Modern manufacturing has an increasingly high demand for the precision and efficiency of complex structural components, and the machining process of multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools plays a key role in this regard. This paper will systematically analyze the core connotation of this advanced machining technology, focusing on how to ensure the high-precision requirements of complex structural parts during the machining process. The paper will delve into its core technical principles, especially the application logic of advanced motion control strategies and various effective error compensation methods in actual production. Through the analysis of these core guarantee mechanisms, it aims to clearly present to readers the complete path of how multi-axis simultaneous CNC technology achieves high-precision and high-efficiency machining goals, laying a foundation for the detailed expansion of subsequent chapters.
Analysis of Multi-Axis Simultaneous Machining Process
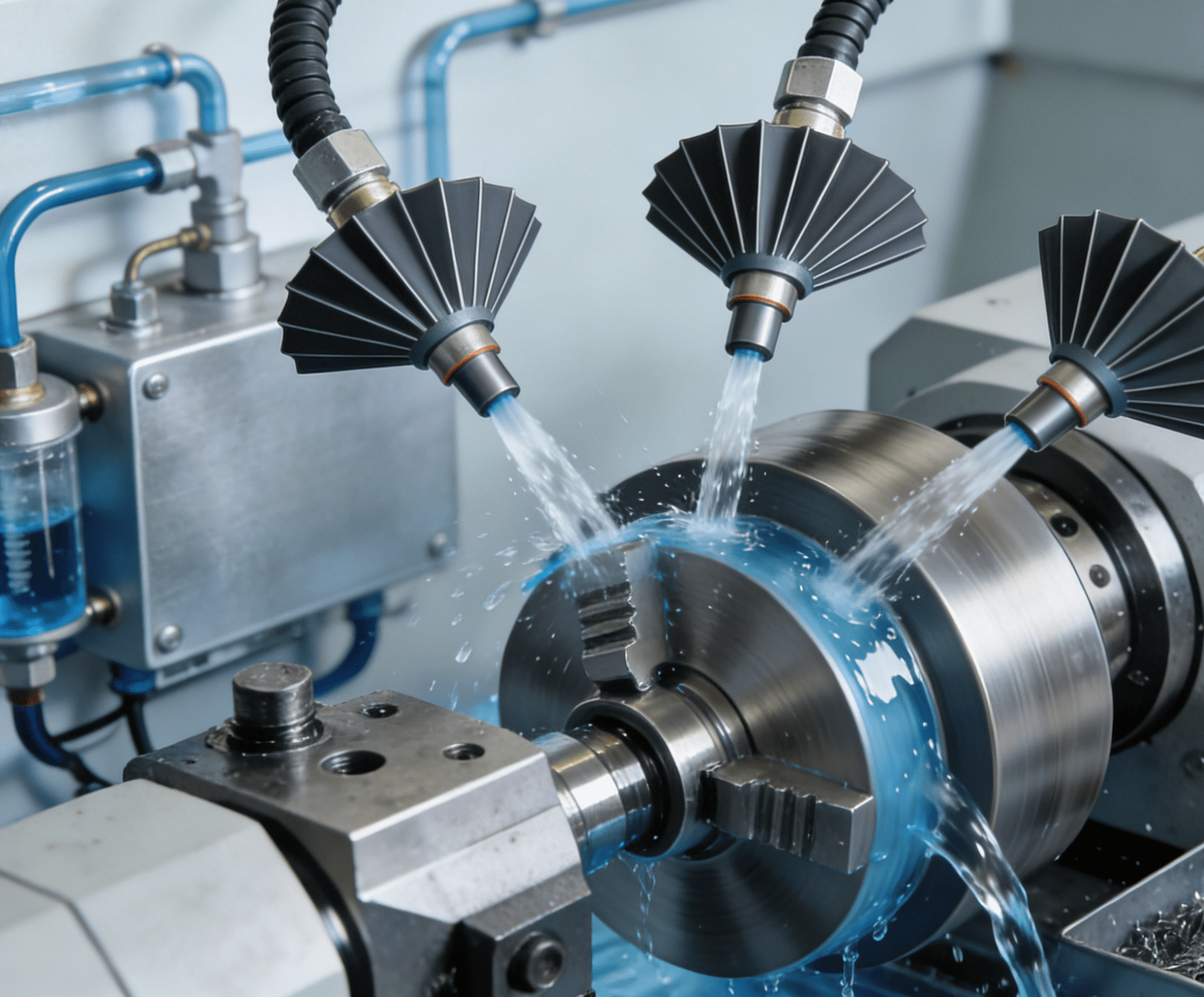
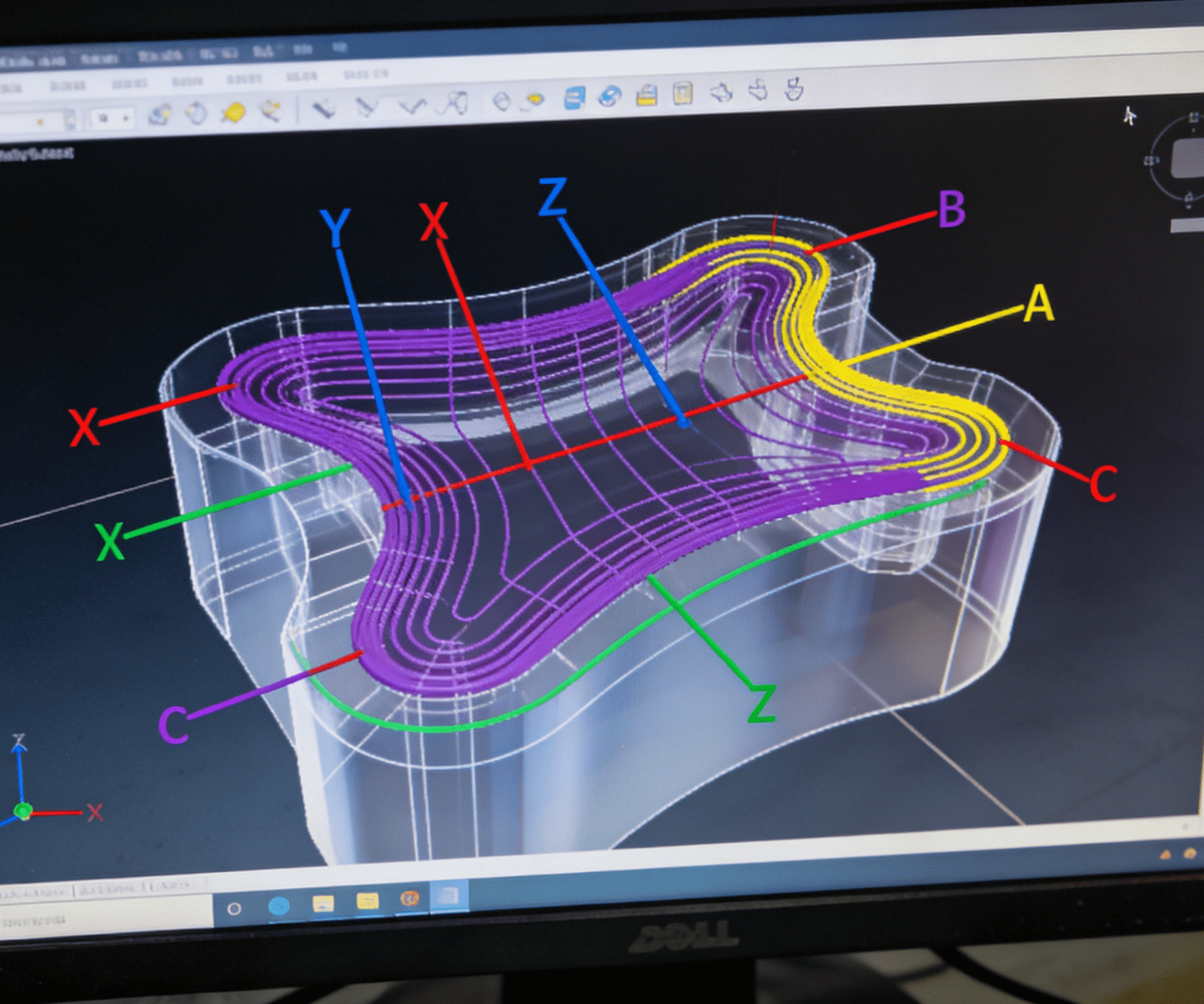
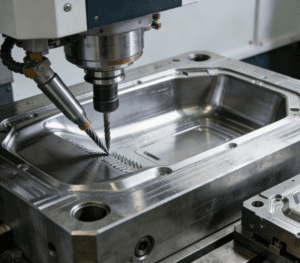
Multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools represent the advanced level of modern manufacturing technology, and their core lies in the ability of multiple motion axes to work collaboratively according to a preset program. This process precisely coordinates the motion trajectories of the spindle and various linear and rotary axes through a computer control system, thereby realizing complex cutting paths in three-dimensional or even multi-dimensional space. Different from the single-axis or simple dual-axis motion of traditional machine tools, multi-axis simultaneous machining can complete the precision machining of multiple curved surfaces of complex structural components in one go, significantly reducing the number of clamping operations and process conversions. Notably, when processing sheet-like complex structural components, the Sheet automatic loading robot further enhances the advantages of this process: it can realize precise and continuous automatic loading of sheets, avoiding positioning deviations caused by manual clamping, and ensuring the consistency of initial clamping accuracy for each workpiece. At the same time, it seamlessly connects with the multi-axis simultaneous machining program, reducing the waiting time between loading and machining, and further improving production efficiency. This synchronous control capability, combined with reliable automatic loading, is the key foundation for the efficient and high-precision manufacturing of workpieces with complex geometric features such as impellers and aerospace structural parts. It is precisely these characteristics that make the multi-axis simultaneous machining process the preferred solution to meet the challenges of high-difficulty and high-precision machining.
