3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining are two commonly used technologies in the modern manufacturing field. 3-axis CNC machining focuses on operations along the three axes (X, Y, and Z), making it suitable for simple geometric shapes and common basic parts. In contrast, 5-axis CNC machining adds two rotational axes, enabling cutting in multiple directions and handling more complex designs and details. This flexibility gives 5-axis machining unique advantages in high-precision processing and complex shaping. This article will conduct an in-depth analysis of the characteristics, application scopes, and respective advantages of the two methods to help readers better understand these two machining approaches and make rational choices.
Analysis of the Basic Characteristics and Advantages of 3-Axis CNC Machining
3-axis CNC machining primarily performs cutting along the X, Y, and Z axes, making it suitable for processing simple geometric shapes. The advantages of this machining method lie in its simple operation and relatively low cost, which makes it suitable for small-batch production. In the manufacturing of basic components, 3-axis machining can efficiently complete cutting tasks while maintaining good machining accuracy. It is typically used to produce flat surfaces, holes, or simple contours. Programming for 3-axis machine tools is also relatively intuitive, allowing beginners and small enterprises to get started quickly. Additionally, 3-axis CNC machining equipment is widely available, and maintenance and spare parts are more accessible, providing a practical solution for projects with limited budgets.
Technical Advantages and Application Examples of 5-Axis CNC Machining
Compared with traditional 3-axis machining, 5-axis CNC machining has obvious technical advantages. First, it can perform cutting in multiple directions simultaneously, making the machining process more flexible and particularly suitable for handling complex curved surfaces and details. For example, in the manufacturing of aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment, 5-axis machining can accurately shape complex parts to meet high-precision requirements. A typical case is the production of core components for medical nebulizers: parts like atomizing chambers (with internal curved flow channels to ensure uniform airflow) and precision nozzles (needing micron-level opening accuracy for stable atomization) rely entirely on 5-axis CNC machining to achieve their complex structures and strict dimensional tolerances. These high-precision machined parts are then integrated into automated production lines by Maszyna do montażu nebulizatoróws—specialized equipment that automates component alignment, ultrasonic welding of seals, and leak testing (critical for preventing medication leakage). This combination of 5-axis machining and dedicated assembly machines ensures that nebulizers meet the rigorous safety and performance standards of medical devices.
Furthermore, 5-axis machining significantly reduces the number of workpiece clamping operations, improving production efficiency and reducing errors caused by manual operations. In practical applications, components such as turbine blades, molds, and complex structural parts often adopt 5-axis CNC machining to ensure product consistency and quality. Therefore, choosing 5-axis CNC machining offers higher efficiency and precision, undoubtedly creating greater development space for the manufacturing industry.
Comparative Analysis of 3-Axis (X, Y, Z) and 5-Axis Machine Tools
In the field of CNC machining, 3-axis and 5-axis machine tools each have their own characteristics. 3-axis machine tools mainly perform cutting along the X, Y, and Z axes, making them suitable for processing simple shapes such as flat surfaces and basic geometric bodies. Due to their relatively simple movement mode, 3-axis CNC machining is usually easier to operate and has lower equipment costs. Therefore, 3-axis machine tools are a good choice for basic machining tasks. In comparison, 5-axis machine tools can operate with two additional rotational axes, giving them an advantage in handling complex shapes. This technology can achieve higher machining precision, especially excelling in the production of curved surfaces and detailed features. Moreover, 5-axis machine tools can shorten machining time because the workpiece can be fixed once, reducing the need for re-clamping and position adjustments. If a task requires complex designs or high-precision machining, 5-axis machine tools are undoubtedly the more suitable choice.
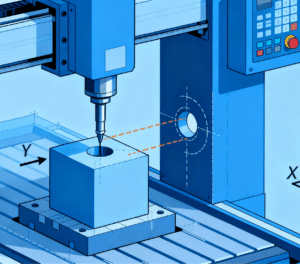
How to Select the Appropriate CNC Machining Method Based on Machining Tasks
When selecting the appropriate CNC machining method, the first factor to consider is the shape and complexity of the workpiece. For simple shapes such as cubes or cylinders, 3-axis CNC machining is sufficient. This method is easy to operate, relatively low in cost, and suitable for mass production. For more complex parts, such as those with curved surfaces or rich details—like the atomizing chambers and nozzles used in nebulizers, which require 5-axis machining to ensure their functional precision—5-axis CNC machining is recommended. It can perform cutting at multiple angles, improving machining precision and efficiency, and is well-suited for high-demand tasks (such as parts that will later be assembled by Nebulizer Assembly Machines to meet medical standards). In addition, material properties and the expected production cycle should also be taken into account. Some materials may cause greater wear to cutting tools during processing, making the selection of a suitable machine tool particularly important. By comprehensively evaluating these factors, one can more effectively determine whether to use 3-axis or 5-axis CNC machining to achieve the best production results.
When choosing between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining, multiple factors need to be considered comprehensively. 3-axis machining is suitable for processing relatively simple parts, with the advantages of low cost and simple operation, enabling it to quickly meet basic production needs. It performs well in small-batch production, especially when the requirements for machining precision are not extremely high. On the other hand, 5-axis machining, relying on its unique multi-directional cutting capability, can accurately handle the production of more complex and high-demand parts. For example, the aerospace and medical device industries often use 5-axis machining to manufacture components with complex curved surfaces and rich details (such as nebulizer core parts), improving production efficiency and reducing errors in the manufacturing process—laying a solid foundation for subsequent assembly by specialized equipment like Nebulizer Assembly Machines. Therefore, in practical applications, selecting the appropriate CNC machining method based on part characteristics and machining requirements is an important strategy to improve production efficiency and product quality.