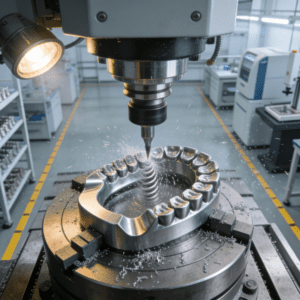
In the field of medical equipment manufacturing, the machining quality of precision spare parts is directly related to the diagnostic accuracy and treatment safety of the equipment. For example, the dimensional error of micro clamping components in surgical instruments or fluid channel parts in laboratory analyzers must be controlled at the micron level to ensure the stable operation of the equipment. As the core components of medical equipment, the market demand for these spare parts is continuously rising with the growth of the global medical and health industry. However, traditional ordinary milling machine processing methods often face bottlenecks such as low efficiency, unstable precision and scattered processes when dealing with such parts with complex contours or high-precision requirements. How to break through these common problems and meet the strict machining standards for medical equipment spare parts? Milling technology is the key technology to solve this dilemma.
Basic Principles and Core Components of Milling Technology
Milling technology realizes precise cutting of parts by controlling the movement of the spindle and worktable of the milling machine through a Computer Numerical Control (CNC) system. Its core components include the control device, spindle system, feed system, worktable and auxiliary parts. The control device controls the rotation speed and direction of the spindle as well as the feed movement of the worktable on the X, Y and Z axes through pre-programmed codes, thus completing the milling of parts. A machining center is an upgraded version of the milling machine, which is equipped with a tool magazine and an Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) to realize automatic tool changing and reduce manual intervention. Some machining centers are also equipped with an automatic indexing rotary worktable, which can machine multiple surfaces after a single workpiece clamping, reflecting the advantage of process concentration.
Comparison Between Milling Technology and Traditional Machining Methods
Traditional ordinary milling machine processing relies on manual operation, with precision greatly affected by the operator’s skill level. In addition, tool changing needs to be completed manually, resulting in low efficiency. For parts with complex contours, traditional processing requires multiple clampings, which is prone to error accumulation and fails to meet the high-precision requirements of medical equipment spare parts. In contrast, milling technology achieves a machining precision of ±0.005mm through program control, and the machining process is stable without being affected by human factors. The automatic tool changing function of the machining center enables continuous multi-process machining, reducing the number of clampings, lowering errors and shortening the production cycle at the same time. For example, a medical part requiring multiple processes may take 3 hours to process with traditional methods, while a machining center can finish it in only 1 hour.
Key Application Scenarios of Milling Technology
Milling technology is widely used in the manufacturing of medical equipment spare parts, life science components and high-end manufacturing fields. In the processing of medical equipment spare parts, it is often used to manufacture parts with complex contours for surgical instruments (such as the occlusal teeth of hemostatic forceps), sample processing modules for laboratory equipment (such as high-precision hole machining) and medical molds (such as syringe molds). In the life science field, milling technology can process microfluidic chip molds, whose micron-level channel structures require high-precision milling technology. In addition, milling technology is also applied in aerospace, automobile manufacturing and other fields, and its application in the medical industry is particularly prominent due to the strict quality requirements.
Core Advantages and Machining Effects of Milling Technology
The core advantages of milling technology include high precision, high efficiency and high adaptability. High precision is reflected in its ability to stably control part dimensional errors and meet the strict standards of the medical industry; high efficiency stems from process concentration and automatic tool changing functions, which reduce production time; high adaptability is manifested in its ability to machine parts with complex contours, such as three-dimensional curved surfaces or irregular shapes. In terms of machining effects, milling technology can reduce the reject rate, improve part consistency and lower labor costs at the same time. For example, after a medical equipment manufacturer adopted milling technology, the reject rate of its spare parts dropped from 5% to 1%, and the production efficiency increased by 40%.
Technical Strength and Customer Cases of Professional Milling Services
To meet the machining needs of medical equipment spare parts, professional milling service providers need to be equipped with highly automated equipment. Their machining centers are fitted with advanced feed servo systems to realize multi-axis linkage and reduce manual intervention. Core components such as spindles and guide rails are made of wear-resistant materials to ensure long-term stable operation and reduce maintenance costs. The R&D team continuously optimizes machining processes and develops special cutting parameters for special materials in the medical industry (such as titanium alloys and stainless steel) to improve machining efficiency and part quality. For example, after a medical equipment manufacturer used professional milling services, the machining precision of its surgical instrument parts was improved by 20%, and the production cycle was shortened by 30%, effectively meeting the market demand for high-quality spare parts.
Market Prospect and Industry Trend of Milling Technology
According to industry reports, the global medical equipment market size is expected to reach 500 billion US dollars in 2025, driving the growth of demand for high-precision spare parts machining. As a key machining technology, the market demand for milling technology will maintain a growth rate of more than 10% annually. At the same time, with the advancement of intelligent manufacturing, milling equipment will develop towards higher precision and greater intelligence, such as integrating AI technology to optimize machining parameters and further improve machining efficiency and quality. In the future, milling technology will play a more important role in the medical industry and become the core technology for high-end spare parts machining.
Key Considerations for Choosing Professional Milling Services
When choosing a professional milling service provider, attention should be paid to the automation level of its equipment, the durability of core components, R&D strength and customer cases. High-automation equipment can ensure machining stability; durable core components can reduce maintenance costs; a strong R&D team can optimize processes for special needs; and customer cases reflect the reliability of its services. For example, the machining centers of a professional provider are equipped with imported spindles with a service life of more than 10 years, and its R&D team has more than 10 years of machining experience in the medical industry and has provided services for many well-known medical equipment manufacturers.
Milling technology, with its characteristics of high precision and high efficiency, has become the core technology for machining medical equipment spare parts. Choosing a service provider with professional strength is the key to ensuring the quality of spare parts and improving production efficiency. In the future, with the progress of industry technology, milling technology will play an important role in more high-end manufacturing fields.