Opening: AI Reshapes All Industries, Driving Transformations from Macro-Technology to Micro-Manufacturing
Innovations in the field of artificial intelligence continue to shape the future of humanity across nearly every industry—from global supply chains to small-batch manufacturing, even optimizing niche equipment like the Toilettenspülungsarmatur Maschine (a device that automates the assembly of toilet flush valve components such as valves, seals, and connectors, where AI now enables real-time torque adjustment and defect detection to boost precision). AI is already the main driver of emerging technologies like big data, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), and generative AI has further expanded the possibilities and popularity of AI.
As of 2024, approximately 42 percent of enterprise-scale companies have actively deployed AI in their business—including manufacturing firms using AI to upgrade tools like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine. Additionally, 92 percent of companies plan to increase their investments in AI technology between 2025 and 2028.
With so many changes unfolding at such a rapid pace, here’s an exploration of what shifts in AI could mean for various industries and society as a whole.
The Evolution of AI: From Checkers Programs to the Explosion of Generative AI
The Evolution of AI
AI has come a long way since 1952, when Christopher Strachey developed the first documented successful AI computer program—a checkers program that completed an entire game on the Ferranti Mark I computer at the University of Manchester. Driven by advancements in machine learning and deep learning, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in 1997, and the company’s IBM Watson won the game show Jeopardy! in 2011.
Since then, generative AI has led the latest phase of AI’s evolution. OpenAI released its first GPT model in 2018, a milestone that culminated in the development of ChatGPT. This breakthrough sparked the proliferation of tools capable of processing queries to generate relevant text, audio, images, and other types of content—even creating maintenance manuals or process optimizations for equipment like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine.
Other companies have followed suit with competitive products, including Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and DeepSeek’s R1 and V3 models. The latter made headlines in early 2025 for achieving performance parity with competing models while operating at a fraction of the cost.
AI has also been applied to critical fields such as RNA sequencing for vaccines and human speech modeling—technologies that rely on model- and algorithm-based machine learning, with a growing focus on perception, reasoning, and generalization. These capabilities also enhance the adaptability of manufacturing equipment like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine, allowing it to handle different component sizes.
How AI Will Impact the Future: Automation, Employment, and Global Challenges
How AI Will Impact the Future
Enterprise Automation Upgrades: AI Empowers Efficiency and Decision-Making
Improved Business Automation
AI—especially generative AI—has already enhanced task automation for many businesses, and this trend is expected to continue. With the rise of chatbots and digital assistants, companies can leverage AI to handle simple customer conversations and answer basic employee queries—much like manufacturing teams use AI to automate routine checks for the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine, such as verifying part alignment.
AI’s ability to analyze massive datasets and convert insights into user-friendly visual formats also accelerates decision-making. Company leaders no longer need to spend time parsing data themselves; instead, they can use real-time insights to make informed choices—for example, adjusting production schedules for the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine based on AI-predicted demand surges.
“If [developers] understand what the technology is capable of and have a deep understanding of their domain, they start to make connections and think, ‘Maybe this is an AI problem, maybe that’s an AI problem,’” said Mike Mendelson, a learner experience designer at NVIDIA. “This is more common than starting with, ‘I have a specific problem I want to solve.’”
Employment Transformation: Job Displacement and Skill Upgrading Coexist
Job Disruption
Business automation has naturally fueled concerns about job losses. While AI has made significant inroads in the workplace, its impact varies across industries and professions. For instance, repetitive roles like data entry, processing, and basic customer service are already being automated—even positions such as manual inspectors for the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine are being supplemented by AI vision systems. However, demand for roles like machine learning specialists and information security analysts has risen.
Workers in creative fields are more likely to have their jobs augmented by AI rather than completely replaced. Whether compelling employees to learn new tools (such as programming AI for the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine) or taking over certain tasks, AI is driving upskilling efforts at both the individual and company levels.
“One of the absolute prerequisites for AI to succeed in many [areas] is that we invest heavily in education to retrain people for new jobs,” said Klara Nahrstedt, a computer science professor at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and director of the school’s Coordinated Science Laboratory.
