In high-end manufacturing, aerospace, electronic equipment and other fields, the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of precision components directly determine the performance of end products. As a core technical means to achieve precision component machining, precision machining relies on digital control and accurate execution capabilities, and provides support for the stable batch production of precision components through standardized and modular process combinations. The selection and execution quality of its processes directly affect the precision qualification rate, structural integrity and operational reliability of precision components. The following will analyze the core processes of precision machining and their practical impacts in detail.
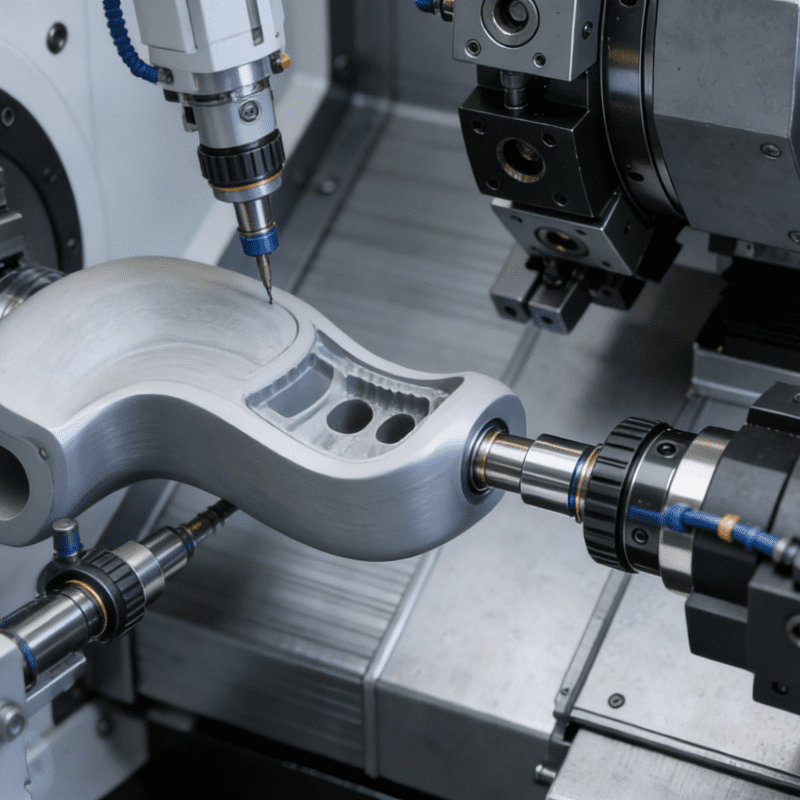
Turning Process: The Cornerstone of Precision for Shaft-type Components
Turning is a widely applied fundamental process in precision machining, mainly for machining rotary precision components such as shafts and sleeves. Through digital program control of the relative movement between the lathe spindle and cutting tools, it achieves the machining of external circles, inner holes, threads, tapered surfaces and other features of workpieces.
The core impacts of this process on precision component machining are reflected in two aspects. First, dimensional accuracy control: the pulse equivalent of the control system can reach the micron level, which can accurately guarantee the tolerance of key dimensions such as component diameter, length and roundness, and avoid the accumulation of errors caused by manual operation. Second, surface roughness optimization: by selecting tool materials and regulating cutting parameters, the surface roughness of components can be controlled within a low range, reducing subsequent grinding procedures and improving the assembly adaptability and motion stability of shaft-type components.
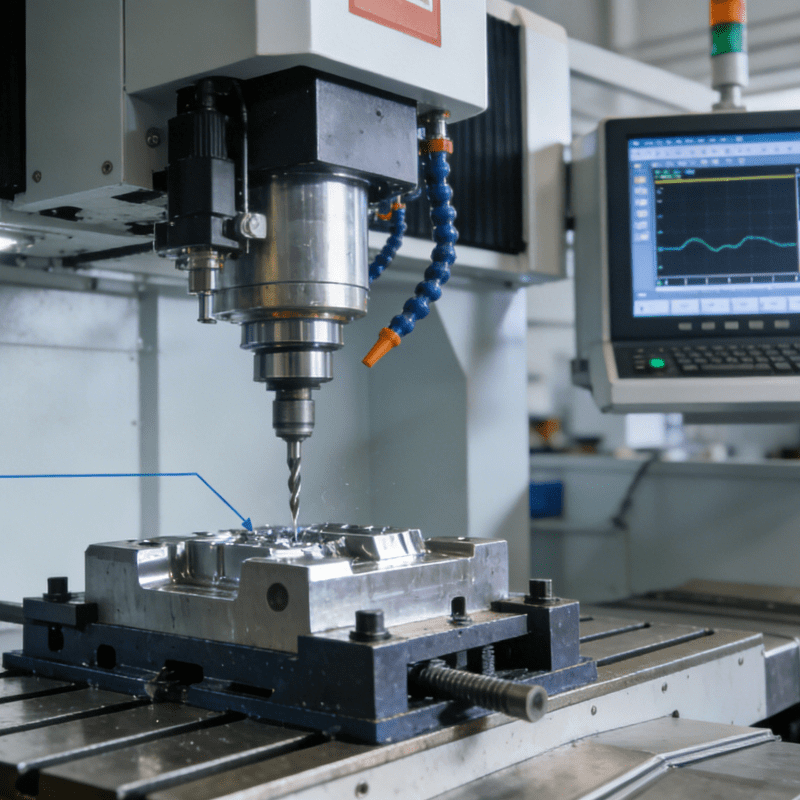
Milling Process: The Core of Forming for Complex Structures
Milling process is suitable for machining precision components with planes, grooves, curved surfaces and complex cavities. Relying on multi-axis linkage (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis) control systems, it realizes the precise cutting movement of tools in three-dimensional space.
