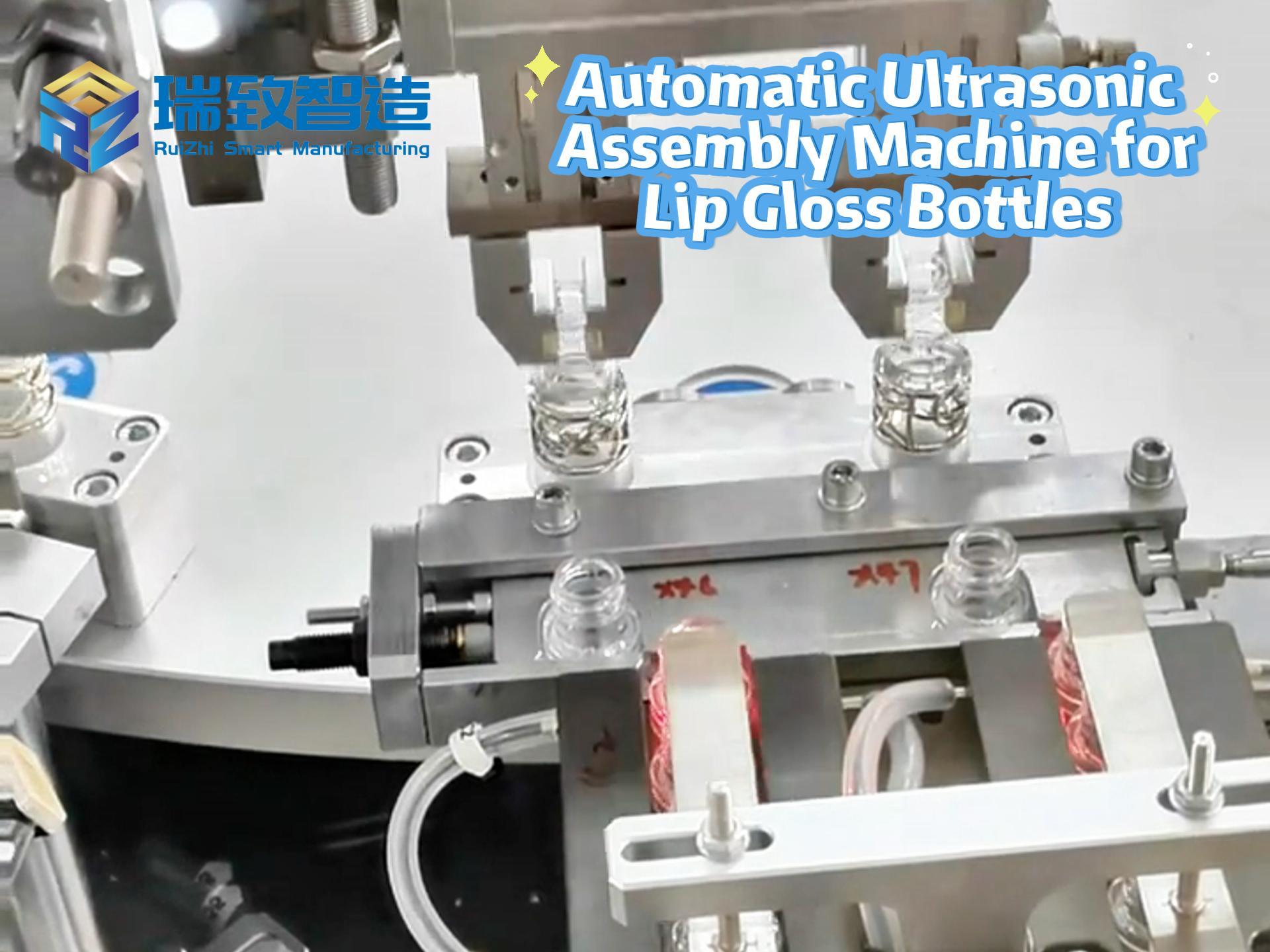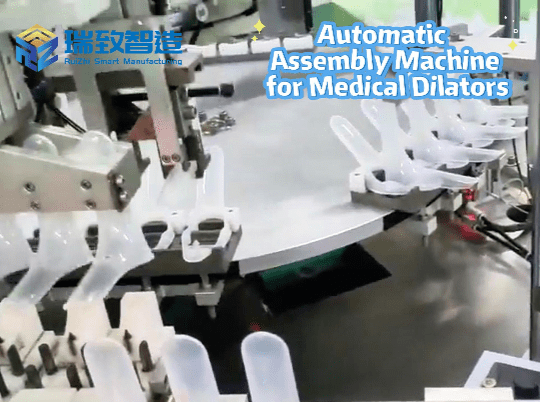
- Fixed vs. Flexible Automation: The Core Choice for Businesses
While fixed systems such as conveyor belts and sortation machines have long been the industry standard due to their efficiency, they lack adaptability. They are also costly to modify, and often require significant downtime to accommodate changes in product lines, volumes or processes—even for equipment like traditional automatic assembly machines that are fixed to specific production tasks (e.g., assembling a single type of component). Now, businesses face a critical choice: stick with traditional fixed warehouse automation systems, or embrace flexible solutions like autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), which have the agility and scalability needed to thrive in a constantly changing market.
