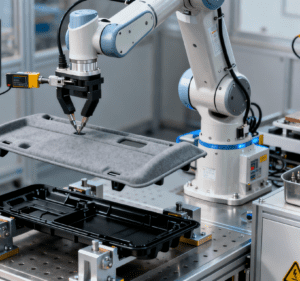
In the era of global manufacturing intelligence, injection molded parts—widely used in automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, and household appliances—are facing growing demands for high-precision, high-efficiency, and low-cost assembly. Traditional manual assembly, plagued by low throughput, high error rates, and heavy reliance on skilled labor, can no longer keep up with the pace of industrial upgrading. Against this backdrop, the Injection Molded Parts Automated Assembly System with Auto-Loading has emerged as a core solution, integrating automatic material feeding, precision assembly, real-time inspection, and data-driven management to build a “one-stop” intelligent production chain for injection molded components.
What Is an Injection Molded Parts Automated Assembly System with Auto-Loading?
At its core, this system is a modular, integrated equipment cluster designed to automate the entire process of assembling injection molded parts—from receiving finished parts from injection molding machines to delivering qualified assembled products. Unlike basic automated assembly lines, its defining feature is the auto-loading unit, which eliminates manual intervention in material transfer by seamlessly connecting to upstream injection molding equipment (e.g., robotic arms, conveyors) and precisely positioning parts for assembly. By combining mechanical precision, machine vision, and intelligent control, the system achieves “lights-out production” capabilities, ensuring consistent quality and stable output even in 24/7 operation.
Core Components: The “Four Pillars” of System Operation
A high-performance auto-loading automated assembly system relies on four interdependent core units, each tailored to address the unique challenges of injection molded parts (e.g., lightweight, fragility, complex geometries):
- Auto-Loading Unit: The “Material Handler” for Precision Feeding
The auto-loading unit is the “starting point” of the assembly process, responsible for safely and accurately transferring injection molded parts from upstream storage or injection molding machines to the assembly station. Key technologies include:
Multi-mode Feeding Mechanisms: For small, standardized parts (e.g., plastic gears, connectors), vibration bowls with customizable tracks sort and align parts; for large or irregular parts (e.g., automotive interior panels), 6-axis robotic arms with vacuum suction cups or grippers perform flexible picking.
Machine Vision Positioning: High-resolution cameras and AI algorithms identify part orientation, detect surface defects (e.g., burrs, warpage), and correct positioning errors in real time—ensuring parts are placed into assembly jigs with a precision of ±0.02 mm, far exceeding manual capabilities.
Buffer Storage Design: A temporary storage module (e.g., rotary tables, conveyor buffers) balances the speed difference between injection molding and assembly, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring continuous operation.
Assembly Execution Unit: The “Craftsman” for High-Precision Joining
This unit executes the core assembly tasks, adapting to diverse injection molded part assembly needs (e.g., snap-fitting, screwing, bonding, welding):
Flexible Robotic Arms: Equipped with force-control technology, 4-axis or 6-axis mechanical arms adjust pressure and speed during assembly—for example, applying just enough force to snap a plastic cover into place without cracking it, or tightening screws to a preset torque to avoid over-tightening.
Specialized Fixtures: Customizable jigs made of wear-resistant materials (e.g., aluminum alloy, POM plastic) fix parts in place, ensuring consistency in assembly posture. Quick-change fixtures allow the system to switch between different part models in 5–10 minutes, supporting small-batch, multi-variety production.
Integrated Joining Tools: Depending on part requirements, the unit can integrate ultrasonic welders (for plastic welding), automatic screw feeders (for threaded connections), or adhesive dispensers (for bonding), achieving seamless integration of assembly steps.
- Quality Inspection Unit: The “Guardian” for Zero Defects
Injection molded parts are prone to dimensional deviations or surface flaws, making real-time inspection critical. The inspection unit embeds quality control throughout the assembly process:
In-line Visual Inspection: Cameras installed at key stations (e.g., post-loading, post-assembly) check part dimensions, assembly accuracy (e.g., whether a snap is fully engaged), and surface quality. Defective parts are automatically rejected and sent to a separate collection bin, with defect data logged for traceability.
Dimensional Measurement: Laser displacement sensors or coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) perform sampling inspections of critical dimensions (e.g., hole position, wall thickness) to ensure compliance with design standards, reducing the risk of batch defects.
- Intelligent Control & Data Unit: The “Brain” for System Coordination
This unit acts as the system’s nerve center, enabling centralized management and continuous optimization:
PLC & HMI Integration: A programmable logic controller (PLC) coordinates the operation of all units, while a human-machine interface (HMI) allows operators to monitor real-time parameters (e.g., production count, defect rate, equipment status) and adjust settings intuitively.