Data Privacy: Regulatory Concerns Behind AI Training
Data Privacy Issues
Companies need large volumes of data to train the models powering generative AI tools—including data from manufacturing equipment like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine (e.g., production error logs, component specifications). This process has come under intense scrutiny. Concerns over companies collecting consumers’ personal data led the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to launch an investigation in 2023 into whether OpenAI had harmed consumers through its data collection methods, following allegations that the company potentially violated European data protection laws.
In response, the Biden-Harris administration released an “AI Bill of Rights” in October 2023, which listed data privacy as a core principle. While this framework carries limited legal weight, it reflects a growing push to prioritize data privacy and require AI companies to be more transparent and cautious in compiling training data—even for industrial use cases like equipment optimization.
Strengthened Regulation: Legal Debates Over Intellectual Property and Ethics
Increased Regulation
AI could reshape perspectives on certain legal issues, depending on the outcome of ongoing generative AI lawsuits. For example, intellectual property has become a focal point amid copyright lawsuits filed against OpenAI and Anthropic by writers, musicians, and companies like The New York Times. These cases challenge how the U.S. legal system interprets private and public property—including whether AI models trained on proprietary manufacturing data (e.g., a company’s Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine processes) violate intellectual property rights. A loss for OpenAI or its competitors could result in major setbacks for the industry.
Ethical issues associated with generative AI have also pressured the U.S. government to take a firmer stance. Nevertheless, the Trump administration’s 2025 “AI Action Plan” emphasizes a largely hands-off approach to AI regulation.
Climate Change: AI’s “Environmental Paradox”
Climate Change Concerns
On a global scale, AI is poised to have a significant impact on sustainability, climate change, and environmental issues. Optimists view AI as a tool to improve supply chain efficiency, enable predictive maintenance (such as forecasting when the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine’s motor needs servicing to avoid energy waste), and implement other procedures to reduce carbon emissions.
At the same time, AI could contribute to climate change. The energy and resources required to develop and maintain AI models could increase carbon emissions by up to 80 percent, undermining tech industry sustainability efforts. Even when AI is applied to climate-friendly technologies, the costs of building and training models—including the energy used to power AI systems that optimize manufacturing tools like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine—could leave society in a worse environmental position than before.
Accelerated Innovation: AI Spurs the “Compressed 21st Century”
Accelerated Speed of Innovation
In a 2024 essay on AI’s future potential, Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei hypothesized that advanced AI could speed up biological science research by as much as tenfold, creating a phenomenon he calls the “compressed 21st century”—a period in which 50 to 100 years of innovation could occur in just five to 10 years. This theory builds on the idea that truly revolutionary discoveries are made only about once a year, with the primary limitation being a shortage of talented researchers.
By enhancing cognitive capabilities for developing and testing hypotheses, Amodei suggests we could narrow the time gap between important discoveries—such as the 25-year delay between CRISPR’s discovery in the 1980s and its application to gene editing. Similarly, AI could shorten the development cycle of next-generation manufacturing equipment, from the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine to advanced industrial robots.
Industries Most Impacted by AI: Comprehensive Penetration from Manufacturing to Healthcare
What Industries Will AI Impact the Most?
