Robotic manipulators (usually referring to robotic arms and dexterous end-effectors) are evolving from traditional automation toward intelligence and flexibility in industrial applications, and 2025 has witnessed breakthroughs in a number of core technologies as well as the in-depth advancement of their practical applications.
Common Applications in Industrial Scenarios
General Industrial Operations
This has become a key expansion focus for humanoid robots and dexterous manipulators in 2025, covering universal tasks in production lines such as material sorting, bin handling and component assembly. For instance, humanoid robots are now capable of sorting, shelving and retrieving bins of varying sizes in engine manufacturing plants.
Automotive and Component Manufacturing
It is one of the most mature application sectors for robotic manipulators. Manipulators are widely adopted in processes including vehicle body welding, precision assembly of components, glue dispensing and handling of engine parts.
3C Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
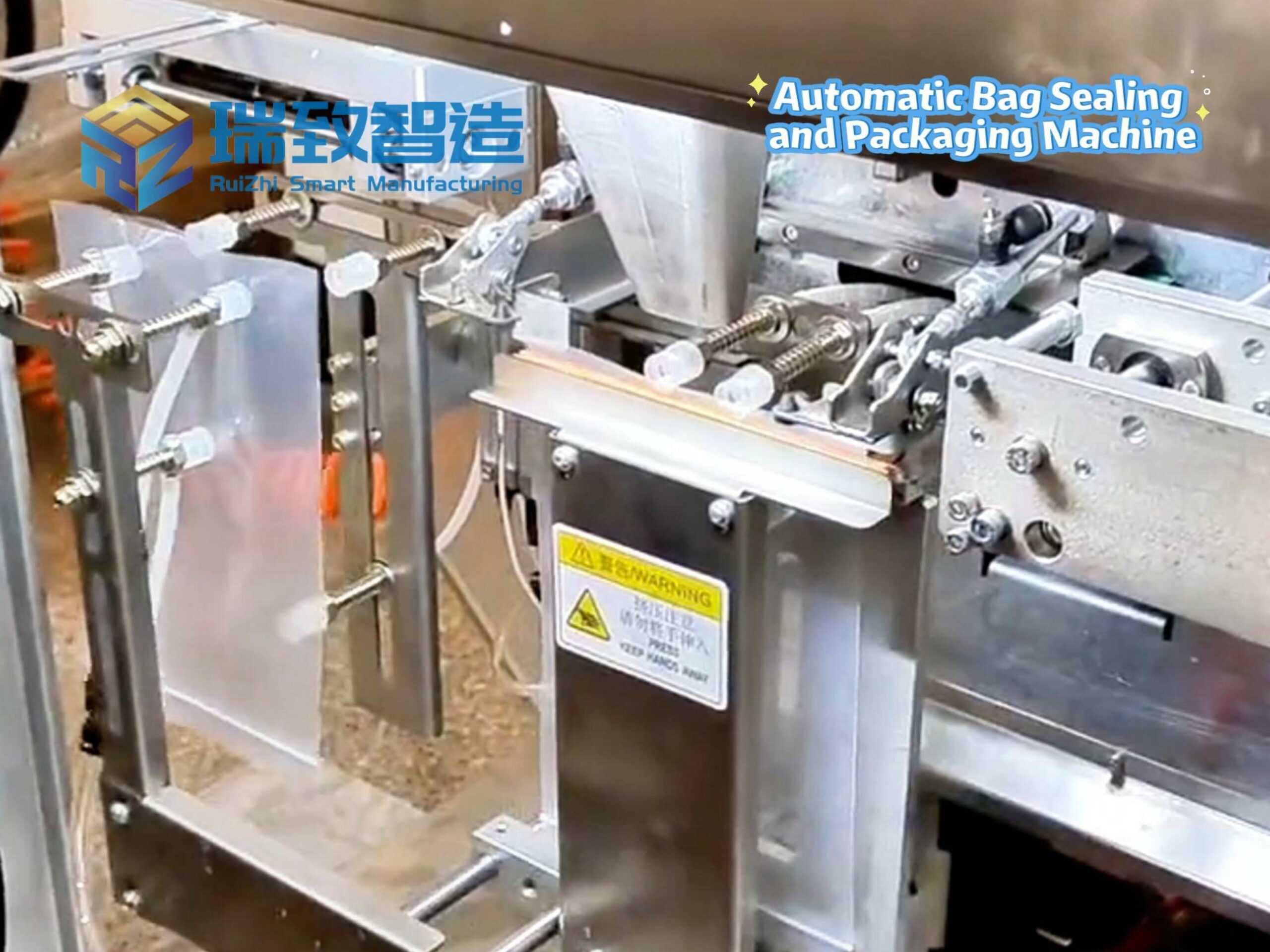
This industry imposes extremely stringent requirements for precision and flexibility. Compact six-axis robotic arms can complete component assembly, screw fastening and visual inspection for products such as mobile phones. Notably, in the production of electrical control components, these robotic arms also work in tandem with contactor assembly machines, undertaking precise feeding, terminal crimping and assembly verification tasks for contactor parts, which significantly improves the automation level and product consistency of contactor manufacturing. In semiconductor clean rooms, robots are able to perform cartridge handling tasks for more than ten thousand times per day stably.
