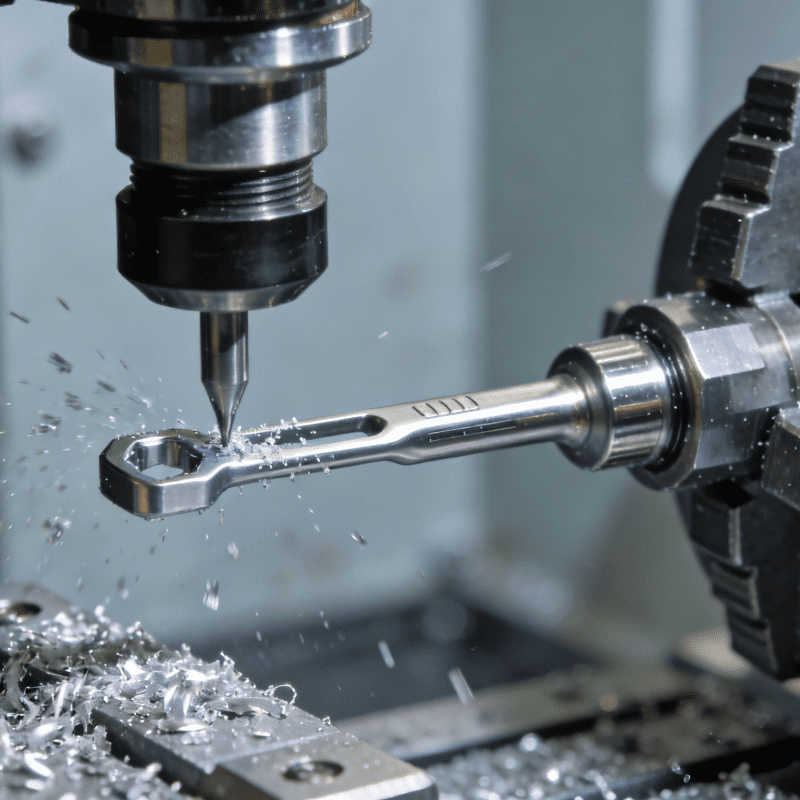
In today’s rapidly evolving precision manufacturing industry, the demand for high-precision components is growing exponentially. As a core foundational process in precision manufacturing, cutting technology directly determines the accuracy, quality, and service life of components. A mechanical processing method that uses cutting tools to shape workpieces, it occupies an indispensable position in precision manufacturing and serves as a crucial link connecting raw materials to finished components, supporting the stable development of numerous high-end industries.
What is Cutting Technology? The Core Processing Method in Precision Manufacturing
Many people view cutting technology merely as “material cutting” on a superficial level, yet it has a rigorous definition and specification within the realm of precision manufacturing. Cutting technology refers to a machining method that utilizes the relative motion between cutting tools (such as turning tools, milling cutters, drills, etc.) and workpieces to remove excess material from the workpiece blank, resulting in a finished product that meets the design requirements for dimensions, shape, surface roughness, and mechanical properties.
Unlike conventional cutting, precision manufacturing cutting technology demands extremely high precision, typically requiring error control at the micrometer or even nanometer level. Its processing relies on high-precision equipment, high-quality cutting tools, and scientific process parameters to ensure that every cutting step is precisely controlled, avoiding any impact on component performance due to processing deviations. This is the core reason why cutting technology is deeply integrated with precision manufacturing.
In simple terms, cutting technology is like “precision carving.” Raw materials are like uncut jade; through the precise “carving” of cutting tools, excess material is removed, ultimately forming qualified products that meet the requirements of precision manufacturing. It is one of the most fundamental and commonly used processing techniques in precision manufacturing.
The Core Functions of Cutting Technology in Precision Manufacturing
The core requirements of precision manufacturing are “high precision, high quality, and high efficiency.” Cutting technology precisely fulfills these three demands, becoming an indispensable core support for the precision manufacturing industry. Its functions are reflected in four key aspects, covering the entire process of precision component machining:
Achieving Accurate Transformation from Raw Materials to Finished ProductsMost raw materials used in precision manufacturing are blanks that cannot be directly put into use. The core function of cutting technology is to complete the accurate transformation of raw materials into finished products. By removing excess material from the blanks through cutting, the workpiece’s dimensions, shape, and surface accuracy are brought into line with design standards, transforming ordinary raw materials into precision components suitable for high-end equipment.
Ensuring the Processing Quality of Precision ComponentsPrecision manufacturing imposes extremely strict requirements on component quality, not only demanding dimensional accuracy but also specifying strict standards for surface roughness and mechanical properties. The level of cutting technology directly determines component quality. High-quality cutting technology effectively controls the surface roughness of workpieces, preventing defects such as scratches and burrs. It also preserves the internal mechanical properties of the workpiece, avoiding component damage or failure caused by stress concentration during processing.
In precision manufacturing, even a 0.1-micrometer processing deviation can render a component unusable. Cutting technology controls processing parameters such as cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth with precision, keeping processing errors within acceptable limits and maximizing the guarantee of component quality.