- The Case for Flexible Automation: Adaptability as a Competitive Edge
The Case for Flexible Automation
The argument for flexible automation is easy to grasp. Unlike fixed automation—including rigid automatic assembly machines that can only handle one product or process—flexible automation empowers warehouses and distribution centers to adapt as demands change. This reduces costs and allows businesses to scale efficiently for peak periods (which are becoming more frequent), all while fostering long-term resilience and competitiveness. “You can build a platform that is flexible so that, no matter what happens, when management calls and says we’re going to run a sale, or we’re going to scale back, you don’t feel whipsawed,” says Mike Johnson, president and chief operating officer of Locus Robotics. “That’s the flexibility right there; the ability to move.”
- Real-World Flexibility: DHL’s Robot-Scaling Strategy for Peaks
“When we get customers in the door, we’ve got a three-to-five-year contract, typically, and nobody wants to bolt much down,” says Matthew Dippold, director of digital acceleration at DHL Supply Chain, which deploys persons-to-goods automation systems in multiple facilities. “With peak scenarios, we’re able to scale more robots into the system to deal with the demands that are coming as holiday season ramps up,” Dippold continues. “You couldn’t do that with a fixed system—even a specialized automatic assembly machine would be limited to its pre-set task. Maybe you could ramp up the speed of the system, but that’s all you could do.”
- Benefits of Automation: Efficiency, Accuracy, and Cost Savings
Benefits of Automation
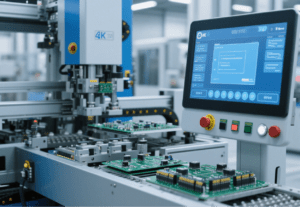
Automation is becoming increasingly vital for warehouse operations, especially given the labor scarcity and rising costs. With strategic planning and clear objectives, warehouses can successfully transition from manual operations to automation—integrating both flexible tools and adaptable versions of equipment like automatic assembly machines—significantly enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- How Automation Streamlines Tasks: From Palletizing to Traceability
Automation can handle low-value manual tasks such as palletizing and transporting products and materials using conveyors, collaborative robots, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). Even automatic assembly machines, when designed with flexible programming, can shift between assembling different components with minimal reconfiguration. Automated traceability and barcode-reading solutions streamline record-keeping and inventory tracking, while scan tunnels ensure the correct product reaches the correct destination, significantly reducing error rates.
- Safety in Automation: Protecting Workers While Boosting Productivity
Safety is a paramount concern in all automation solutions. Modern automation platforms seamlessly integrate safety products like area scanners and light curtains into larger robotic and motion control systems—including those paired with automatic assembly machines—to prevent accidents during component handling. This enables automation to respond safely to human activity and report any errors or safety incidents to the broader system. By automating strenuous and repetitive tasks, warehouses can minimize workplace injuries, particularly musculoskeletal disorders, fostering a safer work environment.
- The Importance of Flexible Automation: Avoiding Obsolescence
The Importance of Flexible Automation
Flexible automation is crucial to avoid falling behind. Flexible automation refers to systems that can be reconfigured and adapted to meet new operational objectives and growth—whether that means reprogramming a automatic assembly machine to handle a new product line or adding AMRs to a warehouse fleet. While the journey to achieving flexible automation is challenging, it is far from insurmountable.
- Preparing for Flexible Automation: Goals, Partners, and Workforce
Preparing for the unpredictable is no simple task. However, as the adage goes, “Fortune favors the prepared.” To reiterate, the first critical step is setting clear goals—such as determining how a automatic assembly machine or AMR should support both current and future production needs. This enables informed decisions about equipment and solutions, aligning them with both near-term and long-term objectives. Additionally, it is vital to identify a partner capable of delivering and updating solutions, or to invest in educating your workforce to evolve these solutions internally. Equipping your teams with the right tools or collaborating with a trusted partner will facilitate future changes seamlessly.
What is the market size and development trend of medical product assembly machines?
What are the advantages of medical product assembly machines?