In the manufacturing of modern medical devices, the precision of core components is directly tied to the performance and safety of the equipment. As a core manufacturing method, intelligent machining technology plays a pivotal role in the production of these components. This paper systematically analyzes the application of intelligent machining in the medical field: first, it explores how precision manufacturing achieves micron-level accuracy requirements; second, it analyzes biocompatible machining processes to ensure material compatibility with human tissues; third, it elaborates on the aseptic control standards for medical materials; and finally, it discusses in depth the importance of quality control systems in safeguarding the overall manufacturing safety. Through the elaboration of these contents, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the key processes and technical requirements for manufacturing core components of medical devices, laying a solid foundation for subsequent chapters.
Core Applications of Intelligent Machining
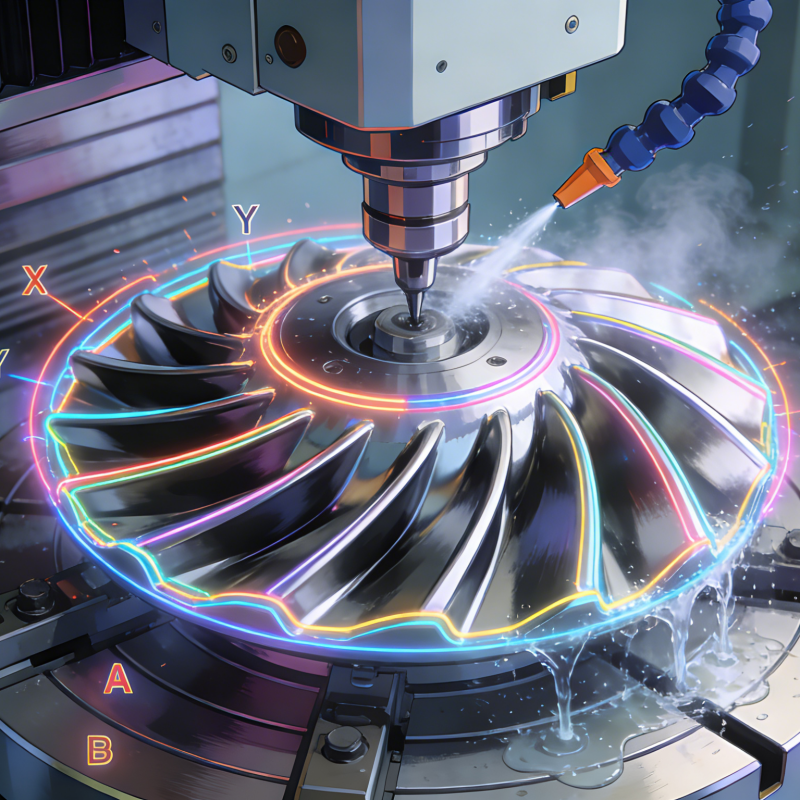
In the field of modern medical device manufacturing, intelligent machining technology serves as the core underpinning for the production of precision components. Leveraging high-precision machine tools controlled by computer programs, it enables strict control of micron-level dimensions, ensuring the structural integrity and functional reliability of core components such as artificial joints and surgical instruments. Especially in key fields including orthopedic implants and minimally invasive surgical tools, intelligent machining can stably process special materials such as titanium alloys and medical stainless steel, meeting the forming requirements of complex curved surfaces and microstructures. Notably, intelligent machining is also extensively applied in Машина для сборки небулайзера, where it realizes automated and precision assembly of nebulizer core components (such as atomizing nozzles, piezoelectric transducers and liquid storage chambers) through integrated vision positioning and multi-axis collaborative control, ensuring the airtightness and atomization efficiency of nebulizers that are critical for respiratory disease treatment. This technology not only guarantees consistency in mass production, but also lays a solid foundation for subsequent biocompatible surface treatment. As medical devices evolve toward miniaturization and personalization, multi-axis linkage intelligent systems have further expanded the boundaries of precision manufacturing, enabling the technological realization of high-end products such as cardiac stents and neurosurgical navigation instruments.
Analysis of Biocompatible Machining Processes
Achieving biocompatibility for core components of medical devices is a core challenge for intelligent precision machining technology. It not only requires the materials themselves to meet safety standards for implantation or human contact, such as titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) or specific medical-grade polymers, but more crucially, the machining process must avoid introducing any factors that may harm the human body. By precisely controlling cutting parameters (such as speed, feed rate and cooling methods), intelligent machining effectively suppresses heat accumulation during processing, thus preventing adverse phase transformation or surface degradation of materials and ensuring that the inherent biosafety characteristics of materials remain intact. Meanwhile, for components in direct contact with human tissues or blood, such as orthopedic implants or the tips of minimally invasive surgical instruments, intelligent machining can achieve an ultra-high surface finish (usually requiring a Ra value of less than 0.4μm). This greatly reduces the risk of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation, laying a solid foundation for subsequent rigorous cleaning, passivation and aseptic treatment. Such fine control over the material microstructure and surface integrity is the fundamental guarantee to meet the stringent biocompatibility requirements of international medical standards.
Aseptic Control of Medical Materials
After the completion of biocompatible machining, medical materials must undergo rigorous aseptic control to eliminate the risk of microbial contamination. This process involves multi-step operations, including thorough cleaning of component surfaces using ultrasonic waves or chemical solvents, followed by sterilization technologies such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide or gamma irradiation. The medical industry complies with international standards such as ISO13485 to ensure the precise control of sterilization parameters—for example, temperature and time must be matched to material characteristics. Meanwhile, aseptic packaging and environmental monitoring are key links to prevent secondary contamination. These measures not only safeguard patient safety, but also support the implementation of subsequent quality control systems to achieve end-to-end reliability.

The Critical Role of Quality Management Systems
In the precision manufacturing of core components for medical devices, establishing and strictly implementing a comprehensive quality control system is the cornerstone of ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the final products. This system runs through every link from raw material selection and intelligent machining processes to final inspection. Especially for devices requiring implantation into the human body or invasive operations, the quality management system must accurately identify and control potential risk points. By implementing internationally recognized quality management standards for medical devices such as ISO13485, manufacturers can adopt a systematic approach to process monitoring, data recording and traceability management. This not only effectively prevents production deviations and ensures that each component meets strict dimensional accuracy and biocompatibility requirements, but also provides a solid evidence chain to meet mandatory audits under national medical device regulations. Therefore, a robust quality management system is a decisive factor in ensuring the reliable performance of core medical device components and the safety of patient use.
It is evident that precision manufacturing technology, especially advanced intelligent machining, forms the cornerstone of reliability for core components of medical devices. It not only ensures the ultimate precision of component dimensions, but also meets the stringent requirements for human implants and contact devices through rigorous biocompatible machining processes. From the sophisticated processing of medical-grade materials to the aseptic control of production environments, every step relies on the support of highly automated and standardized intelligent technologies. More importantly, the entire manufacturing process must be embedded with a rigorous quality control system to continuously monitor each link, so as to ultimately guarantee the safety and effectiveness of these critical components in clinical applications. It is this systematic approach integrating cutting-edge machining and strict management that drives the continuous innovation of medical device manufacturing toward higher quality standards.