Table of Contents
ToggleCollaborative Robots (Cobots): Reconstructing the Production Philosophy of Human-Machine Collaboration
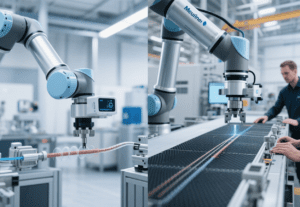
The emergence of collaborative robots (cobots) marks the manufacturing industry’s transition from the 1.0 era of “machine replacement” to the 2.0 era of “human-machine integration”. Data from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) shows that global cobot sales reached 180,000 units in 2023, with an annual growth rate of 45%. Their applications have expanded from simple material handling to complex scenarios such as precision assembly and medical assistance, redefining human-machine relationships in industrial production.
一、Safety Integration: Technological Breakthroughs Reshape Collaboration Boundaries
In the “nerve center” of 3C products—the chip packaging process—TSMC’s Nanjing plant demonstrates the pinnacle of precision engineering with its UR16e cobot: Equipped with an in-built six-axis force sensor, it controls wire bonding pressure with 0.05N precision. When a worker’s arm accidentally enters the workspace, the robot stops smoothly at an acceleration of 0.1m/s², improving response speed from 100ms (traditional industrial robots) to 20ms, meeting the highest ISO/TS 15066 safety standards. This dual protection of “force control + vision” enables robots to collaborate with workers in BGA chip ball planting, increasing yield rates from 92% (manual operation) to 98.7% and achieving safe and efficient “human-machine symbiosis” production.
二、Flexible Production: The Optimal Solution for Small-Batch, Multi-Variety Manufacturing
Zhejiang Deye Holding Group’s “Intelligent Assembly Island” exemplifies the flexibility of cobots in discrete manufacturing: Twelve UR10 cobots with quick-change end-effectors can switch between production lines for electric kettles, coffee machines, and air fryers within 10 minutes, reducing changeover time by 85% compared to traditional rigid lines. More crucially, their drag-and-drop programming interface shortens worker training from 2 weeks to 2 hours, allowing even senior employees to adjust programs easily. This successfully meets e-commerce platforms’ “small-batch, multi-batch” order demands, increasing annual capacity per line by 30% while reducing labor costs by 40%. This “plug-and-play” flexible production model is becoming the standard for digital transformation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
三、Precision Operations: Breaking the Boundaries of Traditional Robot Applications
In medical device manufacturing, Medtronic’s Irish plant pushes cobots to micrometer-level precision: Cobots equipped with force-controlled wrists and 3D vision systems assemble cardiac stent delivery catheters with ±5μm positioning accuracy, improving efficiency by 5 times compared to manual operations while reducing operator fatigue by 70%. This “human-machine skill complementarity” also shines in aerospace—Airbus’s Hamburg plant uses cobots to assist workers in carbon fiber composite layup, correcting 0.1mm positional deviations in real time via vision guidance systems. Material utilization increases from 82% to 95%, while freeing workers from repetitive, harmful bending operations, demonstrating cobots’ irreplaceability in high-value processes.
四、The Democratization Wave: Automation Enlightenment for SMEs
Universal Robots’ e-Series, priced below 100,000 RMB and designed for “plug-and-play”, has sparked a cobot democratization revolution. After a hardware factory in Zhongshan, Guangdong, purchased three cobots, it transformed from a “family workshop” to an “intelligent workshop”: Robots handle repetitive tasks like screw tightening and parts handling, while workers focus on mold debugging and quality control. Per capita output value increased from 500,000 RMB/year to 1.2 million RMB/year, with equipment payback periods shortened to 14 months. According to the China Robot Industry Alliance, cobot penetration in Chinese SMEs reached 65% in 2023, making them the mainstay of “machine replacement” and driving automation from a “luxury” to a “necessity”.
五、Future Vision: Evolution from “Collaboration” to “Integration”
With the maturity of tactile sensors and voice interaction technologies, cobots are advancing from “safety integration” to “intelligent integration”. Siemens’ Cobot-3D system in Germany uses structured light cameras to reconstruct workpiece positions in real time and autonomously adjust gripping postures, solving the assembly challenge of irregular aluminum alloy die-castings— a process once reliant on senior technicians, now automated. In the future, cobots with human-like perception will 开拓 more “unstructured scenarios” in precision instrument assembly, elderly care, medical rehabilitation, etc., finally forming a golden division of labor where “humans focus on innovative decision-making, and robots handle precise execution”, ushering in a new era of “human-machine integration” in smart manufacturing.
The emergence of cobots is not just an upgrade of production tools but a reconstruction of production relations. It breaks the zero-sum game of “machines replacing humans” and initiates a symbiotic model of “human-machine complementary advantages”. When robots learn to perceive human intentions, and humans learn to collaborate innovatively with machines, industrial production will no longer be a cold automated assembly line but a collaborative community filled with wisdom and warmth. This may be the most profound transformation cobots bring to manufacturing—redefining the value of “humans” in production and making creativity the unique core competitiveness of humanity.
“smart manufacturing solutions” “smart manufacturing technology” “smart manufacturing and engineering week“