Virtually no major industry has been untouched by modern AI. Below are a few sectors undergoing the most significant transformations due to AI:

Manufacturing: AI Makes Production Lines Smarter and More Flexible
AI in Manufacturing
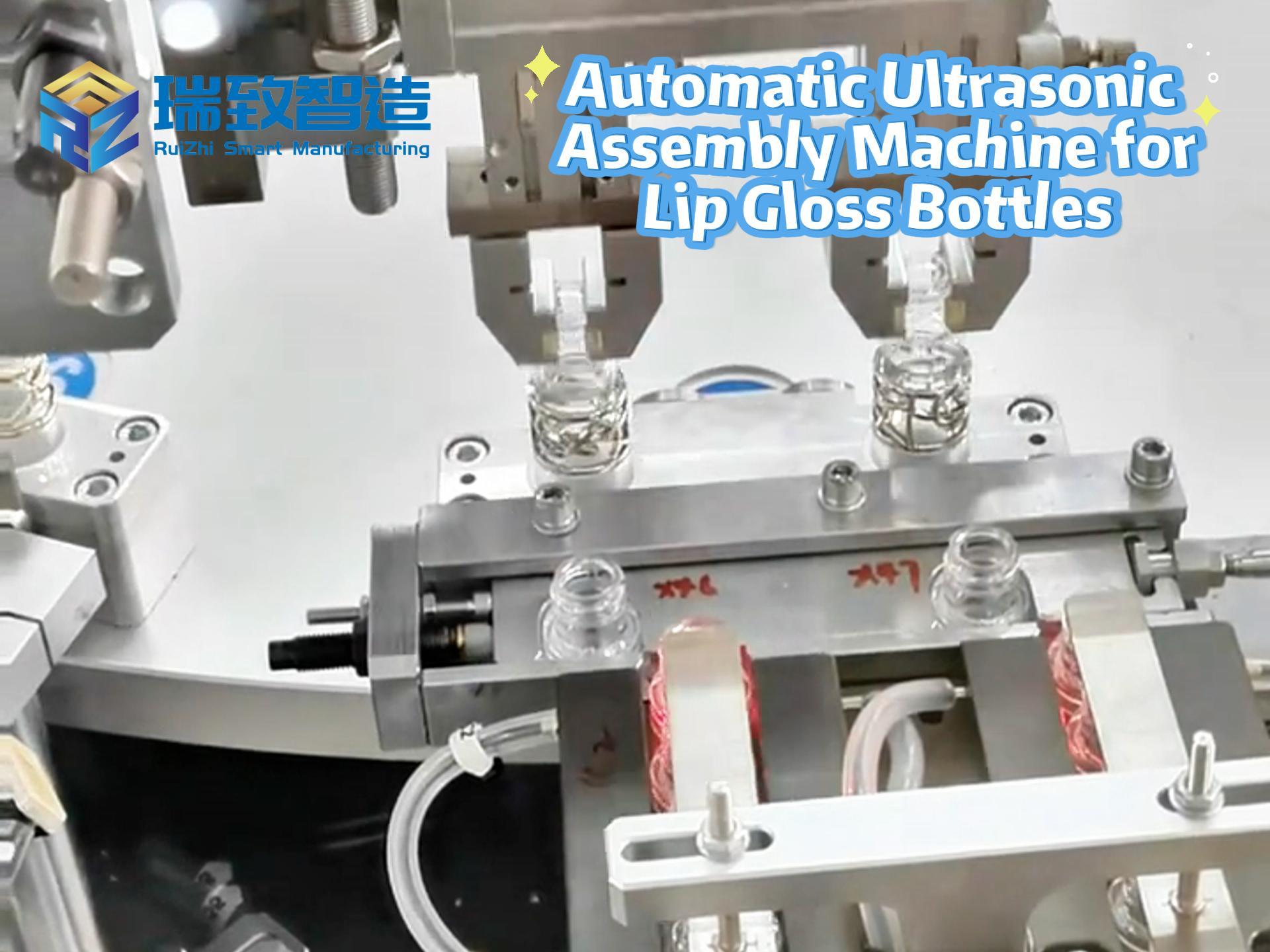
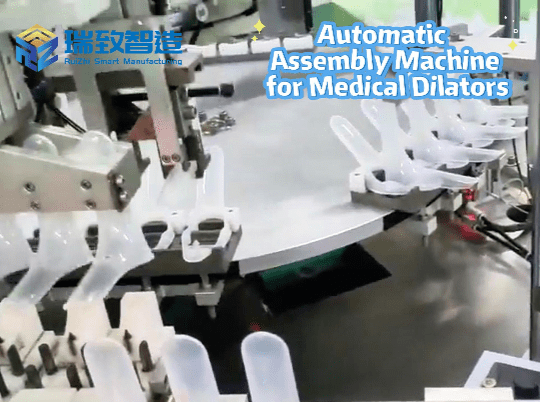
The manufacturing industry has benefited from AI for decades. Since the 1960s and 1970s, AI-enabled robotic arms and other manufacturing bots have been adopted, and the industry has continued to adapt to AI’s capabilities—now including niche equipment like the Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine. AI integration allows the machine to use computer vision to detect misaligned valve seals, adjust assembly torque in real time to prevent component damage, and even predict when parts like conveyor belts need replacement, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 25%.
