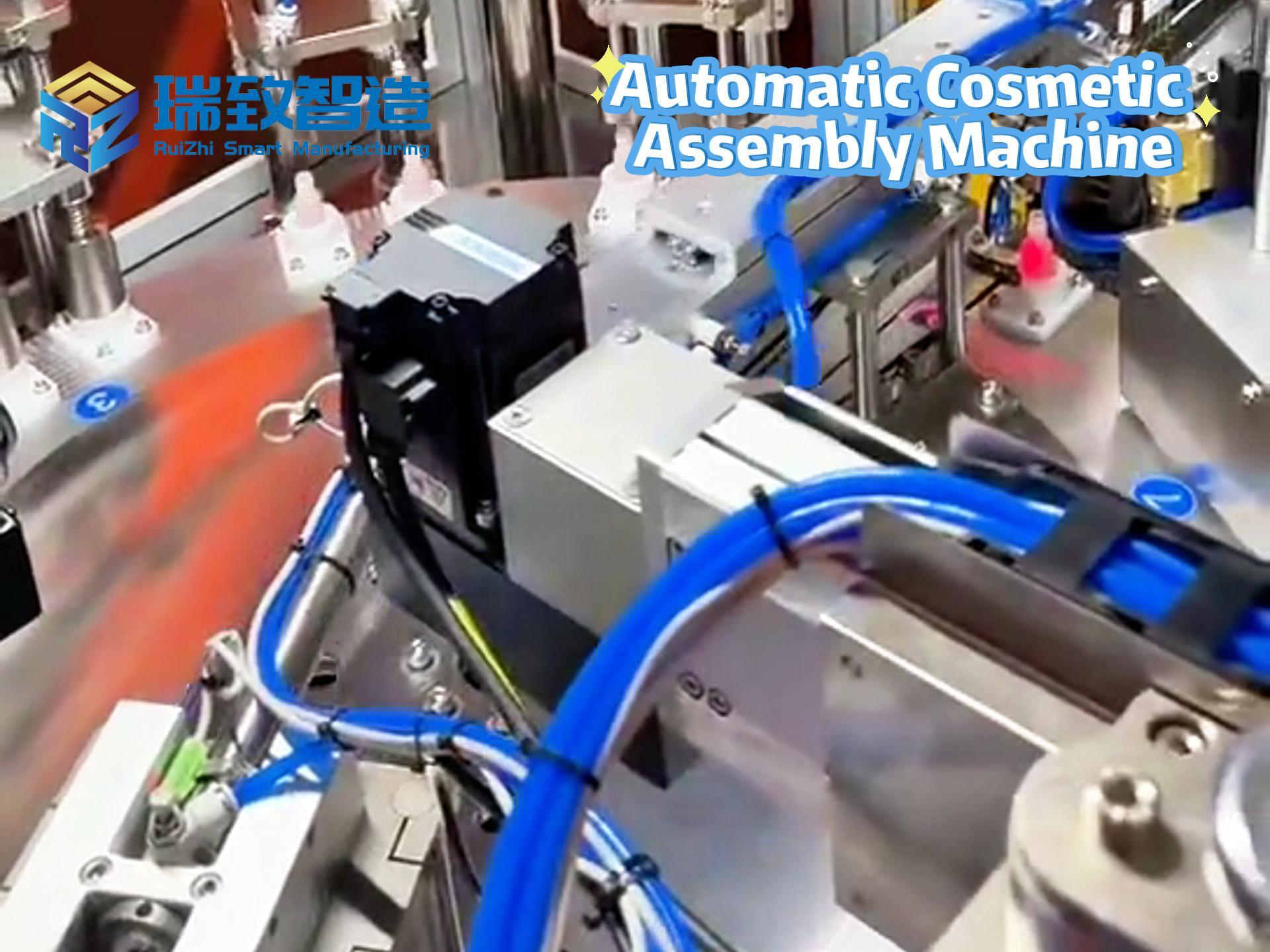
China’s Industrial Robots: From Mechanical Arms to Intelligent Automation Powerhouses
In a 20,000-square-meter overseas warehouse, 700 autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) from Geekplus zip across the floor at two meters per second, exemplifying how intelligent automation is reshaping global logistics. These robots, synchronized with multifunctional workstations, have ditched the traditional “man-to-goods” model, instead moving shelves autonomously to robotic arms that pick items with precision. This isn’t just a showcase of automation equipment; it’s a testament to China’s rise in transforming industrial robots into “all-rounders” capable of AI-driven coordination, real-time decision-making, and cross-industry adaptability.
Gone are the days when industrial robots were confined to repetitive tasks on assembly lines. Driven by advancements in AI and industrial automation, Chinese manufacturers like Midea, Estun, and Geekplus are pushing robots beyond mere mechanical functionality. At Midea’s Lyceem Lab, KUKA six-axis robots undergo rigorous endurance tests, swinging weights to validate durability—a process that mirrors how intelligent automation merges brute force with precision. Meanwhile, in GAC Group’s welding workshop, Estun’s 700-kilogram-payload robots seamlessly switch between welding and handling, achieving a 100% pass rate through AI-optimized workflows. These machines aren’t just tools; they’re strategic assets in China’s mission to lead the fourth industrial revolution.
Innovation Beyond Borders: From Heavy-Duty to Hyper-Precision
China’s robotic evolution spans sectors, from heavy machinery to delicate electronics. In Hubei, Midea’s humanoid robots inspect and maintain washing machine factories, while JAKA’s collaborative robots at Hannover Messe demonstrate ultra-gentle grip capabilities, even handling potato chips without damage. This versatility highlights how automation equipment is being reimagined through AI: heavy-duty robots like EFORT’s 220-kilogram-load models tackle industrial might, while agile AMRs like Geekplus’ fleet optimize logistics with swarm intelligence, managing over 5,000 robots via a single system.
Statistics underscore China’s dominance: 556,400 industrial robots produced in 2024 (up 14.2% year-on-year), with 51% of global installations in 2023. Beyond automotive and electronics, robots are penetrating new energy, ceramics, and furniture manufacturing—proof that industrial automation is no longer niche but a cornerstone of general-purpose industries.
The Future: AI as the Core of Intelligent Automation
As Chen Feng of KUKA China notes, the next frontier is “AI-built-in” robots that require no manual customization. Imagine plug-and-play machines with one-click installation, predictive maintenance, and self-optimizing workflows—standards that are swiftly becoming reality. Geekplus’ partnership with Siemens and CATL to develop intelligent logistics systems exemplifies this shift: robots aren’t just deployed; they’re integrated into broader intelligent automation ecosystems, learning from real-time data to adapt to changing demands.
Conclusion: Redefining Industrial Automation for a Smarter World
China’s industrial robots are no longer mere extensions of human labor—they’re catalysts for a new era of intelligent automation. By fusing AI with automation equipment, these machines are solving challenges from labor shortages to supply chain complexity, all while driving efficiency and precision. As they evolve from specialized tools to “all-rounders” capable of autonomous decision-making, they’re not just transforming factories; they’re rewriting the rules of global manufacturing. In China, the future of industry isn’t just automated—it’s intelligent, adaptive, and ready to tackle the next generation of challenges.