Its impacts on precision component machining focus on structural forming and precision coordination. On the one hand, it can accurately machine complex geometric shapes to meet the special-shaped structural requirements of precision components, such as cavities of mechanical parts and mounting grooves of electronic components. On the other hand, multi-axis linkage technology can reduce the number of component clamping operations, avoid errors caused by repeated positioning, and ensure the positional accuracy (e.g., parallelism and perpendicularity) of each machined surface of the component. It is especially suitable for products with high requirements for structural correlation such as high-precision molds and aerospace components.
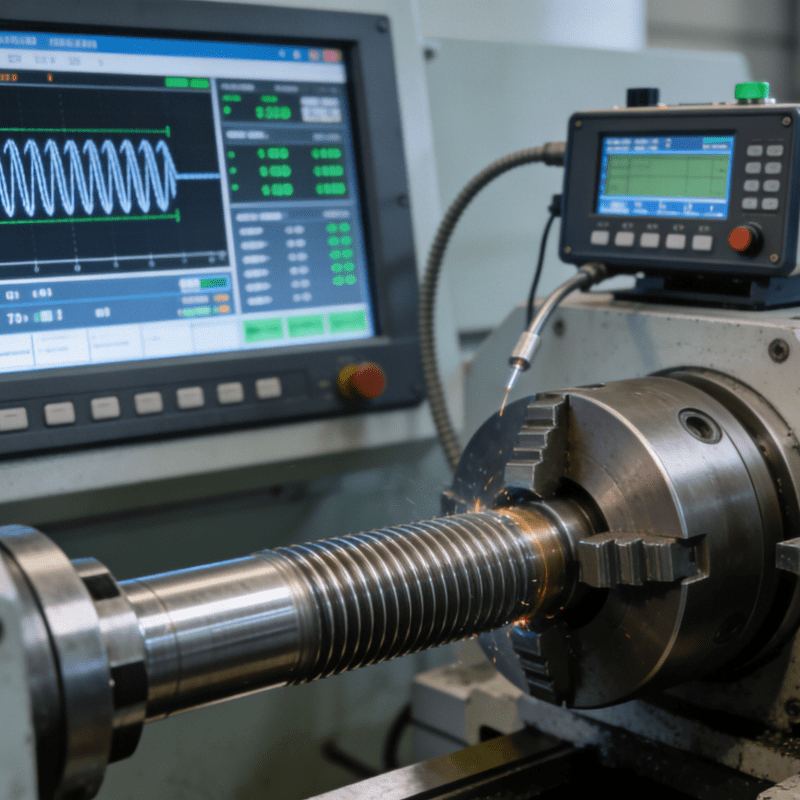
Grinding Process: The Final Guarantee for Ultra-precision Machining
Grinding process is the “precision upgrading” link in precision component machining. It conducts micro-cutting on the workpiece surface through a high-speed rotating grinding wheel, and is commonly used for finish machining after turning and milling, or direct machining of ultra-precision components.
The core value of this process lies in improving the ultimate precision and surface quality of components. First, it can control dimensional tolerance within the range of 0.01-0.05mm, meeting the stringent requirements of ultra-precision components such as core parts of instruments and gauges, and raceways of precision bearings. Second, it can eliminate machining marks left by previous processes, form a smooth and uniform surface, reduce wear and friction loss during component operation, and extend the service life of precision components.

Drilling and Tapping Processes: Accurate Support for Assembly and Connection
Drilling and tapping processes are key auxiliary processes to realize assembly functions in precision component machining. Through the system’s control of the feed rate and rotational speed of drill bits and taps, precise hole positions and threads are machined on components.
Their impacts on precision component machining are reflected in assembly adaptability. Drilling process can ensure the positional accuracy of holes and the tolerance of hole diameters, avoiding assembly jams caused by hole position deviations; tapping process ensures the tight engagement between components and connectors through precise thread machining to prevent loosening. It is especially applicable to components that require frequent disassembly and assembly or load bearing, such as electronic equipment and precision instruments.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): A Processing Breakthrough for Special Materials
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a special machining process for precision components made of high-hardness and high-toughness materials (e.g., cemented carbide and mold steel). It uses pulsed discharge between electrodes and workpieces to generate high temperature, eroding materials to form the required shapes.
The unique value of this process is to solve the machining challenges of special materials without damaging the base performance of components. Since there is no mechanical cutting force during the machining process, it can avoid deformation and cracking of brittle and hard material components. It is suitable for scenarios such as cavity machining of precision molds and complex hole machining of aerospace components, providing more possibilities for material adaptability in precision component machining.
Process Synergy: The Key to Quality in Precision Component Machining
The final machining effect of precision components is not the independent function of a single process, but the collaborative cooperation of multiple processes. The combination of turning and milling can complete the comprehensive machining of complex rotary components; grinding process reinforces the precision of key surfaces; drilling and tapping processes guarantee assembly functions. The parameter matching (e.g., cutting speed and feed rate) and process connection of each process link directly determine the overall quality of components. For electronic components that require high assembly precision and batch production efficiency, the integration of the Automatizovaný nakládací a montážní stroj pro elektronické součástky into the process synergy system can realize seamless connection between machining and assembly, reducing manual intervention-induced errors and further improving the consistency and production efficiency of finished products.
Reasonable process selection should be combined with the material, structure, precision requirements and application scenarios of precision components. Through digital simulation and process optimization, machining efficiency is improved and costs are reduced while ensuring precision. With technological upgrading, the automation and intelligence level of processes are constantly improved, further driving precision component machining towards the direction of higher precision, more complex structures and more stable batch production.
How to choose a multi-component capping assembly machine suitable for your production line?