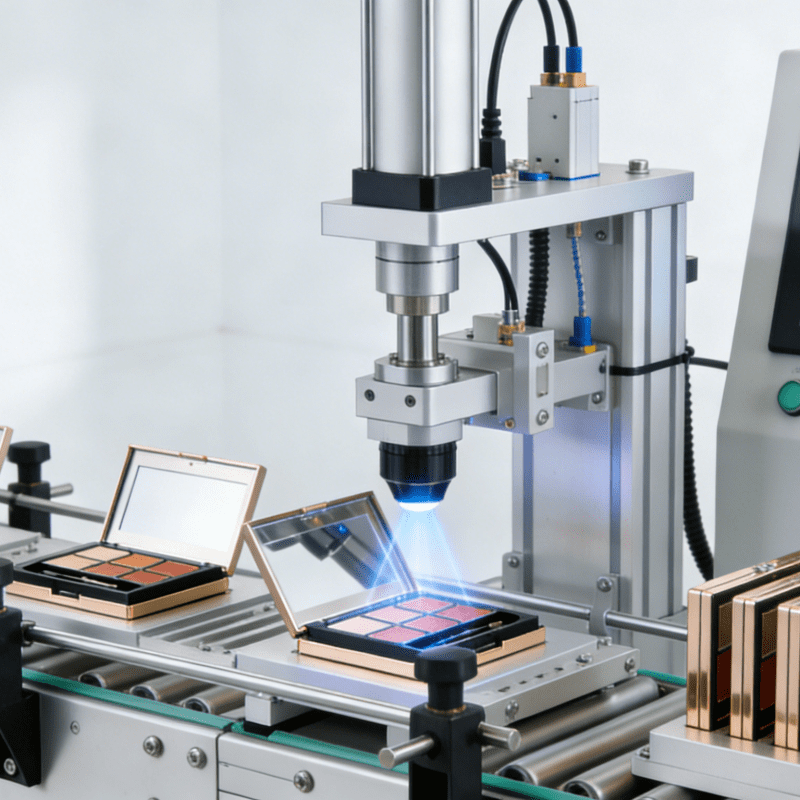
When AI can not only “read medical images” but also “issue test orders, conduct follow-ups, and arrange schedules”; when it generates a draft decision including genomics and clinical trial matching degree in just 30 seconds at an oncology MDT (Multidisciplinary Team) meeting, with doctors only needing to click “confirm” or “revise” — we have entered the era of “Agent Healthcare”. In 2026, practical applications in Guangdong, Shenzhen, and Stanford School of Medicine have shown that AI agents cut the time for early screening of Alzheimer’s disease from 30 minutes to 5 minutes, transformed the “one hospitalization wears out the whole family” situation of inpatient care into “nurse-AI collaboration”, and shortened the duration of edentulous jaw implant restoration from 3–5 days to 3–5 hours. This 3,000-word article breaks down the 6 core roles, 4-step implementation methods, and 1 ROI checklist of “agents” in the healthcare value chain, providing hospital presidents, information technology directors, and entrepreneurs with a guide to “turn AI into a new colleague”.
AI Agents vs. Traditional AI: From “Functions” to “Colleagues”
Traditional medical AI is mostly a “single-point function”: input a CT scan, and it outputs a nodule probability. In contrast, an AI agent has four core capabilities — perception, reasoning, action, and memory — enabling it to continuously “operate” throughout the diagnosis and treatment process:
Perception: Real-time access to PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System), LIS (Laboratory Information System), HIS (Hospital Information System), and wearable devices.
Reasoning: Invokes large language models, knowledge graphs, and clinical guidelines.
Action: Can issue test orders, send follow-up text messages, and adjust work schedules.
Memory: Records patient data over 30 days, doctor preferences, and department KPIs, then automatically optimizes its performance next time.
The result: Doctors no longer “click on AI”; instead, they “work side by side with AI”.
