In the wave of industrial automation, 4-axis robot automatic assembly equipment has emerged as a key player in streamlining production lines. With its compact structure, precise motion control, and cost-effective performance, it has become the backbone of automated assembly in sectors ranging from electronics to automotive parts. This article explores the core characteristics, application scenarios, and transformative impact of 4-axis robot automatic assembly equipment in modern manufacturing.
What Defines 4-Axis Robot Automatic Assembly Equipment?
A 4-axis robot, as the name suggests, operates with four degrees of freedom (DoF), typically consisting of:
J1 (Base rotation): Allows 360° rotation of the robot base, enabling horizontal movement across the workspace.
J2 (Arm elevation): Controls the vertical lifting/lowering of the main arm, adjusting the working height.
J3 (Arm extension): Manages the telescoping of the arm to reach targets at varying distances.
J4 (End effector rotation): Rotates the gripper or tooling at the end of the arm, critical for orienting parts during assembly.
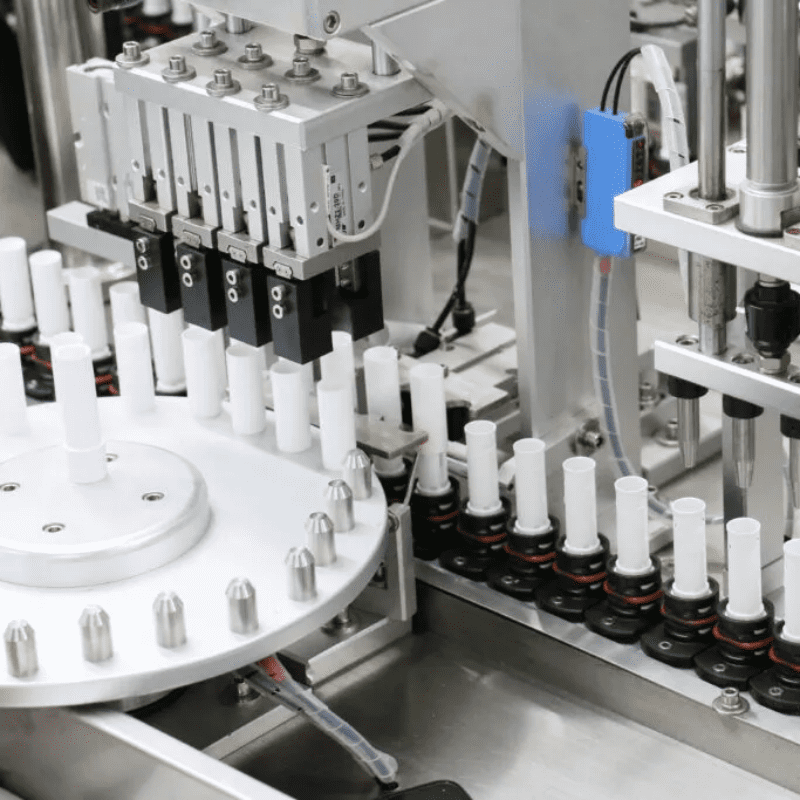
This configuration balances flexibility and simplicity: while it lacks the full spatial mobility of 6-axis robots, its focused range of motion makes it ideal for repetitive, high-precision assembly tasks in confined or standardized workstations. Equipped with advanced sensors (e.g., vision systems, force sensors) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), these robots can execute complex assembly sequences—such as inserting pins, tightening screws, or fitting small components—with micron-level accuracy.
Core Advantages in Automated Assembly
The popularity of 4-axis robot assembly equipment stems from its unique blend of efficiency, reliability, and adaptability:
High Speed & Consistency
Unlike manual assembly, which is prone to fatigue and variability, 4-axis robots maintain stable cycle times—often completing 30–60 operations per minute—with defect rates as low as 0.01%. This consistency is vital for mass production, where even minor errors can cascade into significant losses.