Enhancing Production Efficiency in Precision ManufacturingWith the large-scale development of the precision manufacturing industry, production efficiency has become a core competitive advantage for enterprises. The optimization of cutting technology can effectively improve production efficiency. Traditional cutting methods are inefficient, whereas modern precision cutting technology, 依托 high-precision automated equipment, enables batch and continuous processing, significantly reducing the processing time for individual components.
Simultaneously, optimizing cutting tools and process parameters reduces tool wear and processing downtime during cutting, lowers the defect rate, and further enhances production efficiency in precision manufacturing. This helps enterprises reduce production costs and improve market competitiveness.
Adapting to the Processing Needs of Diverse Precision ComponentsPrecision manufacturing encompasses a wide variety of components with different shapes, sizes, and precision requirements. Cutting technology exhibits strong adaptability, allowing flexible adjustments to processing methods and parameters based on component needs, thus meeting the processing requirements of diverse precision components.
Whether it is simple cylindrical or planar components, or complex curved or irregularly shaped components, they can all be processed through corresponding cutting techniques (such as turning, milling, grinding, drilling, etc.) without the need to replace core processing equipment. This greatly enhances the flexibility and applicability of precision manufacturing.
Main Application Fields of Cutting Technology in Precision Manufacturing
Thanks to its advantages of precision, efficiency, and strong adaptability, cutting technology is widely used in precision manufacturing, covering multiple core industries in high-end manufacturing. It is an indispensable support in almost all fields involving precision component machining. The following are the four most important application areas:
Aerospace Precision ManufacturingThe aerospace industry imposes the most stringent requirements on precision components, where component accuracy directly relates to the safety and reliability of aerospace equipment. Cutting technology is the core process in precision manufacturing for this field. Key components such as aircraft engine blades, casings, and landing gear are all processed using high-precision cutting technology.(For example, aircraft engine blades have complex shapes and extremely high precision requirements. They must be processed through five-axis milling, grinding, and other cutting technologies to precisely control the surface accuracy and thickness errors of the blades, ensuring the stability of engine operation. Casing components, on the other hand, require turning, boring, and other cutting processes to guarantee their sealing performance and dimensional accuracy—all of which rely on the technical support of cutting technology.)
Automotive Precision ManufacturingAs the automotive industry evolves toward high-end and intelligent development, the demand for precision in automotive components is constantly increasing, leading to a wider application of cutting technology in automotive precision manufacturing. Components such as crankshafts, camshafts, and pistons in automotive engines, gears and shaft components in transmissions, and precision components in braking systems all require processing through cutting technology.(Take automotive transmission gears as an example: their meshing precision directly affects the transmission efficiency and service life of the transmission. Cutting technology such as gear hobbing, gear shaping, and grinding is used to precisely control the tooth profile and pitch errors of the gears, ensuring smooth meshing. This is the key reason why cutting technology is indispensable in automotive precision manufacturing.)
Electronic Precision ManufacturingComponents in the electronics industry are characterized by small size, high precision, and large batch production, imposing extremely high requirements on the accuracy and efficiency of cutting technology, which plays a vital role in electronic precision manufacturing. Components such as chip carriers, connectors, heat sinks, and precision casings of electronic devices all require processing through cutting technology.(For example, the pins of mobile phone connectors are tiny and demand extremely high precision. Micro-cutting technology is used to precisely control the diameter and length errors of the pins, ensuring the conduction performance of the connectors. Electronic heat sinks require processing through milling and cutting technologies to create dense heat dissipation fins, improving heat dissipation efficiency—all of which depend on the precision processing capabilities of cutting technology.)
Medical Device Precision ManufacturingThe safety and accuracy of medical devices directly relate to patients’ lives and health, making the precision manufacturing of medical devices subject to extremely strict requirements for component accuracy and quality. Cutting technology is therefore crucial in this field. Precision components of medical surgical instruments, implantable medical devices, and medical testing equipment are all processed using high-precision cutting technology.(For example, precision surgical scissors and forceps require processing through grinding and polishing technologies to ensure sharp blades and precise dimensions, facilitating the operation of medical professionals. Implantable cardiac stents need to be processed through micro-cutting technology to create slender, precise stent structures, ensuring their proper function after implantation—all of which rely on the technical guarantee of cutting technology.)
Conclusion
In summary, cutting technology is the most fundamental and core processing technique in precision manufacturing. It is not only a key means for transforming raw materials into precision products but also ensures component quality, improves production efficiency, and adapts to diverse processing needs. In precision manufacturing fields such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices, cutting technology plays an indispensable role, supporting the continuous development of the high-end manufacturing industry.
With the continuous advancement of precision manufacturing technology, cutting technology is also evolving toward higher precision, higher efficiency, and greater environmental friendliness. In the future, it will be further deeply integrated with precision manufacturing, driving the development of more advanced cutting technologies and process solutions to provide stronger support for the processing of various high-end precision components and propel the precision manufacturing industry to new heights.
Automation engineering of production lines in the automotive industry
AI production line automation robots in the automotive industry