Table of Contents
Toggle6-Axis Robotic Spring Pick-and-Place System: Mastering Precision in Elastic Component Handling
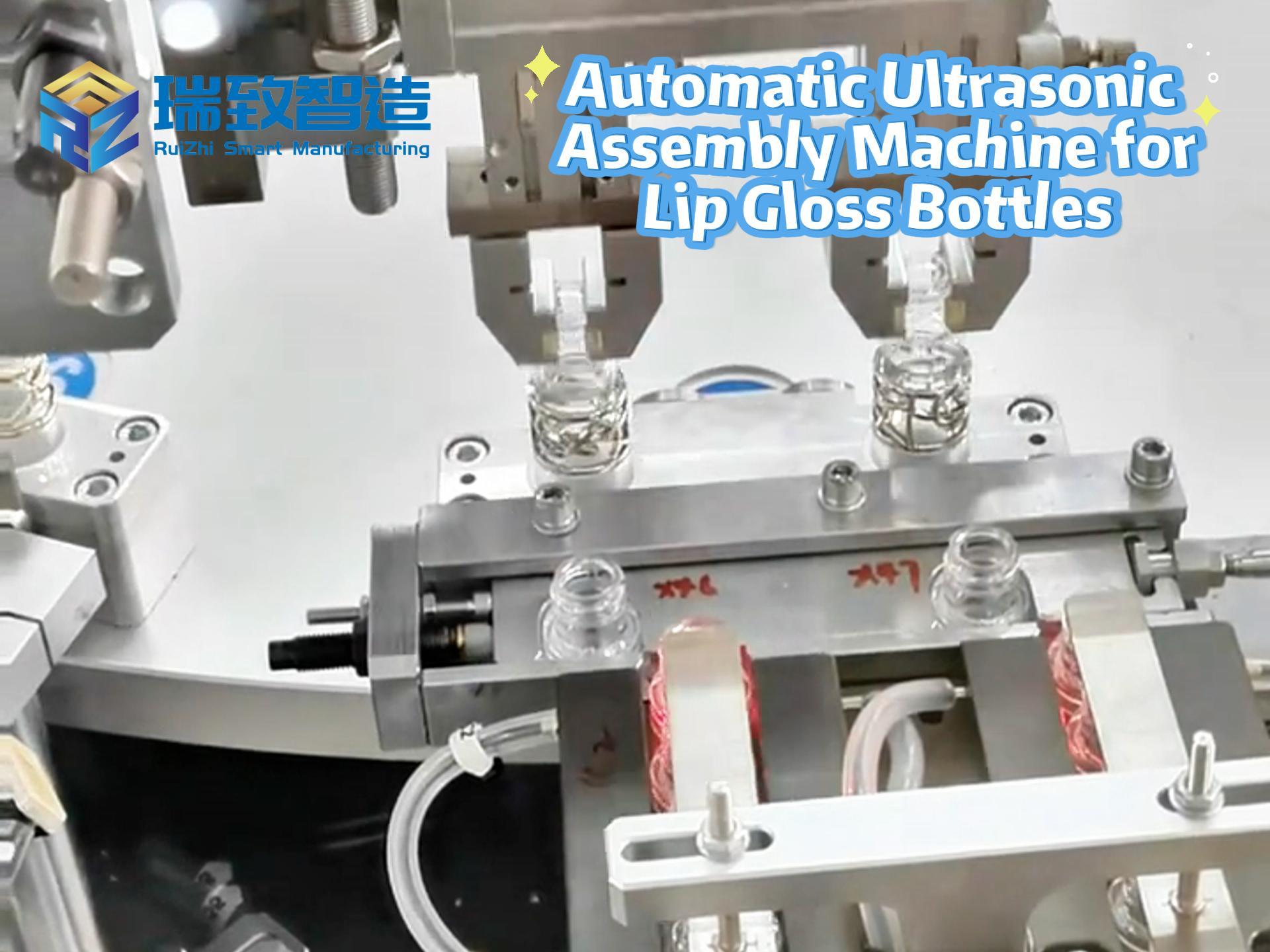
In industries where tiny, elastic components dictate product performance—think automotive suspensions, electronic switches, or medical device actuators—handling springs is a delicate dance of force, precision, and adaptability. Manual pick-and-place operations struggle with inconsistent grip force (leading to deformation or slippage), while 4-axis robots falter with 3D orientation challenges. Enter the 6-Axis Robotic Spring Pick-and-Place System—a versatile solution engineered to tackle these complexities. By combining full 3D dexterity, intelligent force control, and adaptive vision, this system transforms spring handling from a high-risk bottleneck into a streamlined, error-free process.