Space-Efficient Design
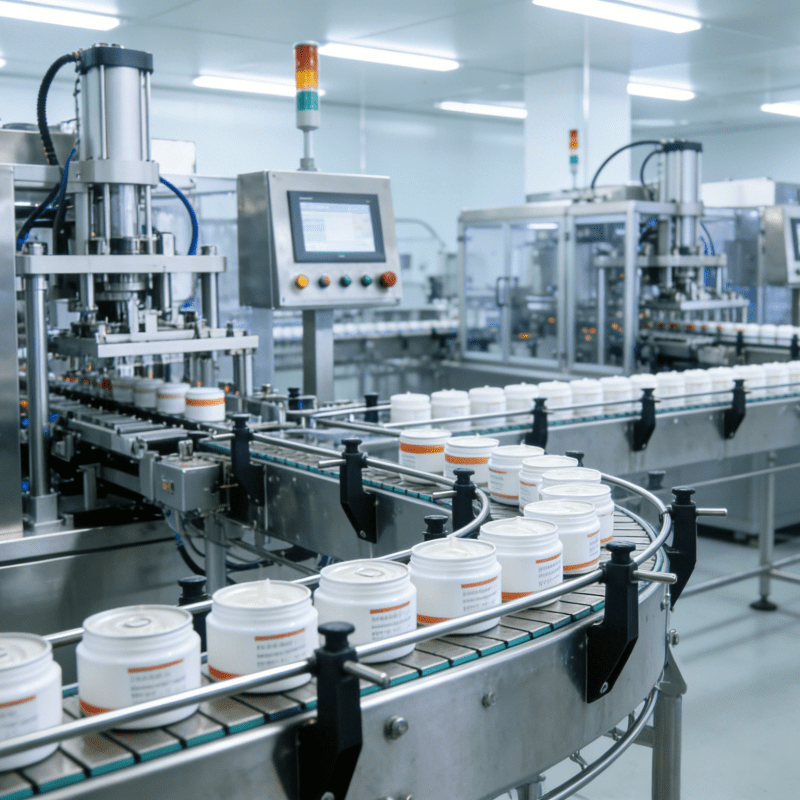
With a compact footprint and fixed working radius, 4-axis robots fit seamlessly into tight production lines. This is particularly valuable in electronics manufacturing, where workshops are often densely packed with machinery.
Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to 6-axis robots, 4-axis models have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance requirements, making them accessible for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) looking to automate without heavy investment. Their energy efficiency also reduces long-term operational expenses.
Easy Programming & Integration
Modern 4-axis robots come with user-friendly programming interfaces, allowing operators to teach new assembly paths via drag-and-drop or teach pendant controls. They integrate smoothly with existing production systems, including conveyors, feeders, and quality inspection tools, minimizing downtime during deployment.
Real-World Applications: From Electronics to Automotive
4-axis robot automatic assembly equipment excels in scenarios requiring repetitive, precision-driven tasks. Key application areas include:
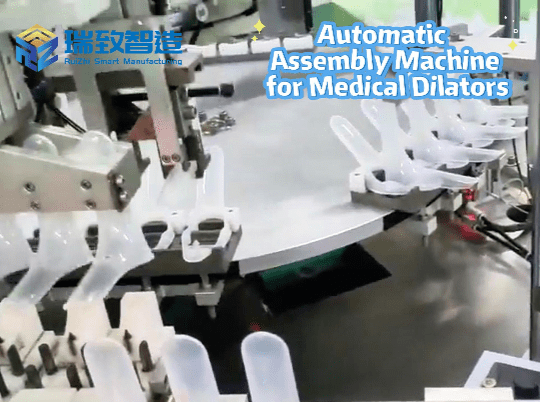
Electronics Manufacturing: Assembling smartphone components (e.g., inserting microchips, soldering connectors), or fitting sensors into circuit boards. The robot’s J4 rotation ensures components align with tiny mounting points, avoiding damage to delicate parts.
Automotive Parts: Assembling small components like door locks, window regulators, or sensor modules. The J1-J3 axes enable quick movement between workstations, while force sensors prevent over-tightening of screws.
Household Appliances: Fitting gears into motor assemblies for washing machines or attaching nozzles to vacuum cleaners. The robot’s compact size adapts to the modular layouts of appliance production lines.
Medical Devices: Assembling precision parts for insulin pumps or diagnostic tools, where sterility and accuracy are paramount. Enclosed workcells with 4-axis robots reduce human contact, lowering contamination risks.
Innovations Shaping the Future
As manufacturing evolves toward Industry 4.0, 4-axis robot assembly equipment is integrating new technologies to expand its capabilities:
AI-Powered Vision Systems: Cameras paired with machine learning algorithms enable robots to adapt to slight variations in part positioning (e.g., warped plastic components), reducing the need for rigid fixturing.
Collaborative Functionality: Safety features like force-limiting joints allow 4-axis robots to work alongside humans, handling repetitive tasks while workers focus on complex quality checks.
Modular Tooling: Quick-change grippers and end effectors let a single robot switch between assembling screws, inserting clips, or applying adhesives, boosting versatility for mixed-product lines.
Conclusion
axis robot automatic assembly equipment embodies the “right tool for the job” philosophy in automation. It may not match the full versatility of higher-axis robots, but its focus on speed, precision, and affordability makes it indispensable for modern manufacturing. As technology advances, these robots will continue to evolve—becoming smarter, more collaborative, and even more integral to the factories of tomorrow. For manufacturers aiming to balance efficiency and cost, 4-axis robot assembly equipment is not just an option; it’s a cornerstone of competitive production.
Axis Robot Automatic Assembly Equipment
What is the difference between 4-axis and 6-axis robotic arms?