New Energy Industry
In battery production and photovoltaic module manufacturing, robotic manipulators act as a quality guardian to ensure operational efficiency and product quality. They can complete palletizing of battery modules, precise lamination and welding of photovoltaic cells with a repeat positioning accuracy of ±0.05 mm.
Pharmaceutical and Food Processing Industries
For these sectors with rigorous hygiene and safety standards, robotic manipulators designed with food-grade or sterile specifications are applied to material palletizing, packaging sorting and other processes, eliminating contamination risks that may be caused by manual contact.
In addition, technological advancement is the fundamental driving force for the in-depth adoption of robotic manipulators. The major technological breakthroughs achieved in 2025 are mainly reflected in the following aspects:

Embodied Intelligence and Synergy of “Hand-Eye-Brain”
Robotic manipulators are evolving from independently executing pre-programmed motions into intelligent agents capable of real-time interaction with the surrounding environment. The core of this evolution is embodied intelligence — enabling manipulators to perceive the environment through sensors and make autonomous decisions.
A landmark progress in 2025 is the advent of integrated controllers, which deeply integrate the control links of robotic arms (hands), mobile chassis (feet), vision systems (eyes) and scheduling systems (brains). This integration empowers robots to become intelligent agents with unified perception, decision-making and execution capabilities, fundamentally improving the efficiency and stability of collaborative operations.
Practicalization and Cost Reduction of Dexterous Manipulator Technology
As the cutting-edge form of robotic manipulators, dexterous end-effectors have achieved remarkable breakthroughs in 2025:
Functional Breakthroughs: Dexterous manipulators developed by multiple enterprises are now capable of completing sophisticated tasks that previously required high-level manual skills, such as screw tightening, flexible component assembly, and cable plugging and unplugging.
Perceptual Breakthroughs: Tactile sensors integrated into the fingertips and finger pads allow dexterous manipulators to perceive grasping force and surface information of objects in real time just like human hands, enabling more delicate operations.
Cost Breakthroughs: Innovative solutions with significant cost advantages have emerged. For example, the 3D printed flexible dexterous manipulator developed by the research team of Fudan University has its material cost per finger controlled within RMB 1, opening up possibilities for large-scale application in the future.
Enhanced Force Control and Flexible Operation Capabilities
The ability of robotic manipulators to precisely control force is critical for their safe interaction with humans and the environment. In 2025, technologies such as cable-driven robotic arms have attracted wide attention. By replacing rigid connecting rods with cable transmission, such arms can effectively absorb impact forces and enable safer human-robot interaction.
Meanwhile, advanced force control algorithms can calibrate the movements of manipulators in real time, allowing them to achieve generalized operational capabilities while meeting industrial-grade precision requirements.
From “Single-Point Application” to “Mass Replication”
2025 has seen robotic manipulators (especially composite robots) achieve a crucial leap from experimental application to large-scale deployment in specific industries. For example, the composite robots developed by Elite Robot have secured single orders of nearly 100 units in the supply chains of top global technology companies, proving that such robotic solutions have matured to undertake core production tasks stably.
Current Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the rapid progress, the industry still faces challenges such as the high cost of core components and the need for further verification of long-term reliability in complex tasks.
In the future, technological development will focus more on in-depth integration with the processes of specific industries to achieve refined deployment in vertical sectors. Meanwhile, large-scale production will drive the continuous decline of manufacturing costs, further accelerating the mass adoption of robotic manipulators across industries.