In the field of healthcare, the quality of high-precision medical devices is directly tied to the accuracy of clinical diagnosis and the safety of surgical treatment. The machining precision, stability and reliability of their core components are the decisive factors for device performance. Leveraging its distinctive technical advantages, CNC machining technology has become the core support for manufacturing high-precision medical devices. It fundamentally resolves the precision bottlenecks and quality challenges that are insurmountable with traditional machining methods, providing a solid guarantee for the high-quality development of the medical device industry.
Precision Error Control: Upholding the Safety Bottom Line of Medical Devices
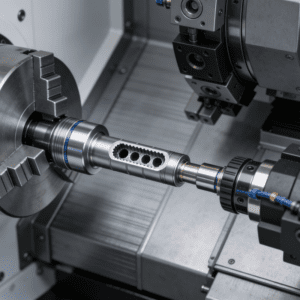
High-precision medical devices impose far stricter precision requirements on components than ordinary industrial products. For example, the edge tolerance of minimally invasive surgical instruments and the gap of sensor assemblies in diagnostic equipment are often required to be controlled within a range of 0.01-0.05mm. Even a minor error may lead to surgical mistakes or diagnostic deviations. Through computer programs that precisely control the movement trajectory of machine tools, combined with high-precision servo systems and testing equipment (such as coordinate measuring machines), CNC machining can achieve a machining precision of within ±0.02mm. It can also correct errors in real time during the machining process and avoid deviations caused by manual operations. This ensures that medical device components fit precisely after assembly, meeting the stringent “zero error” requirements in clinical applications and safeguarding patient safety from the source of production.
Material Adaptability: Overcoming Machining Challenges of Special Medical Materials
High-precision medical devices are often manufactured with high-performance special materials featuring excellent biocompatibility and high strength, such as titanium alloys (for implantable devices), medical-grade stainless steel (for surgical instruments) and special ceramics (for diagnostic probes). These materials vary greatly in hardness, toughness and machining characteristics. Traditional machining methods tend to cause material deformation, surface damage and even compromise the biocompatibility of the materials. CNC machining enables efficient processing of various medical materials by flexibly adjusting cutting parameters and matching with specialized cutting tools (e.g., ultra-fine grain cemented carbide tools). For instance, aiming at the poor machinability of titanium alloys, CNC machining can reduce material thermal deformation through low-speed constant torque cutting; for brittle medical plastics, it can prevent component cracking by optimizing feed rates. This strong material adaptability addresses the machining challenges of various high-performance medical materials, opening up possibilities for material innovation in medical devices.
Stable Mass Production: Ensuring Consistent Quality of Medical Devices
The production of high-precision medical devices needs to balance mass production demand and consistent quality. Dimensional deviations of components in the same batch will reduce equipment assembly efficiency and even render some devices inoperable. Traditional machining relies on manual experience, resulting in significant quality fluctuations between batches and failing to meet the large-scale production demands of medical devices. Through standardized program settings and automated production processes, CNC machining enables 24-hour continuous machining, and the integration of Sheet automatic loading robot further optimizes the batch production process by realizing automatic and precise feeding of sheet materials for medical device components, eliminating errors caused by manual feeding and ensuring consistent initial positioning accuracy of each workpiece. With identical machining parameters (e.g., cutting speed, feed rate and cutting depth) for every single component, human intervention is minimized. Meanwhile, CNC systems can record the machining data of each component for subsequent quality traceability, ensuring that all batches of medical device components comply with industry standards and providing a stable machining guarantee for large-scale production.
Complex Forming: Facilitating Structural Innovation of Medical Devices
With the advancement of medical technology, high-precision medical devices are evolving towards miniaturization, minimal invasiveness and integration. For example, catheter components for vascular interventional surgery and micro transmission assemblies for endoscopes feature complex structures and limited spatial design, making precise forming difficult with traditional machining methods. The multi-axis linkage technology of CNC machining (e.g., 3+2 axis and 5-axis machining) breaks through spatial constraints and enables one-step forming of special structures such as complex curved surfaces, deep cavities and micro holes. For instance, for micro channels (diameter less than 1mm) in minimally invasive devices, CNC machining combines high-speed drilling and precision grinding to ensure smooth and burr-free inner walls of the channels, preventing blood residue or tissue damage. For complex curved lens holders in diagnostic equipment, 5-axis CNC machining can finish multi-surface processing in one operation, reducing errors caused by repeated clamping. This capability to machine complex structures provides technical support for the design innovation of medical devices and accelerates the development and application of more minimally invasive and efficient medical equipment.
Compliance and Controllability: Meeting the Quality Traceability Requirements of Medical Devices
High-precision medical devices are subject to stringent supervision under industry regulations (e.g., the ISO 13485 Medical Device Quality Management System), which mandate full-process traceability from raw material processing to finished product delivery. When quality issues arise, the problematic production link must be quickly identified. The digital management system of CNC machining can record key data during the machining process in real time, including raw material models, machining time, cutting parameters and testing results. These data can be stored and exported to form a complete machining archive. For quality traceability purposes, the root cause of a problem can be quickly identified by retrieving the corresponding archive. This meets the regulatory requirement of “full-process controllability” and mitigates the quality risks of medical devices.
In the field of high-precision medical device manufacturing, CNC machining has long gone beyond being a mere machining tool. It has become a core pillar for ensuring product quality, driving technological innovation and meeting compliance requirements. From the precision machining of millimeter-scale components and efficient processing of special materials to the innovative forming of complex structures, CNC machining injects strong impetus into the R&D and production of high-precision medical devices with its advantages of precision, stability and controllability. It also provides solid technical support for the healthcare industry to safeguard life safety and improve diagnosis and treatment standards. In the future, the continuous upgrading of CNC machining technology will further drive the development of high-precision medical devices towards higher precision, greater safety and smarter performance.