Plant Debut: Core Specifications and Gap-Filling Significance
November 25 News – According to media reports, China’s first large-scale dedicated photonic quantum computer manufacturing plant has officially settled in Nanshan District, Shenzhen.
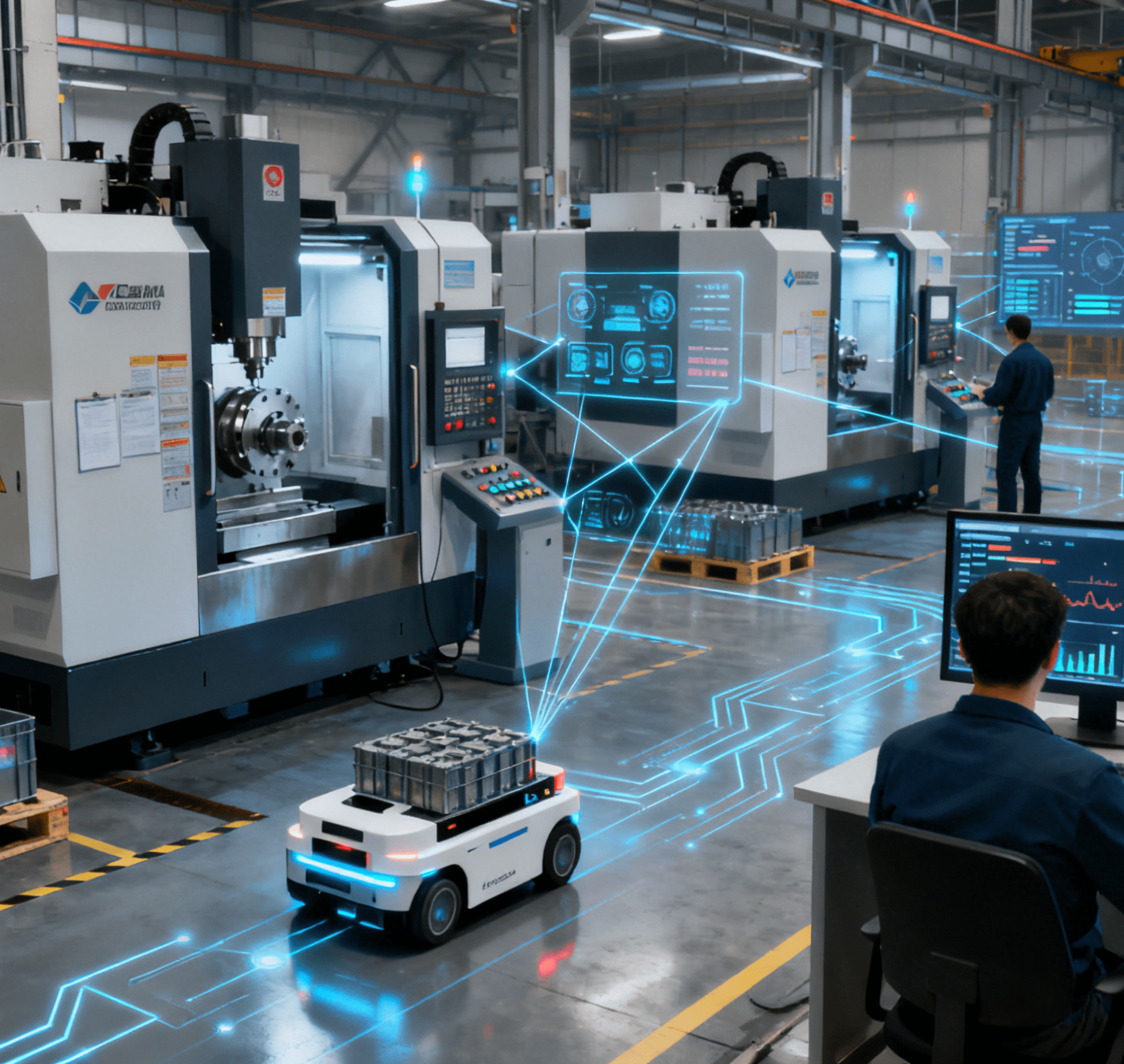
Located in Nanshan Smart City, the manufacturing plant covers a total area of approximately 5,000 square meters. Integrating R&D, manufacturing, and testing, it is designed to realize the engineering, standardization, and large-scale production of photonic quantum computers, essentially creating an “assembly line” for such devices.