Six Core Roles of AI Agents in the Healthcare Value Chain
Accelerator for Cognitive Screening
The SMART System developed by Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University collects eye movement, gait, and micro-expression data through a 5-minute interactive game. The AI agent instantly generates an early screening report for Alzheimer’s disease with 90% accuracy, and has been rolled out in 36 communities and 298 elderly care institutions in Guangzhou.
Ghostwriter for Medical Documentation
Also at Zhujiang Hospital, an AI language model agent replaces doctors in writing admission records and postoperative summaries, reducing the time spent on each medical record from 25 minutes to 5 minutes, allowing doctors to finish work before 4:00 p.m.
New Caregiver for Inpatient Support
The “Beixiaohu” Unattended Care Agent developed by Peking University Shenzhen Hospital integrates nursing data from 158,000 patients. It automatically generates care plans, alerts the risk of pressure ulcers, and sends videos to family members, solving the problem of “one hospitalization wearing out the whole family”.
Gatekeeper for Surgical Safety
The “Beixiaohui” Perioperative Agent constructs a full-process risk profile. It predicts bleeding probability before surgery, reminds medical staff of antibiotic time limits during surgery, and tracks VTE (Venous Thromboembolism) risks after surgery, reducing the surgical complication rate by 1.2 percentage points.
Navigator for Precision Implantation
The dental multi-agent system can complete 3D position acquisition of edentulous jaw implants and restoration design within 3 hours, shortening the denture delivery time from 3–5 days to 3–5 hours, and significantly improving the nutritional status of elderly patients.
Secretary for Oncology MDT Meetings
The Healthcare Agent Orchestrator developed by Stanford School of Medicine can read medical images, pathology reports, genomics data, and clinical trial databases in 30 seconds, and automatically generate a report including mutation targets and trial matching degrees. Doctors only need to click “accept” or “revise”, and the system can serve 4,000 cancer patients annually on average.

Technical Architecture: The Four-Layer Closed Loop That Enables AI Agents to “Operate Continuously”
Multimodal Data Lake
Medical images, pathology reports, genomics data, wearable device data, and HIS data are integrated into a unified data lake, labeled with the HL7-FHIR standard, and support three-dimensional indexing of “patient-time-body part”.
Edge Intelligence Nodes
20 TOPS edge computing boxes are deployed in operating rooms and CT rooms, running lightweight large models with 8 billion parameters. They can perform reasoning even offline, with a latency of less than 200 ms.
Digital Twin Workflow
The entire process of “outpatient consultation-inpatient admission-surgery-follow-up” is divided into more than 200 atomic tasks, each bound to a dedicated AI agent.
Task: Preoperative assessment
Input: EHR (Electronic Health Record) + medical images + laboratory tests
Agent: VTE Risk Agent
Output: Risk score + recommendations + medical order template
Continuous Reinforcement Learning
Every time a doctor clicks “revise”, the system records the “doctor-agent discrepancy” and updates the model weights using RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback), achieving the effect of “the more the department uses it, the better it understands the department’s needs”.
Risk Management and Governance
Hallucination Risk: A dual-interception mechanism of “knowledge graph + confidence threshold” is adopted; results with a confidence level below 85% require mandatory manual review.
Data Security: On-premises deployment of large models is implemented, and reasoning logs are stored on the blockchain to prevent tampering.
Liability Attribution: Hospitals, AI companies, and doctors sign a “joint liability agreement”. The maximum liability of the AI is capped at the equipment purchase price, and doctors retain the final decision-making power.
Conclusion
An AI agent is not just a smarter “tool”; it is a self-evolving “colleague”. It breaks down doctors’ repetitive mental work into 200 automatable tasks, turning the “30% of time saved” into seeing more patients, performing more surgeries, or spending an extra hour with family. In 2026, whoever first equips AI agents with “hospital ID cards” will be able to move AI’s TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) from the cost sheet to the profit sheet. Now, let the first AI colleague write a medical record, and start your “Agent Healthcare” era.