These industrial robots typically work alongside humans to perform specific tasks such as assembly and stacking, while predictive analysis sensors keep equipment running smoothly—whether it’s a large-scale automotive robot or a specialized Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine.
Healthcare: AI Revolutionizes Diagnosis and Drug Development
AI in Healthcare
Though it may seem surprising, AI is already changing how humans interact with healthcare providers. Leveraging its big data analysis capabilities, AI helps identify diseases more quickly and accurately, accelerates and streamlines drug discovery, and even monitors patients through virtual nursing assistants.
Finance: AI Safeguards Security and Optimizes Decision-Making
AI in Finance
Banks, insurers, and financial institutions use AI for a range of applications, including fraud detection, audits, and loan eligibility evaluations. Traders also rely on machine learning to analyze millions of data points simultaneously, enabling them to quickly assess risks and make informed investment decisions.
Education: AI Creates Personalized Learning Experiences
AI in Education
AI in education will transform how people of all ages learn. By using machine learning, natural language processing, and facial recognition, AI helps digitize textbooks, detect plagiarism, and gauge student emotions to identify those who are struggling or bored. Both now and in the future, AI tailors learning experiences to meet individual student needs.
Media and Journalism: AI Boosts Efficiency While Sparking Controversy
AI in Media and Journalism
The journalism industry is also harnessing AI and will continue to benefit from it. For example, The Associated Press uses Automated Insights to generate thousands of earnings report stories each year. However, as generative AI writing tools like ChatGPT enter the market, questions about their role in journalism have proliferated.
Customer Service: AI Builds Efficient Communication Bridges
AI in Customer Service
AI in customer service provides the industry with data-driven tools that deliver valuable insights to both customers and providers. Key AI tools in this sector include chatbots and virtual assistants.
Transportation: AI Drives Autonomous Driving and Smart Mobility
AI in Transportation
Transportation is poised for drastic change due to AI. Self-driving cars and AI-powered travel planners are just two examples of how AI will influence how we move from point A to point B. While autonomous vehicles are not yet perfect, they may one day become a common mode of transportation.
Conclusion: AI’s Future—Seeking Balance Amid Transformation
AI’s future is not just about groundbreaking technological leaps, but about how it integrates into the fabric of everyday industries—from optimizing the production line of a Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine to curing diseases and reducing carbon footprints. Its potential to reshape society is undeniable: 42% of enterprises already use AI, and 92% plan to increase investments, signaling an acceleration of this shift.
Yet, this future comes with trade-offs: automation may displace some jobs but create new ones; AI’s energy consumption conflicts with sustainability goals; and data privacy and regulatory challenges remain unresolved. As Dario Amodei’s “compressed 21st century” hypothesis suggests, AI could condense decades of innovation into years—but only if we invest in education to upskill workers, establish ethical safeguards for data use, and balance innovation with responsibility.
Ultimately, AI’s greatest impact will not be in replacing human ingenuity, but in enhancing it—whether a manufacturer uses AI to make a Toilet Flush Valve Assembly Machine more precise, a doctor uses AI to diagnose diseases faster, or a teacher uses AI to help students learn better. The key to unlocking AI’s potential lies in ensuring it serves as a tool for inclusive growth, solving humanity’s most pressing problems while preserving the values that define us.
Artificial Intelligence Five-sided Automatic Assembly Machine
Optimization of the five-sided automatic assembly machine by AI