Precision Guarantee for Complex Components
Complex structural components, such as impellers in the aerospace field and precision molds, feature intricate geometric shapes, numerous spatial curved surfaces, and extremely strict tolerance requirements. Ensuring their machining precision is the core value of multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools. This relies on a comprehensive guarantee mechanism: first of all, the geometric accuracy, motion accuracy, and dynamic stability of the machine tool itself are the foundations. The high-rigidity mechanical structure, precision guide rails, and bearing systems ensure the accuracy of motion trajectories. Secondly, advanced multi-axis simultaneous interpolation algorithms can precisely coordinate the motion of each axis, realizing smooth and continuous machining of complex spatial trajectories, and effectively avoiding impact errors caused by sudden speed changes. It is particularly worth noting that the impact of dynamic factors such as ambient temperature changes, spindle thermal deformation, and cutting force fluctuations on precision cannot be ignored, so real-time monitoring and compensation strategies need to be implemented. Among them, error compensation methods are the key link to improve the final machining precision.

Application of Advanced Control Strategies
In the process of ensuring the machining precision of complex structural components, the application of advanced control strategies is crucial. Modern multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools generally integrate intelligent algorithms such as feedforward control, adaptive control, and Model Predictive Control (MPC). Feedforward control can predict and compensate in advance for dynamic errors caused by changes in tool paths or sudden load changes, significantly improving trajectory tracking precision. Adaptive control monitors the machining status in real time and automatically adjusts control parameters according to changes in material properties or tool wear conditions. For example, data shows that it can reduce dimensional deviations caused by tool wear by more than 40%. Model Predictive Control establishes an accurate machine tool dynamics model to predict the system behavior of multiple future steps and optimize control inputs, effectively suppressing vibration and improving contour precision. Especially when machining complex curved surfaces, it can reduce thermal deformation by about 30%. These strategies work collaboratively, providing a solid data foundation and dynamic response capability for the implementation of more refined error compensation in the follow-up.
Practice of Error Compensation Methods
In actual machining, error compensation is the core link to improve the machining precision of multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools. For complex structural components, common compensation methods are mainly divided into two types: real-time compensation and offline compensation. Real-time compensation relies on high-precision sensors to continuously monitor thermal deformation, vibration, or force changes during the machining process, and the control system adjusts tool paths or feed parameters in real time for correction. Offline compensation is usually implemented before or after machining. For example, precision instruments such as laser interferometers are used to measure the geometric and motion errors of the machine tool, a detailed error model is established, and the compensation data is preset into the CNC system. Through the effective combination and application of these two methods, the impact of inherent system errors and fluctuations in the machining environment can be significantly offset, providing a solid guarantee for the high-precision machining of complex components.
In the machining process of multi-axis simultaneous CNC machine tools, the precision guarantee mechanism for complex structural components is the key to improving overall production efficiency. By integrating advanced control strategies and efficient error compensation methods, machine tools can effectively reduce machining deviations and ensure the high-precision requirements of components. These technologies not only optimize the process flow, but also significantly reduce the scrap rate, providing solid support for high-efficiency production in the manufacturing industry. Therefore, the continuous research, development, and application of these guarantee mechanisms will drive the industry towards a smarter and more reliable direction, meeting the growing quality demand.