap button assembly, helps enterprises reduce costs and improve quality, and even promotes the upgrading of entire industries—from consumer electronics to automotive, from medical devices to smart homes.
In the future, as human-machine interaction becomes more diverse (e.g., thinner, more sensitive tap buttons), the Tap Control Button Assembly Machine will continue to iterate, becoming an indispensable part of the global (smart manufacturing) ecosystem. For enterprises seeking to gain a foothold in the fierce market competition, mastering this “precision assembly technology” is not an option, but a necessity.