Why 6-Axis? The Imperative for Elastic Component Dexterity
Springs are inherently complex: their coiled geometry, varying wire diameters (0.1mm to 5mm), and elastic properties demand 6 degrees of freedom (6DOF) for optimal manipulation. Here’s why 6-axis robots outperform alternatives:
1. Unlimited 3D Orientation Control
Unlike 4-axis SCARA robots (limited to planar motion), 6-axis arms rotate freely around all axes, enabling:
- Angled Grasping: Pick springs from tilted trays or vertical magazines at precise angles (e.g., 30° to align with a coil’s pitch).
- Twist-Free Placement: Orient compression springs with ±0.5° rotational accuracy to avoid pre-load errors in assembly.
2. Force-Sensitive Manipulation
A payload capacity of 2–10kg (depending on arm model) combined with 6-axis force-torque sensing lets the robot:
- Apply 0.1–5N of grip force for delicate 0.2mm-thick watch springs.
- Handle heavy-duty automotive suspension springs (1kg+) without deformation.
3. Complex Path Planning
Navigates tight spaces between tooling or fixtures using advanced inverse kinematics, critical for high-density spring storage racks.
Core Technologies: The Backbone of Precision Spring Handling
1. 3D Vision with Deep-Learning Inspection
A stereo vision system paired with AI algorithms solves the chaos of spring orientation and defect detection:
- Chaotic Bin Picking: Identifies nested or overlapping springs in bulk bins, even for identical-looking compression/torsion springs, with 99.8% accuracy.
- Real-Time Feature Analysis: Measures spring height, coil pitch, and wire diameter in milliseconds, rejecting defective parts (e.g., misshapen coils or uneven ends) before handling.
Example: In a micro-spring factory, the system distinguishes between 0.3mm and 0.5mm wire diameter springs in a mixed bin, eliminating manual sorting.
2. Adaptive Gripping with Force Feedback
The end effector is a marvel of customization:
- Compliant Grippers: Soft rubber jaws conform to spring contours, preventing marring on plated surfaces (common in consumer electronics).
- Magnetic-Electric Hybrid Tools: Use adjustable electromagnets for ferrous springs and vacuum suction for non-magnetic variants (e.g., titanium alloy springs in aerospace).
- Force-Torque Sensor Integration: Maintains grip force within ±0.05Nduring pick-and-place, critical for preventing over-compression of delicate extension springs.
3. AI-Optimized Motion Planning
Machine learning algorithms continuously refine the robot’s path to:
- Minimize Spring Swing: Predict and counteract elastic oscillations during high-speed movement (e.g., reducing swing from 2mm to 0.2mm for 10mm-long springs).
- Avoid Collisions: Navigate around adjacent springs in dense trays using real-time 3D mapping.
Transforming Industries: Applications in High-Stakes Spring Handling
1. Electronics: Micro-Spring Assembly in Switches
In a smartphone button factory, where 0.5mm-thick torsion springs must align with ±0.03mm precision:
- The robot picks springs from a 1000-unit feeder tray using vision-guided precision.
- Places them into plastic switch housings with 0.1° rotational accuracy, eliminating misalignment that causes button stickiness.
Result: Defect rate drops from 15% (manual) to 0.8%, and cycle time per switch reduces from 12 seconds to 4 seconds.
2. Automotive: Heavy-Duty Suspension Spring Loading
For a car suspension plant handling 500g compression springs (100mm height, 20mm wire diameter):
- Robust mechanical grippers with anti-slip coatings securely hold springs during transport to CNC machines.
