Overshooting and tool vibration are common issues in intelligent machining, which lead to reduced workpiece precision and tool damage. To address these challenges, this paper systematically introduces a 4-step solution. First, we explore precise tool selection strategies to help you choose suitable cutting tools and apply compensation methods. Second, we elaborate on key parameter optimization methods, including adjusting rotational speed, feed rate and depth of cut. Third, we discuss measures to improve clamping stability for a more reliable machining process. Finally, we provide practical and actionable improvement strategies that can be immediately applied to actual production work. Through these steps, you can gradually reduce vibration and the risk of overshooting, and improve overall machining efficiency.
Precise Tool Selection Strategies
Selecting the right cutting tool is the crucial first step to resolve overshooting and tool vibration in intelligent machining. A cutting tool is like the “working arm” in machining, and its quality directly affects machining results.
Priority should be given to the rigidity of the tool. Tools with high rigidity are less prone to bending and deformation during cutting, which can effectively reduce vibration and avoid tool vibration issues.
The tool length should not be excessively long. An overly long tool overhang will increase the risk of wobbling during cutting; selecting the shortest possible tool can improve machining stability.
The nose radius of the tool is also important. A smaller nose radius is more suitable for finish machining and contour machining, which enables precise control of the cutting path and reduces the likelihood of overshooting.
For example, when machining parts with complex shapes, choosing a milling cutter with a short shank, high rigidity and a small nose radius usually yields better machining results.
Key Parameter Optimization Methods
Correctly setting machining parameters is the core step to solve overshooting and tool vibration problems:
The rotational speed should not be excessively high, otherwise the tool is prone to thermal deformation; yet an overly low speed will compromise machining efficiency. A balance must be struck based on the tool material and workpiece material.
Feed rate is critical. An excessively high feed rate will increase the impact force on the tool, easily causing vibration and subsequent overshooting; an overly low feed rate will reduce production efficiency. Generally, on the premise of ensuring machining quality, the feed rate can be appropriately reduced to ease tool load.
The depth of cut also needs strict control. An overly deep single cut will subject the tool to excessive force, which not only triggers tool vibration easily but also accelerates tool wear. Therefore, it is recommended to adopt a smaller depth of cut and complete the machining task with multiple passes.
By fine-tuning these three key parameters, vibration and the risk of overshooting during machining can be significantly reduced.

Improving Clamping Stability
Secure workpiece clamping is a key step to prevent overshooting and tool vibration:
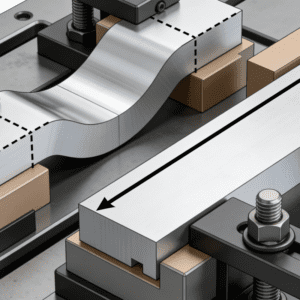
Ensure that the workpiece is firmly fixed on the machine tool table by clamps, with no looseness or wobbling whatsoever.
Check whether the clamps themselves are sufficiently rigid. If the clamps lack rigidity, the cutting force generated during machining will cause clamp deformation, which in turn leads to workpiece displacement, vibration and overshooting.
Take the workpiece shape and size into consideration. For thin-walled parts with special shapes or poor rigidity that are prone to deformation, special support blocks or additional pressure plates may be required to provide better support and distribute cutting forces evenly. Notably, this requirement is particularly critical in the machining of core components for Автоматично подаване и сглобяване на уплътнителни пръстени equipment—such as precision sealing ring positioning seats and feeding guide rails—where even minimal workpiece displacement caused by unstable clamping will lead to overshooting, affecting the dimensional accuracy of the parts. This, in turn, will result in poor fitting of sealing rings during subsequent assembly, or jamming of the feeding mechanism, seriously impacting equipment performance.
Experience shows that more than 20% of vibration problems stem from unstable clamping. Careful inspection and reinforcement of the clamping process can significantly reduce tool wobble during machining, laying a solid foundation for subsequent precision machining.
Practical & Actionable Solutions
After optimizing tool selection and key machining parameters, the following actionable strategies can be put into practice immediately:
Precisely select the tool type according to workpiece material hardness (e.g., use cemented carbide tools to reduce the risk of overshooting).
Adjust rotational speed and feed rate: reducing the feed rate can effectively suppress vibration and avoid tool vibration issues.
Strengthen workpiece clamping stability with specialized fixtures to ensure a firm machining process.
For example, a manufacturing plant successfully eliminated overshooting by precisely controlling the depth of cut and feed rate parameters. These simple and feasible steps can immediately improve CNC machining efficiency and quality.
By precisely selecting cutting tools, optimizing machining parameters and enhancing clamping stability, overshooting and tool vibration in CNC intelligent machining can be effectively controlled. These steps complement each other, helping operators reduce vibration and improve machining precision. For instance, selecting the right tool type can reduce cutting force, while adjusting rotational speed and feed rate balances production efficiency and machining stability. Meanwhile, stable clamping fixtures ensure no workpiece displacement, preventing accidental overshooting. Integrating these methods into daily machining operations allows you to quickly resolve common machining challenges and achieve a smoother, more efficient machining process.
Assembly line for mass production by artificial intelligence