MES Data Linkage: The system connects to the factory’s Manufacturing Execution System (MES), uploading production data (e.g., assembly cycle time, material consumption, defect types) for process analysis. For example, if the defect rate of a certain part rises, MES can trace it back to a specific injection molding machine or assembly station, enabling targeted improvements.
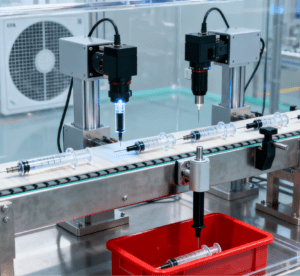
Key Application Scenarios: Empowering Diverse Industries
The flexibility and precision of the auto-loading automated assembly system make it indispensable across industries where injection molded parts are core components:
- Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, the system assembles plastic parts such as door handle components, dashboard connectors, and battery case accessories. For example, in new energy vehicle (NEV) battery pack production, it automates the assembly of plastic insulation sleeves and terminal blocks—achieving a cycle time of 15 seconds per unit and a defect rate below 0.05%, far outperforming manual assembly lines. A typical application of the Injection Molded Parts Automated Assembly System with Auto-Loading here involves its auto-loading unit using magnetic grippers to handle thin-walled plastic battery brackets (which are prone to deformation if gripped too tightly), while the assembly execution unit uses torque-controlled screwdrivers to fasten 4 screws simultaneously—ensuring no bracket warping and consistent screw tightness, a critical factor for preventing battery short circuits.
- Consumer Electronics
For small, high-precision injection molded parts (e.g., smartphone camera modules, wireless earbud casings), the system’s micro-assembly capabilities shine. It can assemble 5–8 tiny components (e.g., lenses, gaskets, connectors) in a single cycle, with a positioning accuracy of ±0.01 mm—meeting the strict quality requirements of consumer electronics.
- Medical Device Industry
Medical injection molded parts (e.g., syringe barrels, inhaler components) require high cleanliness and traceability. The system uses food-grade lubricants, stainless steel fixtures, and HEPA filters to maintain a Class 100,000 cleanroom environment. Additionally, each part is assigned a unique QR code, allowing full traceability from raw material to finished product—critical for compliance with FDA and CE regulations.
Why Adopt This System? The Competitive Advantages
Compared to traditional manual or semi-automated assembly, the Injection Molded Parts Automated Assembly System with Auto-Loading delivers transformative value:
Efficiency Boost: 24/7 uninterrupted operation increases production capacity by 30–50% compared to manual lines. For example, a system assembling plastic automotive clips can produce 8,000–10,000 units per shift, vs. 3,000–4,000 units for a manual team.
Cost Reduction: By replacing 3–5 manual workers per station, the system cuts labor costs by 40–60% annually. It also reduces material waste (e.g., fewer damaged parts) and lowers rework costs, with a typical ROI period of 1–2 years.
Quality Consistency: With precision control and real-time inspection, the defect rate is reduced to less than 0.1%, ensuring compliance with strict industry standards.
Flexibility & Scalability: Modular design allows easy addition of new units (e.g., extra assembly stations, advanced inspection tools) as production needs grow. Quick-change fixtures support rapid product switching, helping manufacturers respond to market demands faster.
Future Trends: Toward More Intelligent and Sustainable Systems
As manufacturing technology evolves, the auto-loading automated assembly system for injection molded parts is moving in three key directions:
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance: Sensors embedded in mechanical arms and feeding mechanisms collect vibration, temperature, and load data. AI algorithms analyze this data to predict equipment failures (e.g., worn grippers, faulty cameras) and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing unplanned downtime by 20–30%.
Digital Twin Integration: A virtual replica of the system allows operators to simulate assembly processes, test new part programs, and optimize parameters (e.g., feeding speed, assembly force) in a virtual environment—cutting the time to launch new products by 40%.
Green Manufacturing: Energy-efficient motors, recyclable fixtures, and waste reduction (e.g., precise material feeding) reduce the system’s carbon footprint. For example, LED lighting in vision systems and energy recovery modules in robotic arms lower energy consumption by 15–20%.
Conclusion
The Injection Molded Parts Automated Assembly System with Auto-Loading is more than just a piece of equipment—it is a catalyst for manufacturing transformation. By automating material feeding, precision assembly, and quality control, it solves the pain points of traditional manual assembly and empowers manufacturers to achieve higher efficiency, better quality, and greater flexibility. As smart manufacturing accelerates globally, this system will become a cornerstone for enterprises seeking to stay competitive in the age of precision and intelligence.