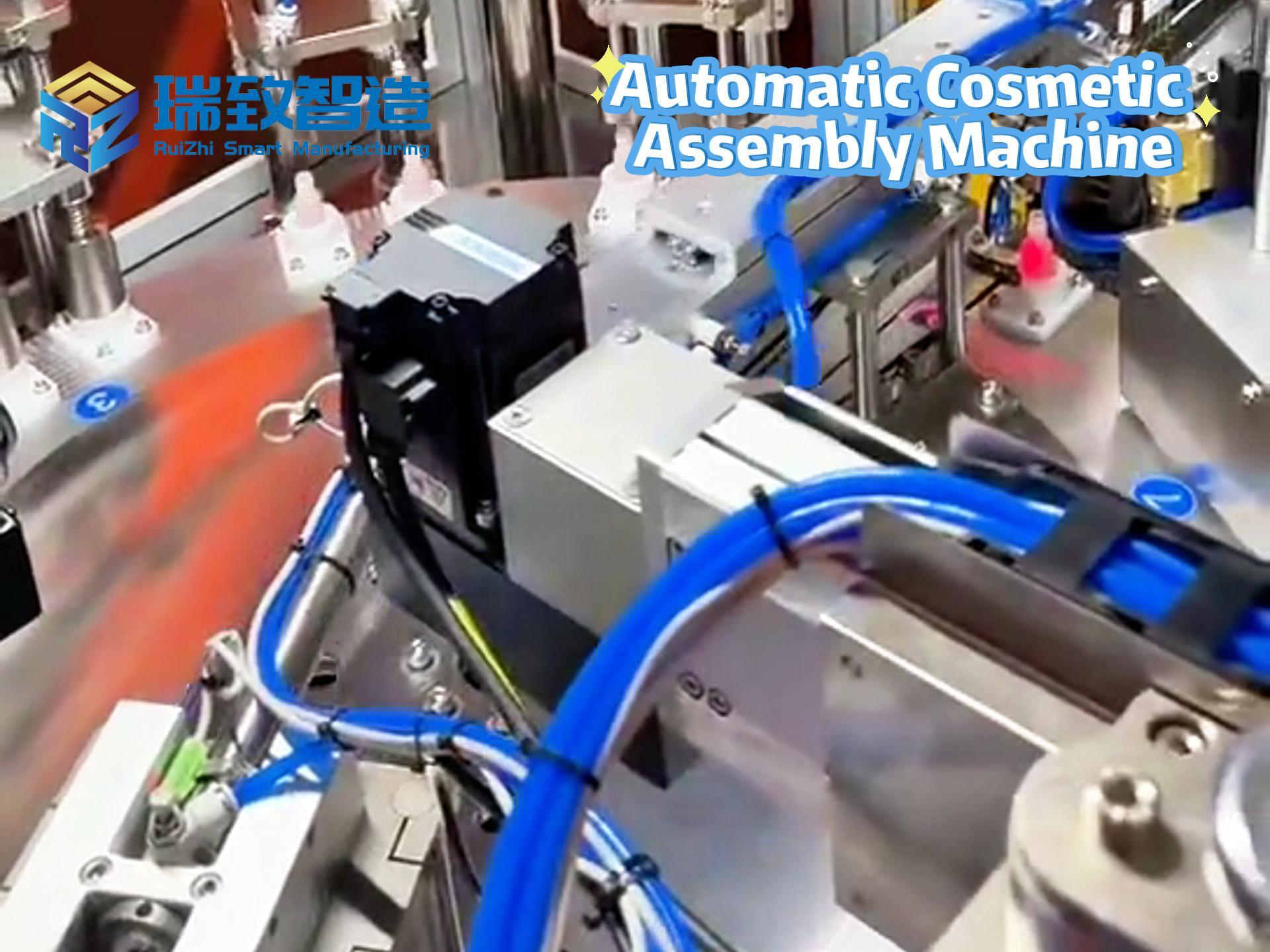
Intelligent Automation: The Catalyst for Transforming Manufacturing Quality, Productivity, and Efficiency
Laikmetā, kurā industrial automation and automation equipment ir sen definēti ražošanas kritēriji, intelligent automation tagad pārveido nozares nākotni. Apvienojot mākslīgo intelektu (MI), mašīnmācīšanos un uz datiem balstītas atziņas, ražotāji pārvar tradicionālos ierobežojumus — pārejot no reaktīviem, manuāliem procesiem uz proaktīvām, MI optimizētām darbplūsmām. Šīs pārmaiņas nav tikai cilvēku darba aizstāšana ar mašīnām; tās ir par simbiozes izveidi starp pirmās līnijas darbiniekiem un progresīvām tehnoloģijām, piemēram, mašīnredzi, RFID un autonomiem robotiem, kas visas ir apvienotas zem… intelligent automation.