“This plant has the capacity to produce dozens of dedicated photonic quantum computers annually, filling the global gap in large-scale manufacturing in this field,” said Wen Kai, founder and CEO of Boson Quantum.
Photonic Quantum Advantage and Plant’s Manufacturing System
As the name suggests, photonic quantum computing is a technology that leverages the quantum properties of light for computation, and it represents a mainstream quantum computing technology route.
Compared with other technical routes, photonic quantum computing does not require ultra-low temperatures. It also boasts advantages such as a large number of quantum bits, stable operation at room temperature, and long coherence time. Given these merits, it can be engineered for practical use in the short term and stands as an emerging form of commercial quantum computers.
According to incomplete statistics, globally, five quantum computer manufacturing plants have been successively established by companies including Finnish quantum computing firm IQM, European quantum computing service provider Quandela, U.S. quantum computing company IonQ, and French quantum computing enterprise Pasqal. In China, only a small number of quantum computing enterprises have focused on building production lines for core components in the industrial chain, with no large-scale integrated machine manufacturing lines deployed yet.

The newly settled large-scale dedicated photonic quantum computer manufacturing plant in Nanshan District, Shenzhen – the first of its kind in China – has filled this gap. With a total area of about 5,000 square meters, the plant integrates R&D, manufacturing, and testing, and is mainly divided into two functional sections: a Class 10,000 clean production area and a comprehensive supporting service area.
According to Wei Hai, CTO of Boson Quantum, the clean production area is like a “dust-free operating room” for photonic quantum computers. To maintain the stability of quantum states, Boson Quantum has established a five-fold guarantee system, including a personnel purification system, an air purification system, precise microclimate control, special floor design, and standardized operation management.
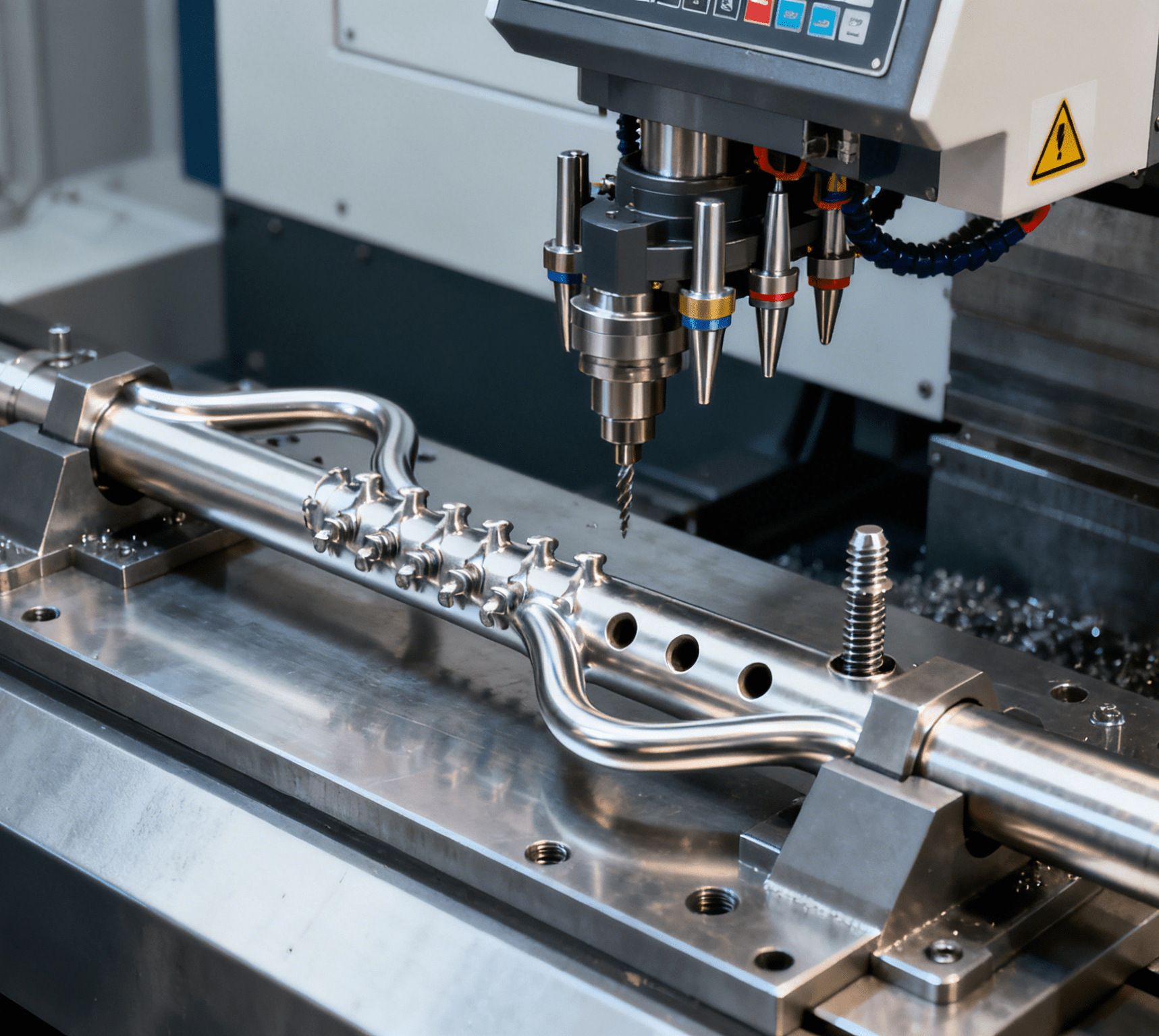
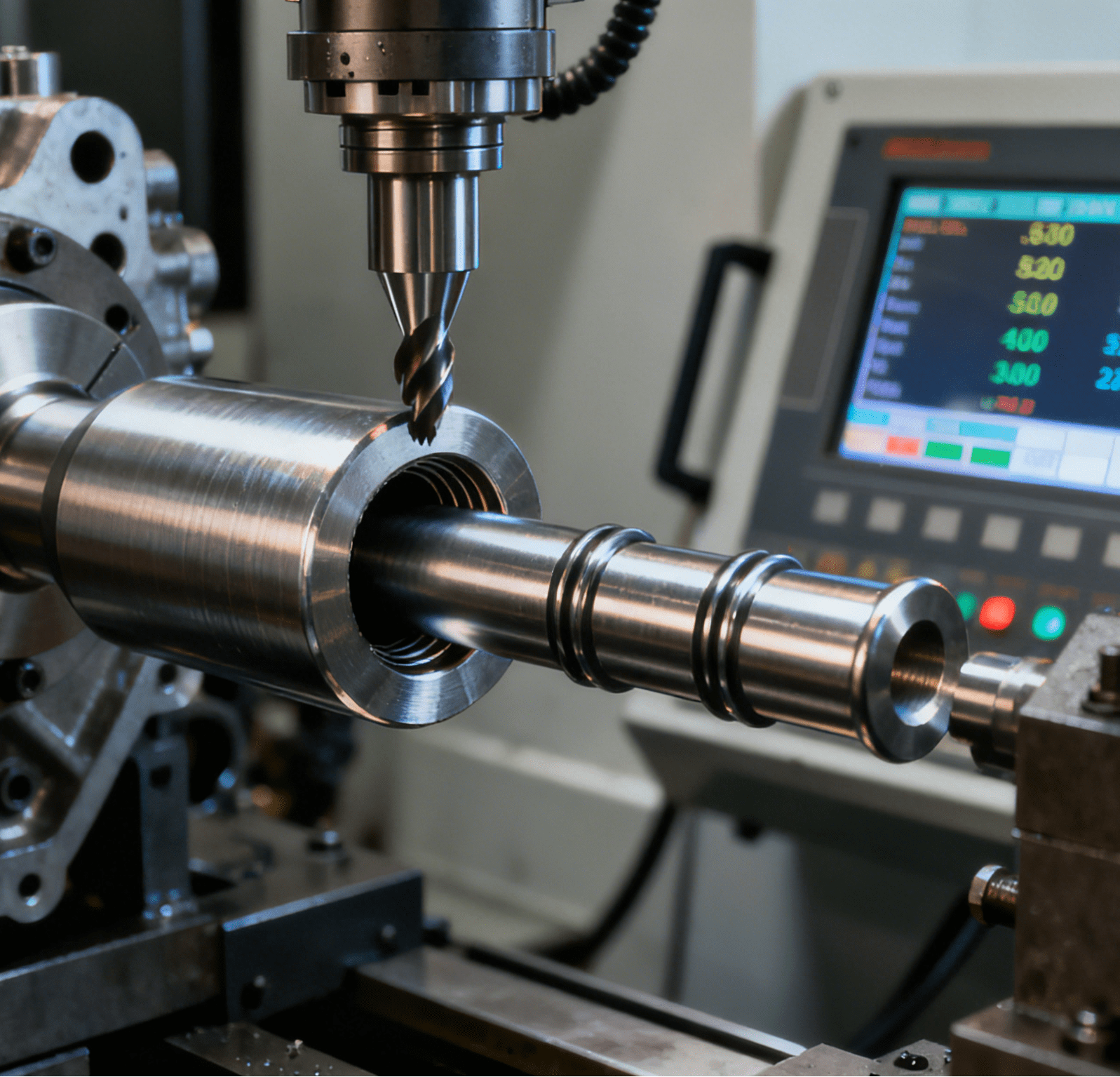
It is reported that the manufacturing process of a photonic quantum computer involves 7 major manufacturing stages, 223 processes, and more than 1,000 work steps. Therefore, the manufacturing plant has set up two core equipment production areas (north and south): the southern area focuses on nanoscale precision alignment and fixation of optical modules, while the northern area is responsible for the integration of quantum bit initialization and reading systems. These two areas work in synergy to form a complete closed-loop core manufacturing process for quantum computers. In the production process, specialized ヒューズ組立機s are also applied to the precision assembly of fuses in core optical modules, ensuring the stable operation of the modules during quantum state transmission.
The plant has also built a robust comprehensive support system, which includes a warehousing and logistics area that manages core spare parts (such as lenses, chips, and optical fibers) under constant temperature and humidity conditions, as well as a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) room that provides millisecond-switching uninterruptible power to eliminate interference from power grid fluctuations on quantum states.
Industry Landscape: Demand Surge and Market Outlook
With the end of the traditional Moore’s Law, AI and big data have put forward higher requirements for computing power, bringing enormous development opportunities to quantum computing. What once only existed in sci-fi movies is gradually “entering the homes of ordinary people”.
The Research Report on the Development Trend of Quantum Computing (2025) shows that in recent years, the number of quantum computing enterprises has continued to grow. As of August 2025, there are over 400 quantum computing enterprises worldwide, among which more than 300 were established after 2014. The United States leads with 107 quantum computing enterprises, followed by China with 42. The number and activity of enterprises in China and the United States are among the highest in the world.
Additionally, according to McKinsey’s forecast, the global quantum technology market size will reach 97 billion U.S. dollars by 2035, among which quantum computing has the greatest potential and will account for the largest share.