In the era of the Internet of Things, sensors are the “nerve endings” of intelligent systems—from the fingerprint recognition under our fingertips to the temperature monitoring in smart factories, from the heart rate detection in wearable devices to the environmental sensing in autonomous vehicles, nearly all intelligent interactions rely on high-performance sensors. Behind the mass production of these precision components, the sensor printing and packaging machine has emerged as a key equipment, integrating the two critical processes of sensor core circuit manufacturing and protective packaging, and becoming a cornerstone of the sensing industry’s leap forward.
What is a Sensor Printing and Packaging Machine?
As the name suggests, this equipment integrates two core functions: sensor printing and sensor packaging, forming a one-stop production line.
Sensor printing: Focuses on the manufacturing of the sensor’s “core sensing layer”. Depending on the sensor type (such as pressure, temperature, or optical sensors), it uses technologies like screen printing, inkjet printing, or laser etching to precisely deposit functional materials (conductive inks, semiconductor materials, or sensitive films) onto substrates (ceramic, glass, or flexible polymers). For example, in flexible pressure sensors used in smart gloves, the machine prints a grid of conductive silver paste with a precision of ±5μm to ensure uniform pressure response.
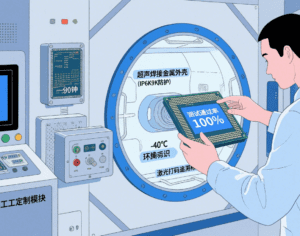
Sensor packaging: Focuses on protecting the “core” after printing. It involves sealing, encapsulating, and labeling the sensor to isolate it from external factors such as dust, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical stress. For automotive sensors, the packaging process may include ultrasonic welding of metal casings to achieve IP6K9K-level dust and water resistance; for medical wearable sensors, it uses sterile film sealing to meet biocompatibility standards.
Core Technologies: Precision, Adaptability, and Intelligence
The sensor printing and packaging machine is not a simple combination of two processes, but a system engineering integrating multiple cutting-edge technologies, which directly determines the performance and yield of sensors.
- Ultra-precision printing control
Sensors, especially micro-sensors, have extremely high requirements for the accuracy of the sensing layer. For example, the electrode line width of a micro pressure sensor for smartphones is only 20-50μm, equivalent to 1/3 of a human hair. The machine achieves this through:
High-precision motion platforms with positioning accuracy up to ±1μm, ensuring that the printing head and substrate do not shift during high-speed movement.
Adaptive ink supply systems that adjust the flow rate and viscosity of conductive inks in real-time according to ambient temperature and humidity, avoiding defects like “line breaks” or “burrs”.
- Multi-material and multi-substrate compatibility
Sensors are increasingly diversified in materials—from rigid ceramic substrates for industrial sensors to flexible PI films for wearable devices, and even biodegradable materials for environmental sensors. The machine must adapt to this diversity:
Modular printing heads: Replaceable nozzles or screens can handle materials ranging from high-viscosity silver paste to low-surface-tension semiconductor inks.
Temperature-gradient drying systems: After printing, different substrates (such as heat-sensitive polymers vs. high-temperature-resistant ceramics) are dried at precise temperatures (30°C-150°C) to ensure material stability without damaging the substrate.
- Intelligent quality control and closed-loop adjustment
A tiny defect (such as a 1μm air bubble in the conductive layer) can cause a sensor to fail. The machine is equipped with a “visual + data” dual inspection system:
High-speed cameras (up to 10,000 frames/second) capture printing details, and AI algorithms automatically identify defects like uneven thickness or missing prints.
Real-time feedback to the printing module: If a defect is detected, the system adjusts parameters such as printing pressure or ink supply within 0.1 seconds, reducing the scrap rate from over 5% (in manual processes) to less than 0.5%.
- Flexible packaging customization
Different application scenarios demand vastly different packaging requirements. The machine achieves “one machine for multiple purposes” through:
Quick-change packaging modules: Switch between ultrasonic welding (for metal casings), hot-press sealing (for plastic films), and laser marking (for traceability codes) in 5-10 minutes.
Environmental simulation testing: Built-in small-scale climate chambers simulate high temperature (85°C), low temperature (-40°C), and high humidity (95% RH) environments to verify packaging reliability before mass production.
Application Scenarios: From Consumer Electronics to Industrial Sensing
The sensor printing and packaging machine’s versatility makes it a “multi-tasker” across industries, empowering the mass production of high-performance sensors.
Consumer electronics: In smartphone camera modules, the machine prints infrared cut-off filters with nanoscale precision and packages them in anti-reflective casings, ensuring clear imaging even in strong light. For TWS earphone touch sensors, it uses flexible printing technology to fit the curved surface of the earphone shell, and then seals it with waterproof glue to resist sweat erosion.
Automotive electronics: Automotive radar sensors (used in adaptive cruise control) require packaging to withstand vibration, high temperatures, and electromagnetic interference. The machine uses laser welding to seal the sensor in an aluminum alloy casing and prints conductive gaskets to achieve EMI shielding, ensuring stable operation for 10+ years.
Industrial IoT: In smart factories, pressure sensors for pipeline monitoring need to resist corrosion from chemicals. The machine prints a PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) protective layer on the sensor surface and packages it in a stainless steel shell, enabling long-term use in harsh environments.
Medical health: Disposable blood glucose sensors require sterile packaging to avoid cross-contamination. The machine integrates a Class 8 cleanroom-level printing environment and uses gamma-ray-sterilized packaging films, ensuring that each sensor meets ISO 13485 medical device standards.
The Industry Value: Accelerating the Sensing Revolution
The popularization of sensor printing and packaging machines is reshaping the sensor industry in three key ways:
Efficiency leap: Traditional processes require separate printing, drying, and packaging workshops, with material transfer accounting for 30% of production time. The integrated machine shortens the production cycle by 50%, enabling a single line to produce 50,000+ sensors per day.
Cost reduction: Automation reduces manual operations by 80%, and intelligent defect detection cuts material waste by 70%. For mass-produced consumer sensors (such as smartwatch heart rate sensors), the unit cost can be reduced by 20-30%.
Driving innovation: By supporting flexible substrates and micro-printing, the machine has accelerated the commercialization of new sensors—such as ultra-thin skin-attachable temperature sensors (only 0.1mm thick) and stretchable strain sensors for sports equipment.
As the “sensing economy” continues to expand, the sensor printing and packaging machine will not only be a production tool but also a “technology translator”—turning laboratory innovations (such as self-healing sensor materials) into mass-produced products. In the future, with the integration of 5G and digital twins, these machines may even achieve “remote debugging + predictive maintenance”, further lowering the threshold for high-end sensor manufacturing. For a world increasingly dependent on intelligent sensing, this equipment is not just about production—it is about building the foundation of a smarter future.