- Vision system checks for surface cracks or uneven coils, integrating with MES to flag defective batches.
Case Study: A Tier 1 supplier achieves 99.5% first-pass yield, saving $3M annually in scrap and rework.
3. Medical Devices: Precision Spring Placement in Syringes
In insulin pen manufacturing, where 2mm-long extension springs require sterile handling:
- Sterile-grade grippers and stainless-steel tooling meet ISO 13485 standards.
- Force control ensures springs are compressed to exactly 80% of their free length during assembly, critical for consistent injection force.
6-Axis vs. Traditional Methods: A Performance Showdown
| Metric | 6-Axis Robotic System | Manual Handling | 4-Axis Robot | Pneumatic Picker |
| 3D Orientation Control | Yes (6DOF) | Limited (2–3DOF) | No (4DOF) | No (2DOF) |
| Force Control Accuracy | ±0.05N | ±0.5N (variable) | ±0.2N (planar only) | ±1N (fixed pressure) |
| Cycle Time (small spring) | 2–3 seconds | 10–15 seconds | 5–6 seconds | 8–10 seconds |
| Defect Rate | <1% | 10–15% | 5–8% | 3–5% |
| Changeover Time (new spring type) | <20 minutes | 60+ minutes | 40 minutes | 120+ minutes |
Poslovni primer: od elastičnih izzivov do oprijemljivih koristi
1. Hitra donosnost naložbe, ki jo spodbujata kakovost in hitrost
- Labor SavingsZamenja 2–4 operaterje na linijo, kar letno prihrani od 140.000 do 140.000 rupij pri stroških dela (zlasti v regijah z visokimi plačami).
- Izboljšanje pridelkaZmanjša deformacijo vzmeti in napake zaradi napačne poravnave za 90%, kar je ključnega pomena za aplikacije, kjer 0,1 mm napačna poravnava povzroči okvaro izdelka.
- ScalabilityObvladuje 24/7 proizvodnjo z 98% uptime, podprto s prediktivnim vzdrževanjem (npr. opozorila o obrabi prijemala ali zračnosti spojev).
2. Prilagodljivost, pripravljena na prihodnost
- Prilagodljivost več SKU-jemV svoji bazi podatkov shranjuje več kot 100 vzmetnih profilov, kar omogoča hitro preklapljanje med tlačnimi, torzijskimi in razteznimi vzmetmi brez ročnega programiranja.
- IoT IntegrationPosreduje podatke v realnem času (sila prijema, časi ciklov, lokacije napak) platformam za analitiko tovarne, kar omogoča napovedni nadzor kakovosti.
Razvoj ravnanja z vzmetmi: Kjer se spretnost sreča z inteligenco
Ker industrije zahtevajo manjše, bolj kompleksne vzmeti (npr. mikro tuljave za naprave MEMS ali vzmeti s spremenljivo hitrostjo za električna vozila), se 6-osni sistem razvija z:
- Samokalibrirajoča orodjaSenzorji na orodju samodejno zaznajo dimenzije vzmeti, kar skrajša čas nastavitve za nove številke delov.
- Napovedovanje napak s pomočjo umetne inteligenceUporablja zgodovinske podatke za predvidevanje tveganj deformacije vzmeti glede na vrsto materiala in hitrost ravnanja.
- Collaborative SafetyOpremljen s 3D varnostnimi skenerji, deluje skupaj s tehniki v skupnih delovnih celicah – idealno za izdelavo prototipov za raziskave in razvoj ali proizvodnjo vzmeti po meri v majhnih količinah.
V svetu, kjer je delovanje celotnih sistemov odvisno od natančnosti drobnih vzmeti, 6-osni robotski sistem za pobiranje in nameščanje vzmeti ni le nadgradnja – je nuja. Inherentne izzive ravnanja z elastičnimi komponentami spreminja v konkurenčno prednost, ki proizvajalcem omogoča doseganje novih ravni kakovosti, hitrosti in prilagodljivosti.
#6-osno ravnanje z vzmetmi #Robotski vzmetni sestav #Precision Pickand Place System