Vēsturiski ražošana uzplauka industrial automation, piemēram, konveijera lentes un robotizētas rokas, lai veicinātu efektivitāti. Taču mūsdienu videi ir nepieciešams vairāk: reāllaika datu integrācija, paredzamā apkope un adaptīvas ražošanas sistēmas. Kā uzsvērts Zebra 2024. gada ražošanas vīzijas pētījumā, tikai 161 TP3T ražotāju pašlaik ir reāllaika pārskatāmība par savu ražošanas ciklu, un šī nepilnība ir ievērojama. intelligent automation ir gatavs aizpildīt. Līdz 2029. gadam 61% ražotāju sagaida, ka mākslīgais intelekts būs izaugsmes virzītājspēks, salīdzinot ar 41% 2024. gadā, kas signalizē par seismisku pāreju uz tehnoloģiju virzītu transformāciju.
Galvenās tehnoloģijas, kas veido nākotni
- Mašīnredze un fiksētā rūpnieciskā skenēšana (MV/FIS)Šie ar mākslīgo intelektu darbināmie rīki darbojas kā rūpnīcas “acis”, izmantojot viedās kameras un skenerus, lai atklātu defektus, validētu komponentu izvietojumu un reāllaikā izsekotu darbplūsmas. Atšķirībā no tradicionālajām sistēmām, MV/FIS integrējas ar centralizētām programmatūras platformām, pārvēršot neapstrādātus datus par praktiski izmantojamām atziņām. Piemēram, automobiļu montāžā MV kameras var pamanīt nepareizi novietotas detaļas, pirms tās sasniedz nākamo staciju, samazinot atkārtotas apstrādes nepieciešamību līdz pat 30%.
- RFID drukāšanas un kodēšanas tehnoloģijaRFID tagi, kas aizstāj novecojušus svītrkodus, piedāvā izturīgu un elastīgu izsekošanu haotiskā vidē. Mūsdienu RFID sistēmas ne tikai identificē produktus, bet arī automatizē krājumu pārvaldību un kvalitātes kontroli. Veselības aprūpes ražošanā RFID kodētas etiķetes var izsekot farmaceitiskās partijas sterilā vidē, nodrošinot atbilstību un izsekojamību, kas ir būtisks uzlabojums salīdzinājumā ar manuālu reģistrēšanu.
- Robotika AutomatizācijaAutonomie mobilie roboti (AMR) maina noliktavu un rūpnīcu grīdas. Apvienojumā ar mākslīgā intelekta vadītu programmatūru tādi AMR kā Zebra risinājumi sinhronizējas ar cilvēkiem, optimizējot preču savākšanas un novietošanas darbplūsmas. Samazinot robotu dīkstāves laiku, izmantojot noņemamus ratiņus un reāllaika analīzi, šīs sistēmas var palielināt kubatūras ietilpību par 300%, vienlaikus izmantojot mazāk robotu, pierādot, ka intelligent automationuzlabo efektivitāti, neupurējot mērogu.
Ceļš uz mērogojamu inovāciju
Skaistums intelligent automation slēpjas tā mērogojamībā. Atšķirībā no atsevišķas automation equipment, kas bieži darbojas silosos, intelektuālās sistēmas nemanāmi integrējas dažādās darbībās. Piemēram, automašīnu ražotājs var izmantot MV/FIS metinājumu pārbaudei, RFID komponentu izcelsmes izsekošanai un AMR detaļu transportēšanai — to visu organizē vienota platforma, kas reāllaikā prognozē apkopes vajadzības un pielāgo ražošanas grafikus. Šī savstarpējā saistība ne tikai uzlabo redzamību, bet arī veicina nepārtrauktas uzlabošanas kultūru, kur uz datiem balstīti lēmumi aizstāj minējumus.
Secinājums: no automatizācijas līdz autonomijai
Ražotājiem pārvarot darbaspēka trūkumu un globālo konkurenci, intelligent automation kļūst par tiltu starp mantojumu industrial automation un ražošanas nākotni. Runa nav par cilvēku lomu likvidēšanu, bet gan par viņu pilnvarošanu: pirmās līnijas darbinieki kļūst par problēmu risinātājiem, savukārt mākslīgais intelekts un automation equipment tikt galā ar atkārtotiem, kļūdām pakļautiem uzdevumiem. Izmantojot tehnoloģijas, kas piešķir prioritāti sadarbībai, piemēram, ar mākslīgo intelektu papildinātu redzi, adaptīvo RFID un autoparka pārvaldītu robotiku, uzņēmumi var sasniegt to, kas kādreiz bija neiedomājams: saražot vairāk ar mazāk, nodrošināt kvalitāti bez defektiem un pielāgoties tirgus izmaiņām datu pārraides ātrumā.
Galu galā solījums par intelligent automation ir vienkārša: padarīt ražošanu ne tikai ātrāku vai lētāku, bet arī viedāku. Kā uzsver Zebra pētījums, ražotāji, kas vadīs šo izaicinājumu, būs tie, kas tehnoloģijas neuztvers kā revolucionāru ieroci, bet gan kā partneri — tādu, kas izejvielas pārvērš inovācijās, datus — prognozēšanā un rūpnīcas — bezgalīgu iespēju ekosistēmās.