In modern manufacturing, precision machining technology is one of the core links to ensure product accuracy and quality. With the continuous advancement of technology, precision machining has been widely applied in aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical and other fields. The adoption of different machining processes can meet the requirements of various products for precision, complex shapes and high-efficiency production.
This article will introduce several commonly used processes in precision machining, including their principles, applications and advantages. By understanding these technologies, you will better grasp how they boost production efficiency and machining accuracy.
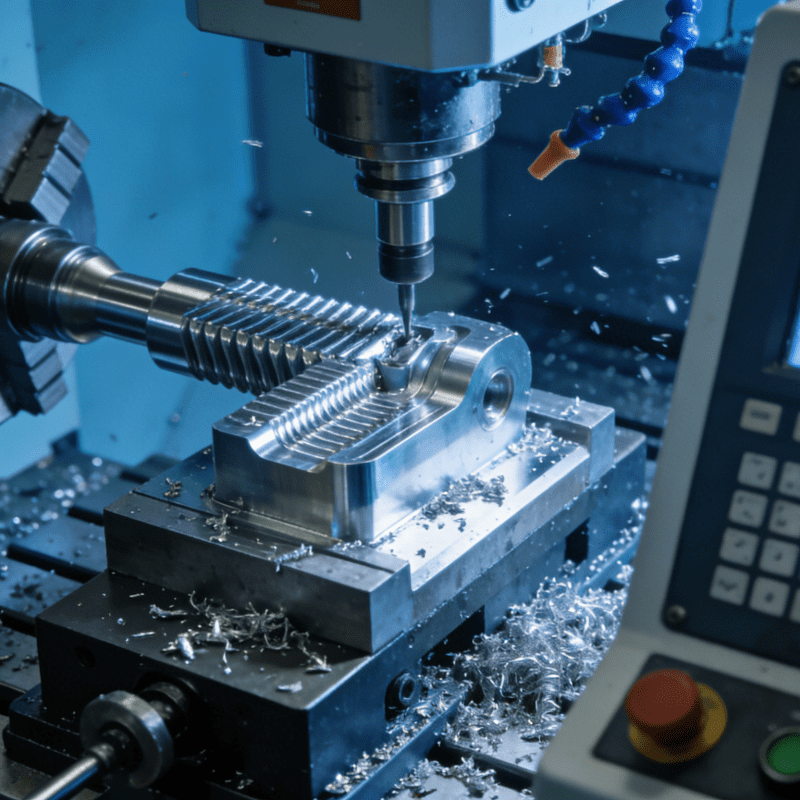
Milling: A Versatile Solution for High Efficiency and Precision
Milling is one of the most common processes in precision machining. It removes excess material by bringing a rotating cutting tool into contact with the workpiece surface, thereby achieving the desired shape and dimensions. Milling is widely used in manufacturing complex shapes such as flat surfaces, slots and gears.
Advantages of Milling
High precision: Milling can achieve extremely high accuracy, typically with micron-level dimensional tolerances.
Flexibility: Applicable to a variety of materials, including metals, plastics and composite materials.
Complex shape machining: Capable of processing intricate geometric shapes such as curved surfaces, spirals and inclined planes.
Common Applications
Machining of mechanical parts
Production of electronic product housings and detailed components
Manufacturing of precision molds
Cutting: Precisely Controlled Material Removal for Metals
Cutting is a machining process that gradually removes excess material by applying force to the workpiece with a cutting tool to achieve the required dimensions and shape. Common cutting methods include turning, milling and drilling. Especially in high-precision applications, cutting can deliver extremely fine machining results.
Advantages of Cutting
Wide applicability: Can process materials of various hardness levels, with particularly strong adaptability to metal materials.
High-precision control: With precision cutting tools and equipment, cutting can meet extremely stringent dimensional and shape requirements.
Excellent surface quality: Cutting produces an ultra-smooth surface, reducing the need for subsequent surface treatment.
Common Applications
High-precision shaft parts
Precision gears and mechanical structural components
Aerospace and automotive parts
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): The Ideal Solution for Hard Materials
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a precision machining method that removes material using the high temperature generated by electric sparks between an electrode and the workpiece. EDM is widely used in manufacturing parts with complex shapes from difficult-to-machine materials, especially high-hardness metals.
Advantages of EDM
Machining of high-hardness materials: EDM can effectively process high-hardness and high-toughness metals such as tool steel and alloy steel.
Complex shape machining: Capable of producing intricate and fine holes, tiny structures and micro profiles.
High fineness: Boasts extremely high machining accuracy with micron-level dimensional precision.
Common Applications
Manufacturing of precision molds
Production of complex parts in the aerospace field
Machining of electrodes and conductive tools
Laser Cutting: High-Speed and Precision Non-Contact Machining
Laser cutting technology locally heats the workpiece to its melting or vaporization point using a laser beam, and blows away the molten material with high-pressure airflow to form a cutting surface. Thanks to its high precision and high speed, laser cutting has been widely used in precision machining.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
High precision: Laser cutting can achieve ultra-high cutting accuracy, even at the micron level.
Non-contact machining: As a non-contact process, laser cutting avoids mechanical stress and reduces workpiece deformation.
High processing speed: Faster than traditional mechanical cutting methods, making it suitable for mass production.
Common Applications
Cutting and forming of precision parts
Machining of small components in the electronics industry
Production of high-precision metal parts in the aerospace field
3D Printing: Additive Manufacturing with High Design Freedom
3D printing (additive manufacturing) is an emerging technology in the field of precision machining in recent years. It forms parts by stacking materials layer by layer in accordance with computer-designed drawings. Breaking through the limitations of traditional machining methods, it is particularly suitable for manufacturing complex structures and small-batch customized products.
Advantages of 3D Printing
High design freedom: Capable of producing extremely complex geometric shapes, including internal cavities and intricate structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining.
Tool-free production: Unlike traditional machining, 3D printing requires no molds or tools, reducing manufacturing costs.
Advantages for small-batch production: Ideal for customization and small-batch production, especially in the product R&D and prototyping stages.
Common Applications
Prototyping of complex structures
Customized manufacturing of medical devices
Production of parts in the aerospace field